Periodic Table Basics Worksheet: Your Ultimate Answer Guide

The periodic table of elements is an essential tool for students, scientists, and anyone curious about the building blocks of our universe. It's a map that organizes elements by their atomic number, chemical properties, and electron configuration, providing insights into how these particles interact, bond, and form compounds. This comprehensive guide will walk you through understanding, utilizing, and excelling with the periodic table basics worksheet.
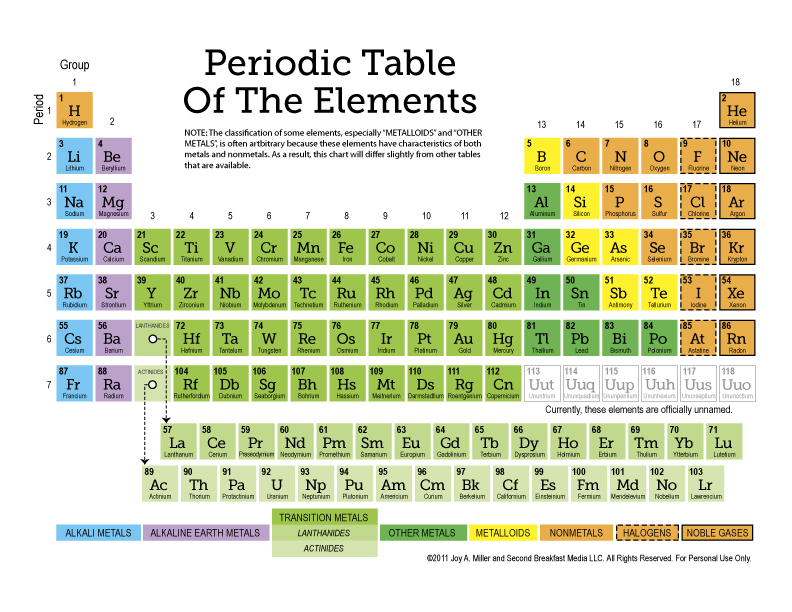
Understanding the Periodic Table Layout

Before diving into the worksheet, it’s crucial to understand the layout of the periodic table:
- Rows (Periods): The horizontal rows indicate the number of electron shells an element has.
- Columns (Groups/Families): Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
- Blocks: The periodic table is divided into s, p, d, and f blocks based on electron configuration.
Types of Elements

The periodic table categorizes elements into several types:
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Metals | Good conductors of heat and electricity, shiny, malleable, ductile. |
| Nonmetals | Poor conductors, brittle when solid, generally not lustrous. |
| Metalloids | Properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. |
| Noble Gases | Inert, low reactivity, usually colorless, odorless gases at room temperature. |

How to Use the Periodic Table Basics Worksheet

The worksheet typically includes exercises to:
- Identify elements by their atomic number, symbol, name, and atomic mass.
- Understand element classifications.
- Analyze electron configuration.
- Explore trends like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
Here’s how to approach each section:
Element Identification

When faced with identifying elements:
- Start with the atomic number. This is the number of protons in the nucleus and also determines the electron number in a neutral atom.
- Look at the element symbol, which is either one or two letters.
- Check the name and atomic mass.
Use the periodic table to cross-reference and confirm your answers.
Element Classification

Classify elements by recognizing the physical and chemical properties:
- Metals are usually on the left side and center of the table.
- Nonmetals are on the upper right side.
- Metalloids form a “staircase” line between metals and nonmetals.
- Noble gases are in the last column (Group 18).
Electrons and Configurations

Here’s where understanding the electron structure becomes vital:
- Each period (row) corresponds to the number of electron shells.
- The group number for main group elements (Groups 1, 2, 13-18) tells us the number of valence electrons.
- Sub-levels (s, p, d, f) determine the electron filling order.
Remember the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli Exclusion Principle when dealing with electron configurations.
🔎 Note: Valence electrons are critical for predicting reactivity, as they are involved in chemical bonding.
Periodic Trends

Periodic trends like:
- Atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Ionization energy increases across a period but decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity follows a similar trend to ionization energy.
Understand the rationale behind these trends; for example, atomic radius increases down a group due to the addition of more electron shells.
Practical Applications
The periodic table isn’t just theoretical; it has numerous practical applications:
- Chemistry: Helps predict chemical reactions, bond formation, and reactivity.
- Industry: Understanding element properties for materials science and engineering.
- Environment: Classifying elements and compounds for environmental science.
In conclusion, mastering the periodic table through the basics worksheet provides a strong foundation for chemistry education. From recognizing element symbols to understanding the electron configurations, this guide helps bridge the gap between memorization and comprehension. The periodic table isn't just a chart; it's a key that unlocks the secrets of the atomic world, guiding us through the intricacies of chemistry with every element organized for our understanding.
What are the main parts of the periodic table?

+
The main parts include periods (rows) showing electron shells, groups (columns) indicating chemical behavior, and blocks (s, p, d, f) based on electron configuration.
Why are some elements colored differently in the periodic table?

+
Elements are often color-coded to quickly identify different classifications, like metals (blue), nonmetals (yellow), and metalloids (green).
How can I remember the periodic table for exams?

+
Mnemonics, songs, periodic table apps, flashcards, and interactive learning tools can help. Practicing regular review and understanding trends can also aid memorization.
Why do elements in the same group have similar properties?

+
They have the same number of valence electrons, which largely determine how an element will behave chemically.
What is the significance of electron configurations in understanding chemistry?

+
Electron configurations show how electrons are distributed in an atom, which affects bonding, reactivity, and chemical properties of elements.