Pedal Brake Pedal Function Explained

Introduction to Pedal Brake Function

The pedal brake is a crucial component of a vehicle’s braking system, responsible for slowing or stopping the vehicle when the driver presses the brake pedal. The pedal brake function is a complex process that involves the coordination of multiple components, including the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake fluid, and brake calipers or wheel cylinders. In this article, we will delve into the details of the pedal brake function, exploring its components, operation, and importance in ensuring vehicle safety.
Components of the Pedal Brake System

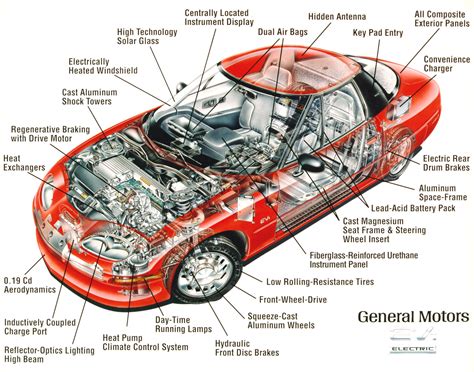
The pedal brake system consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the braking process. These components include: * Brake Pedal: The brake pedal is the driver-activated component that initiates the braking process. When pressed, it transmits the driver’s input to the master cylinder. * Master Cylinder: The master cylinder is a critical component that converts the non-hydraulic pressure from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is then transmitted to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. * Brake Fluid: Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid that plays a vital role in the pedal brake function. It transmits the pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, enabling the vehicle to slow or stop. * Brake Calipers or Wheel Cylinders: The brake calipers or wheel cylinders are responsible for applying pressure to the brake pads or shoes, which then contact the rotor or drum to slow or stop the vehicle.
Operation of the Pedal Brake System

The operation of the pedal brake system is a complex process that involves the coordination of multiple components. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process: * When the driver presses the brake pedal, it activates the master cylinder, which converts the non-hydraulic pressure into hydraulic pressure. * The hydraulic pressure is then transmitted to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders through the brake fluid. * The brake calipers or wheel cylinders apply pressure to the brake pads or shoes, which then contact the rotor or drum to slow or stop the vehicle. * As the brake pads or shoes contact the rotor or drum, they convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle into heat energy, which is then dissipated into the atmosphere.
Importance of the Pedal Brake Function

The pedal brake function is crucial in ensuring vehicle safety. A properly functioning pedal brake system enables the driver to slow or stop the vehicle quickly and efficiently, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, the pedal brake system plays a critical role in maintaining vehicle stability and control, particularly during emergency braking situations.
🔧 Note: Regular maintenance of the pedal brake system is essential to ensure its proper functioning and to prevent brake failure.
Troubleshooting Common Pedal Brake Issues
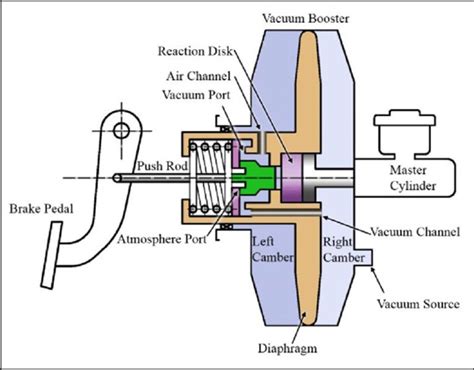
Common issues with the pedal brake system can compromise vehicle safety and performance. Here are some common issues and their possible causes: * Spongy Brake Pedal: A spongy brake pedal can be caused by air in the brake system, worn-out brake pads or shoes, or a malfunctioning master cylinder. * Hard Brake Pedal: A hard brake pedal can be caused by a malfunctioning brake booster, worn-out brake pads or shoes, or a blockage in the brake fluid lines. * Brake Fluid Leaks: Brake fluid leaks can be caused by damaged brake lines, loose connections, or a malfunctioning master cylinder.
Maintenance and Repair of the Pedal Brake System
Regular maintenance and repair of the pedal brake system are essential to ensure its proper functioning and to prevent brake failure. Here are some maintenance and repair tips: * Brake Pad Replacement: Replace brake pads every 30,000 to 50,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. * Brake Fluid Check: Check brake fluid levels regularly and top off as needed. * Brake Line Inspection: Inspect brake lines for damage or corrosion and replace as needed.
| Component | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | Initiates braking process | Critical component of the pedal brake system |
| Master Cylinder | Converts non-hydraulic pressure into hydraulic pressure | Enables the transmission of pressure to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders |
| Brake Fluid | Transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders | Essential for the proper functioning of the pedal brake system |

In summary, the pedal brake function is a complex process that involves the coordination of multiple components to facilitate the braking process. Regular maintenance and repair of the pedal brake system are essential to ensure its proper functioning and to prevent brake failure. By understanding the components, operation, and importance of the pedal brake system, drivers can appreciate the critical role it plays in ensuring vehicle safety and performance.
What is the function of the brake pedal in a vehicle?

+
The brake pedal is responsible for initiating the braking process by transmitting the driver’s input to the master cylinder.
What are the common issues with the pedal brake system?
+
Common issues with the pedal brake system include a spongy brake pedal, hard brake pedal, and brake fluid leaks.
How often should brake pads be replaced?

+
Brake pads should be replaced every 30,000 to 50,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer.