5 Essential Facts About the Periodic Table Worksheet

Understanding the periodic table is essential for anyone studying chemistry, from high school students to professional chemists. The periodic table worksheet can be a useful tool to learn about elements, their properties, and how they interact with each other. Here are five crucial facts you need to know about the periodic table worksheet:
1. Elements are Organized by Atomic Number

In the periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, which reflects the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. This organization leads to a pattern where elements with similar properties are grouped together. Here’s how this can be utilized in a worksheet:
- Atomic Number Sequence: Students can practice identifying elements by their atomic number, fostering a deeper understanding of atomic structure.
- Periodic Trends: Worksheets can include activities that explore trends like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity, which vary predictably across periods and groups.
💡 Note: Each row in the periodic table is called a period, and each column is called a group or family. These terms are essential for understanding element classification.
2. Worksheets Highlight Element Categories
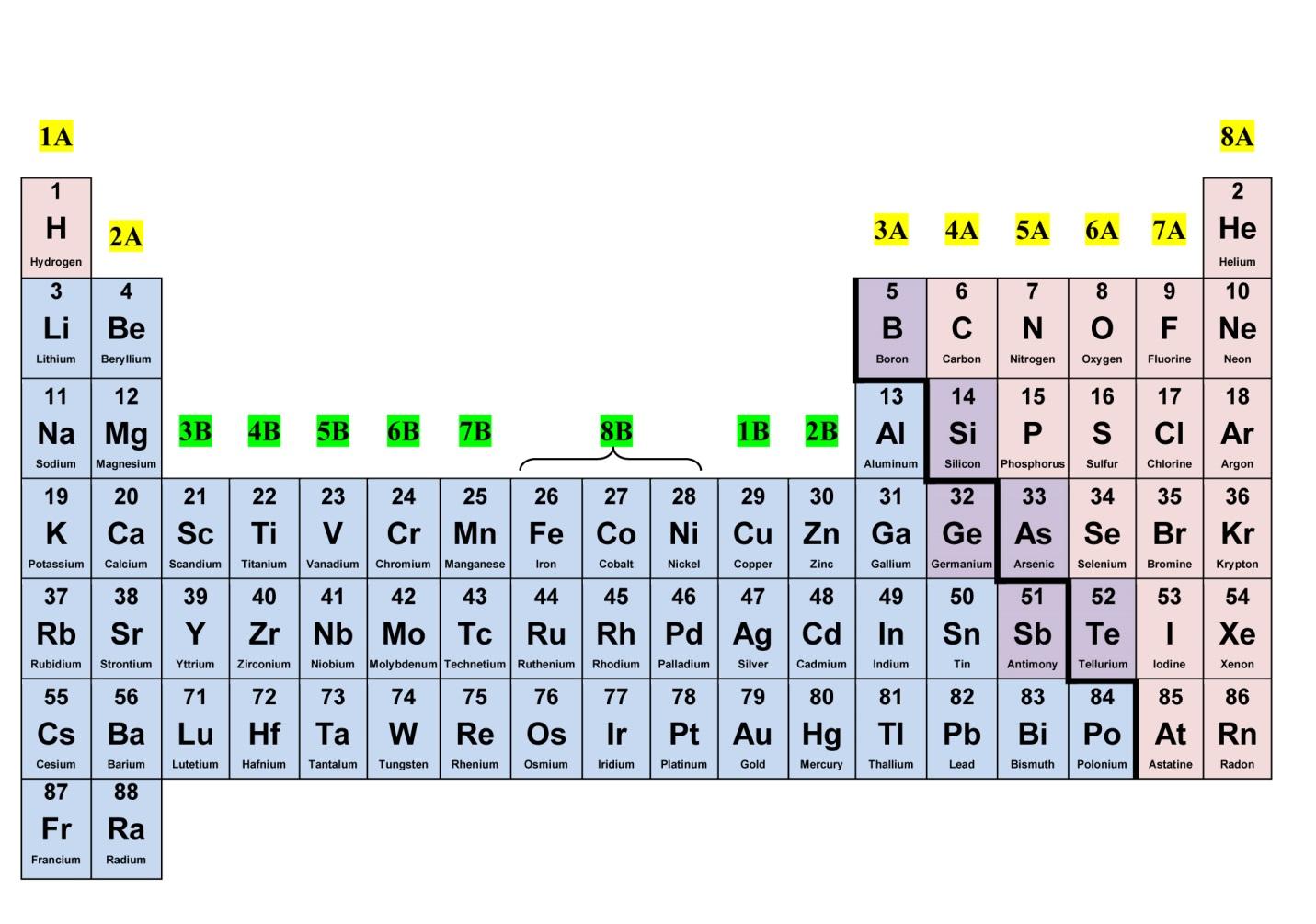
Elements are categorized into metals, non-metals, and metalloids, which is often reflected in periodic table worksheets. Here’s what that means:
- Metals: Typically, metals are to the left of the table, and they share characteristics like being shiny, good conductors of heat and electricity, and malleable.
- Non-metals: Found on the right side, non-metals have properties like being brittle, poor conductors, and often existing in various forms (solids, liquids, gases).
- Metalloids: These elements have properties intermediate between metals and non-metals. They are found along the "staircase" line dividing metals from non-metals.
| Category | Properties | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Shiny, good conductors, malleable | Iron, Gold, Silver |
| Non-Metals | Poor conductors, brittle, varies in states | Oxygen, Chlorine, Carbon |
| Metalloids | Mixed properties | Boron, Silicon, Germanium |

