Unlock the Periodic Table: Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

Unlocking the mysteries of the periodic table is an exciting journey that introduces students to the world of chemistry. As you delve into the elements, their properties, and their reactions, you will discover the pattern and order that govern the natural world. Today, we are going to explore the answer key to the periodic table worksheet, providing insights and explanations for better understanding.
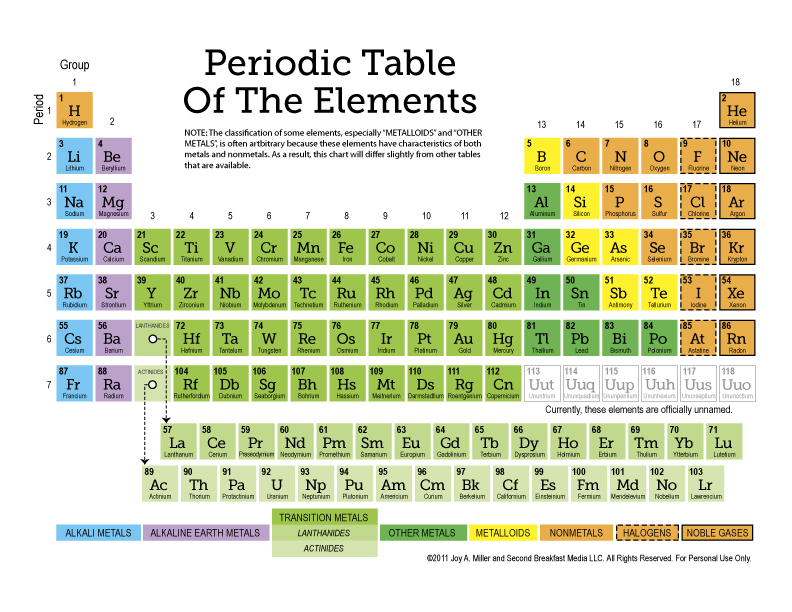
The Basics of the Periodic Table


The periodic table is an organized layout of elements. Here are some fundamental points to remember:
- Groups: Vertical columns in the table where elements have similar chemical properties.
- Periods: Horizontal rows, which show the trend in atomic number and properties.
- Atomic Number: Indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic Weight: The average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element.
Worksheet Answer Key

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Name three elements in Group 1. | Hydrogen (H), Sodium (Na), and Potassium (K) |
| 2. What is the atomic number of Helium? | 2 |
| 3. Identify the gas at the top of Group 18. | Helium (He) |
| 4. How many elements are in the third period? | Eight (from Sodium to Argon) |
| 5. Which element has the symbol ‘C’? | Carbon |
| 6. Name the element that is liquid at room temperature. | Mercury (Hg) and Bromine (Br) |
| 7. Which element has the highest atomic weight in the first period? | Argon (Ar) |
| 8. What is the difference between a metal and a non-metal? | Metals are typically good conductors of heat and electricity, are malleable, and form positive ions. Non-metals tend to form negative ions or covalent bonds and are usually poor conductors. |
| 9. Describe the electronic configuration of an element from the second row of the periodic table. | Elements in the second row have the electron configuration starting with 2s2 2p6, for example, oxygen would have the configuration 1s2 2s2 2p4. |

🚀 Note: Always pay attention to the atomic number as it determines the position of an element in the periodic table and its electronic configuration.
Understanding Chemical Properties

Chemical properties are influenced by an element’s electron configuration. Here are some points to remember:
- Reactivity increases as you move down in Group 1 (Alkali Metals) due to an increase in atomic radius.
- In Group 17 (Halogens), reactivity decreases down the group as the atomic size increases, making it harder for these elements to attract electrons.
- The noble gases (Group 18) are generally inert because of their stable full outer electron shells.
Periodic Trends
Understanding the trends within the periodic table helps in predicting the behavior of elements:
- Atomic Radius: Tends to decrease from left to right across a period due to increasing nuclear charge.
- Ionization Energy: Also increases across a period for the same reason, it takes more energy to remove an electron from an atom with a higher nuclear charge.
- Electronegativity: Follows the same trend as ionization energy; higher electronegative elements are better at attracting electrons.
- Metallic Character: Increases down a group and decreases across a period. Metallic elements are more reactive and tend to lose electrons.
🔧 Note: The understanding of periodic trends not only helps in predicting chemical reactions but also aids in material science and engineering applications.
To truly master the periodic table, one must not only memorize elements but also understand the underlying principles governing their arrangement. As we've explored, the periodic table is a reflection of the atomic properties and behaviors, making it an essential tool for chemists and students alike.
This comprehensive guide through the periodic table offers a glimpse into the intricate beauty of chemistry. Remember, mastering the periodic table is not just about learning facts; it's about understanding the language of nature, where every element tells a story, and every reaction unveils a mystery of the universe. So, embrace this journey with curiosity, and let the periodic table be your map to unraveling the chemical universe.
What are the benefits of understanding the periodic table?

+
Understanding the periodic table allows you to predict chemical reactions, understand element properties, and aids in various scientific fields like material science, medicine, and environmental science.
Why do elements in the same group have similar properties?

+
Elements in the same group have similar properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell, leading to similar valence electron configurations and thus similar chemical behaviors.
What does the atomic weight signify?

+
The atomic weight signifies the average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, reflecting its relative abundance in nature.