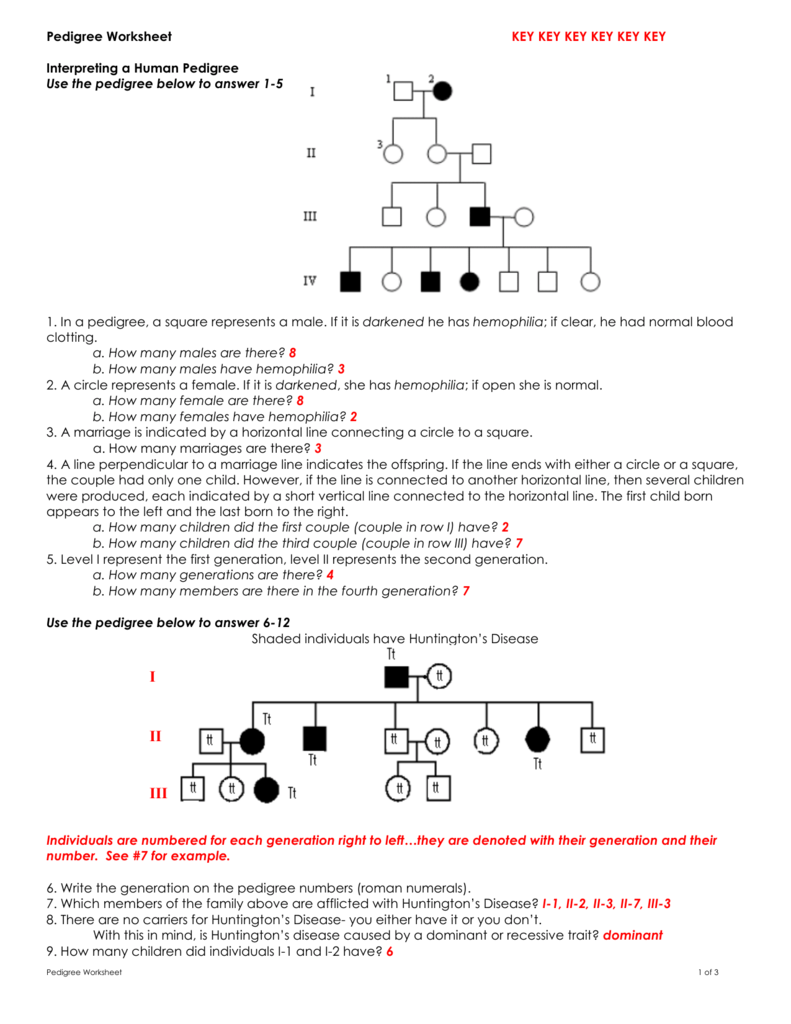
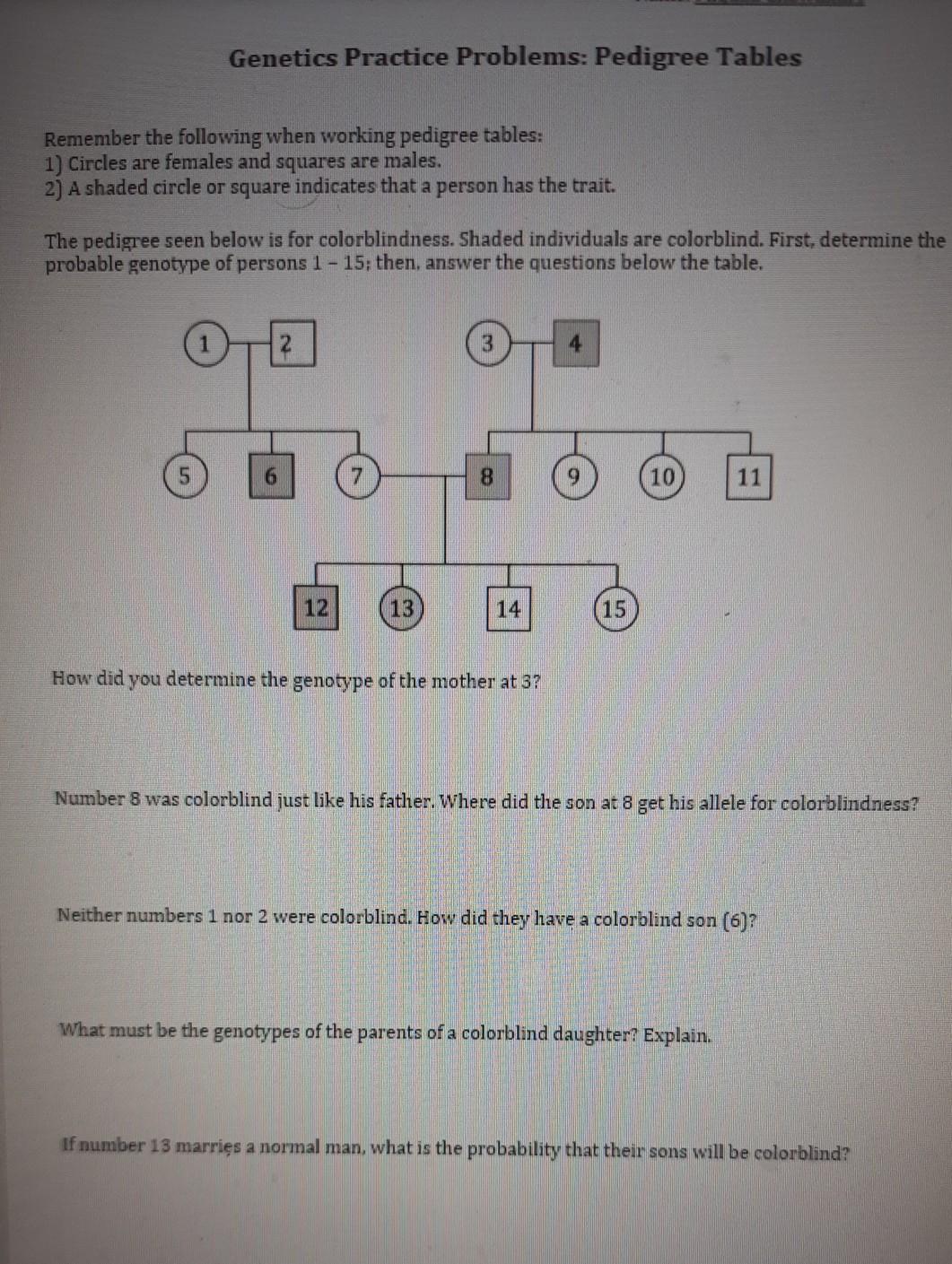
Pedigree Problems Worksheet: Mastering Genetics Analysis Easily