3. Trends in Reactivity and Electron Configuration
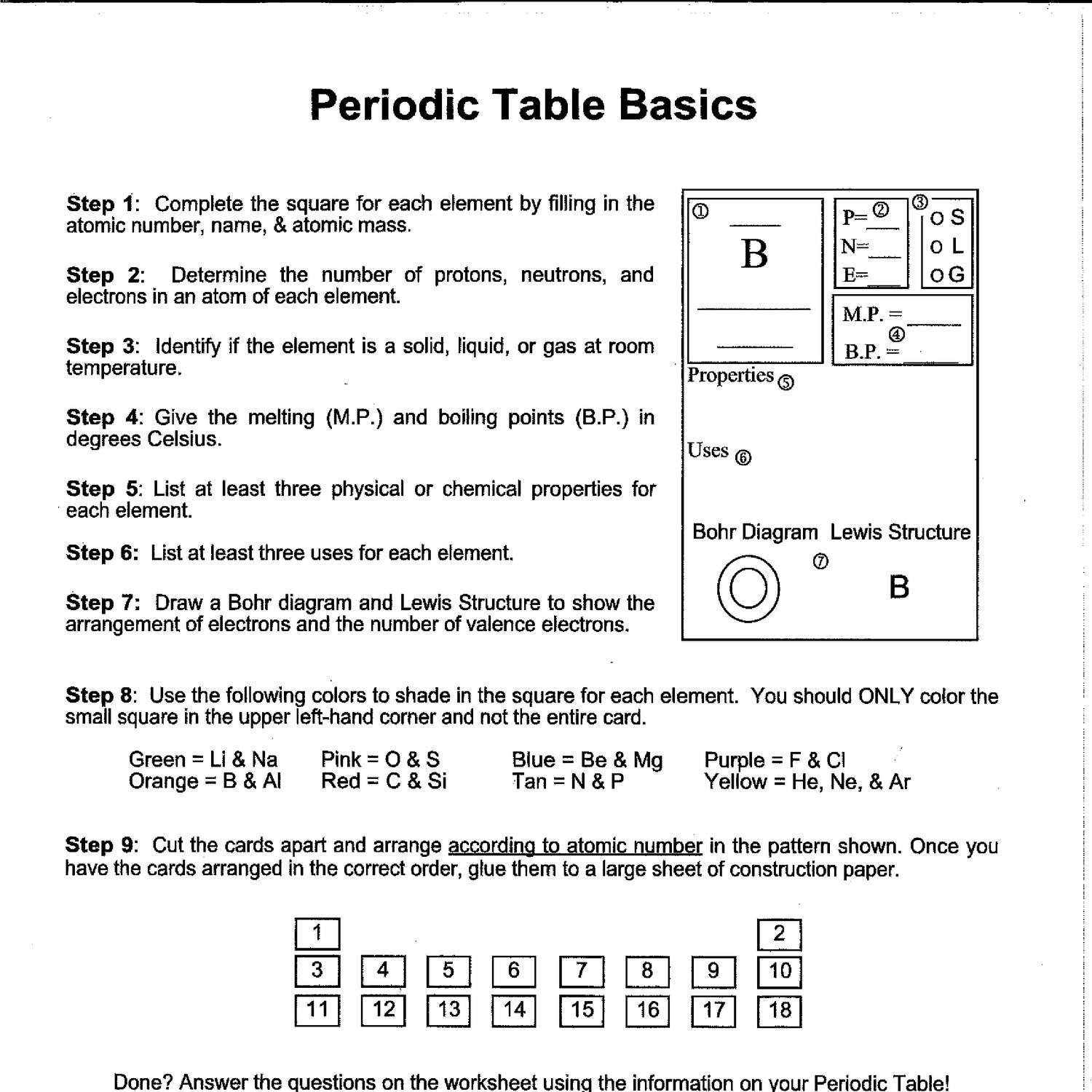
One of the beauties of the periodic table is that it displays trends in element reactivity and electron configuration, making it an invaluable tool for chemical education. Here's how:
- Reactivity: Alkali metals on the left side of the table are highly reactive, while noble gases on the right are inert due to their full valence electron shells.
- Electron Configuration: Worksheets can help students practice writing electron configurations and understand how elements achieve stable electron shells.
💡 Note: Understanding electron configurations can help predict how elements will bond with each other.
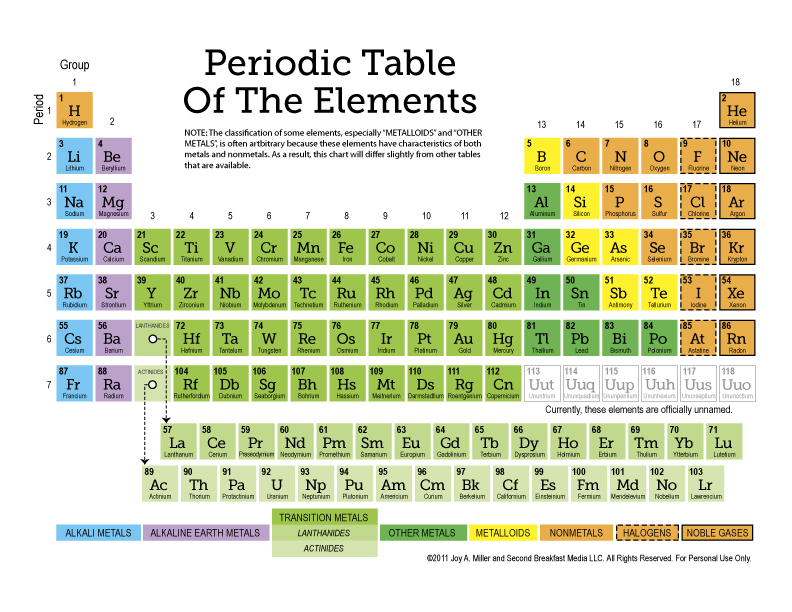
4. Classification by Periodic Table Groups

The periodic table groups are another key feature for organizing elements:
- Alkali Metals (Group 1): These are extremely reactive, with sodium and potassium being common examples.
- Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2): Less reactive than Group 1 but still reactive, like magnesium and calcium.
- Transition Metals: This wide group in the middle has varying properties, used for their strength and conductivity.
- Halogens (Group 17): Highly reactive non-metals like chlorine and fluorine.
- Noble Gases (Group 18): Known for their low reactivity due to full valence shells.
5. Worksheets Help in Learning Chemical Properties

Periodic table worksheets often include exercises that focus on the chemical properties of elements:
- Valence Electrons: Understanding how many valence electrons an element has is key to predicting its behavior in chemical reactions.
- Electronegativity: Worksheets can teach how electronegativity varies across the table, affecting bond polarity.
- Ionization Energy: Practice questions on ionization energy help students understand why elements gain or lose electrons.
Throughout these facts, the periodic table worksheet acts as an educational platform to deepen the understanding of chemistry. By engaging with different aspects of the periodic table through worksheets, students not only memorize but truly comprehend the underlying principles of chemistry.
In summary, the periodic table worksheet is an indispensable tool for learning. It enables students to explore atomic structures, periodicity, reactivity, and chemical behavior in a structured and interactive way. With these five essential facts, learners can better navigate the complexities of the elements, paving the way for a deeper appreciation and understanding of chemistry.
Why is the periodic table organized by atomic number?

+
The periodic table is organized by atomic number because this number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. This ordering allows elements with similar properties to appear in columns, facilitating the study of patterns and trends in chemistry.
What are some common trends in the periodic table?
+
Some common trends include atomic radius (decreases from left to right across a period and increases down a group), ionization energy (increases from left to right and decreases down a group), and electronegativity (similar trends to ionization energy).
Why are worksheets beneficial for learning the periodic table?

+
Worksheets provide structured exercises that help reinforce understanding through practice. They allow students to actively engage with the information, helping them remember and apply concepts better than passive learning methods.
Can you explain the importance of groups in the periodic table?

+
Groups in the periodic table are vertical columns where elements share similar chemical behavior due to having the same number of valence electrons. This helps in predicting how elements will interact chemically.