In genetics, understanding pedigrees is essential for unraveling the mystery of inherited traits and diseases. This pedigree problems worksheet aims to guide both students and enthusiasts through the complexities of genetic analysis, making the process not just informative but also engaging. By diving into various pedigree scenarios, you will sharpen your skills in interpreting genetic patterns, probabilities, and potential outcomes.
What is a Pedigree?


Before we delve into the problems, let’s establish what a pedigree chart represents. A pedigree is a family tree diagram used to illustrate inheritance patterns of traits or diseases over several generations. Each symbol on the chart has a specific meaning:
- Circles - Represent females.
- Squares - Represent males.
- Shaded symbols - Indicate individuals affected by the trait or disease in question.
- Unshaded symbols - Show unaffected individuals.
- Dotted lines - Used for showing adoption or other non-biological relationships.
This visual representation helps in tracking genetic information and aids in predicting inheritance patterns.
Basic Pedigree Interpretation

Understanding pedigrees begins with recognizing patterns:
- Autosomal Dominant Inheritance: The trait appears in every generation, often with affected parents having an equal chance of passing the trait to offspring of either sex.
- Autosomal Recessive Inheritance: The trait might skip generations, appearing in individuals where both parents are carriers (heterozygous).
- X-Linked Dominant: Affects females more than males, with a distinctive pattern of affected males passing the trait to all their daughters but none of their sons.
- X-Linked Recessive: Males are more commonly affected because they only need one copy of the allele on their single X chromosome.
Problem 1: Identifying Inheritance Patterns

Here’s a simple exercise to get you started:
| Generation | Mating Couples | Offspring | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male (1) x Female (1) | 4 Females, 2 Males | 2 Males affected |
| 2 | Male (2) x Female (2) | 2 Females, 1 Male | All unaffected |
| 3 | Male (3) x Female (3) | 3 Females, 3 Males | 1 Female affected, 1 Male affected |

🔍 Note: This pedigree suggests X-linked recessive inheritance due to the occurrence in males and the pattern of transmission.
Probability Calculations
Calculating the probability of inheritance in pedigree analysis involves understanding Punnett Squares, segregation ratios, and simple probabilities. Here are key steps to calculate:
- Identify the genotypes of the parents based on the pedigree.
- Determine the mode of inheritance (dominant/recessive, autosomal/X-linked).
- Use Punnett Squares to predict the outcome of each mating.
- Apply the laws of probability (addition or multiplication rule) to find the chances of having an affected or unaffected child.
Problem 2: Calculating Inheritance Probability

Consider this scenario:
- A couple, both carriers of a recessive genetic condition, wants to know the probability of their child being affected.
The calculation would look like this:
X AX a (Mother) x X AY (Father)┌───┐ ┌───┐ │XAXA│ │XAY │ 3⁄4 Chance Unaffected ├───┤ ├───┤ │XAXa│ │XaY │ 1⁄4 Chance Affected └───┘ └───┘
🔍 Note: Remember, for X-linked recessive traits, only males who inherit the affected allele on their single X chromosome will be affected.
Advanced Pedigree Analysis

Advanced analysis includes:
- Complex inheritance patterns involving multiple genes (polygenic inheritance).
- Interactions between alleles (epistasis).
- Variable penetrance where not all individuals carrying the gene express the trait.
Here, you can delve deeper into:
- Population genetics.
- Non-Mendelian inheritance (incomplete dominance, co-dominance).
- Mitochondrial inheritance.
🔍 Note: These concepts often require understanding of linkage, gene mapping, and recombinant DNA technology to make accurate predictions.
Summing up, mastering pedigree analysis through this worksheet equips you with a robust understanding of genetics, which is invaluable in diagnosing genetic disorders, advising on genetic testing, and counseling families on potential inheritance patterns. The journey through pedigrees allows you to appreciate the complexity and beauty of genetic inheritance, preparing you for more advanced genetic studies and real-world applications in medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology.
Why is pedigree analysis important?

+
Pedigree analysis helps in understanding how traits and diseases are inherited, predicting the likelihood of traits appearing in future generations, and can assist in genetic counseling for family planning.
Can pedigrees predict genetic risks?
+
Yes, by analyzing the inheritance pattern within a family, pedigrees can provide insights into the probability of inherited genetic conditions, allowing for proactive health management.
What are the limitations of pedigree analysis?

+
Pedigree analysis might not account for new mutations, environmental influences, or the complexity of polygenic traits. Additionally, incomplete or inaccurate family history can skew results.