5 Essential Pea Plant Punnett Square Answers Revealed

Understanding Pea Plant Genetics

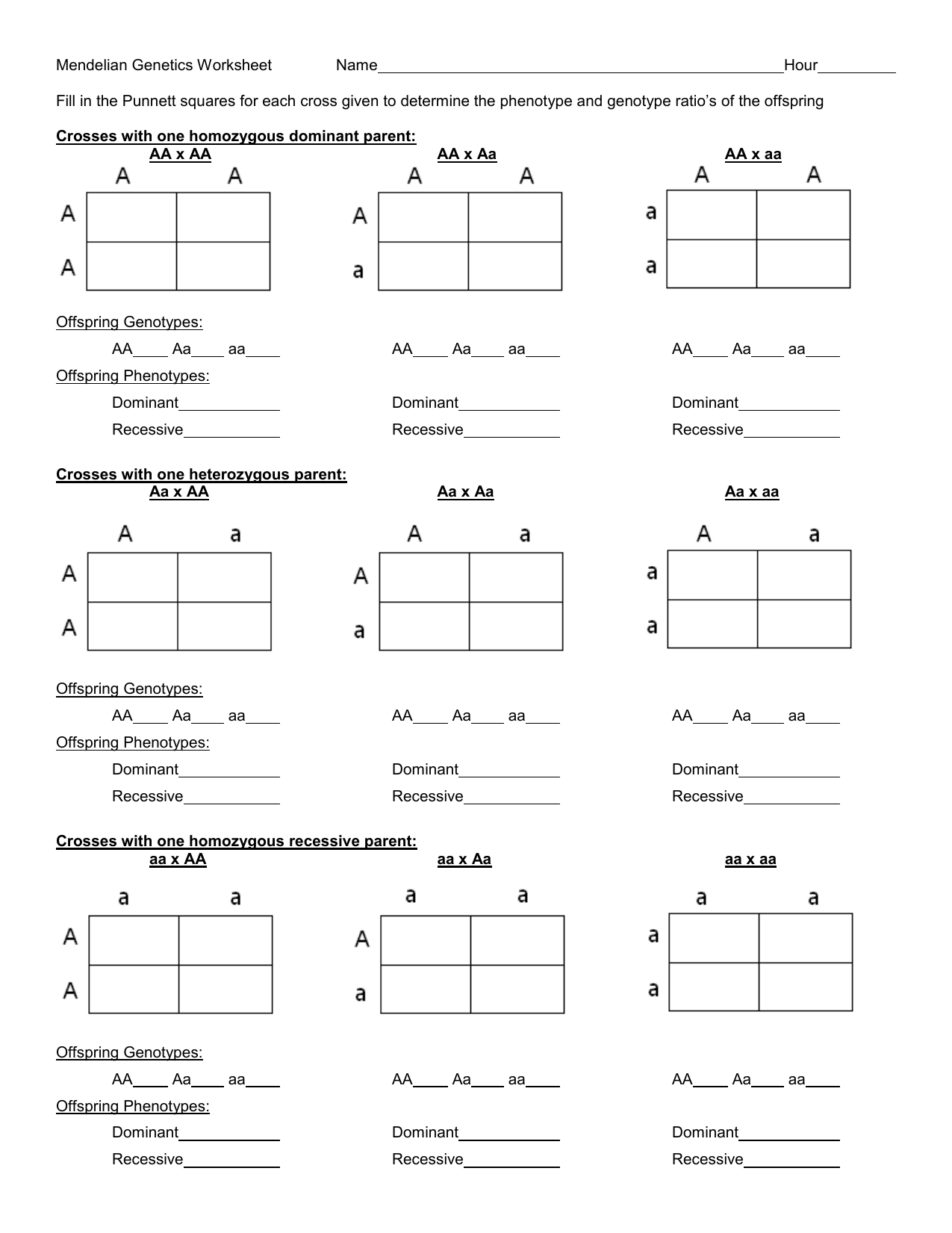
The study of genetics can seem overwhelming, but the principles of inheritance become clearer through the use of simple yet effective tools like the Punnett square. Developed by Reginald Punnett, this diagram helps us predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from given parent combinations. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into five essential answers regarding pea plant Punnett squares, using the iconic experiments of Gregor Mendel as our starting point.
1. What is a Punnett Square?

The Punnett square is a diagram that visualizes all possible genotypes of offspring resulting from the breeding of two individuals. Here’s how it works:
- Select Parents: Choose the genotypes of the two parents for a particular trait.
- Create the Grid: Draw a square grid with enough cells for each possible combination.
- Fill in Parental Genotypes: Write the alleles of one parent along the top and the alleles of the other parent along the left side.
- Determine Offspring: Combine the letters in each cell to see the potential genotypes of the offspring.
📝 Note: Remember, each cell in the grid represents the probability of an offspring inheriting that particular combination of genes.

2. How Can We Predict the Ratio of Pea Plant Offspring?

Mendel’s experiments with pea plants are legendary, and his findings laid the groundwork for modern genetics. Here’s how we can use a Punnett square to predict offspring ratios:
- Monohybrid Cross: If we cross pure-bred tall (TT) plants with pure-bred dwarf (tt) plants, all F1 offspring will be heterozygous (Tt) and tall.
- Dihybrid Cross: For two traits, the ratios become more complex. For example, when crossing plants with round yellow seeds (RRYY) with wrinkled green seeds (rryy), the offspring will be heterozygous for both traits (RrYy).
Here’s a simple Punnett square for a monohybrid cross:
| T | t | |
|---|---|---|
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | Tt | tt |
3. Exploring Dominant and Recessive Traits in Pea Plants

Mendel discovered that certain traits in pea plants, like height, are inherited as:
- Dominant: Tall (T) is dominant over dwarf (t). If an offspring inherits even one T allele, it will be tall.
- Recessive: Both alleles must be t for the plant to be dwarf.
When setting up a Punnett square for traits like these, remember that:
- The dominant allele is typically written first in a heterozygous genotype (e.g., Tt, not tT).
💡 Note: Phenotype refers to the observable traits, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup.
4. Genetic Linkage and Crossover Frequency

When dealing with multiple traits, genes that are close to each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together, which is known as genetic linkage:
- Linked Genes: Genes like those for seed color and shape in pea plants are often linked. However, they can still recombine through a process called crossing over.
- Crossover Frequency: The frequency of crossovers helps determine how closely linked genes are; lower frequency indicates closer linkage.
5. How to Use Punnett Squares for Genetic Predictions

Here are the steps to use Punnett squares effectively:
- Define Genotypes: Determine the alleles for the traits you’re interested in for both parents.
- Construct the Square: Set up a grid based on the number of gamete combinations from each parent.
- Fill in the Square: Place the alleles of one parent along the top and the other along the side, then combine to form genotypes.
- Interpret Results: Count the frequencies of different genotypes and phenotypes to predict the offspring ratios.
By understanding and applying the principles we've discussed, you're better equipped to delve into the fascinating world of genetics. These Punnett square answers not only help with understanding Mendelian genetics but also give insight into the complexities of inheritance, linkage, and gene interaction.
🚀 Note: As you explore genetics further, remember that while Punnett squares are simple models, they help form the basis for more complex genetic studies.
What are the differences between genotypes and phenotypes?

+
The genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual, represented by the alleles it inherits (e.g., Tt). The phenotype, on the other hand, is the observable traits (e.g., tall or dwarf) resulting from the interaction of the genotype with the environment.
Can you explain what is meant by a dihybrid cross?

+
A dihybrid cross involves the breeding of two individuals that differ in two traits, aiming to understand how these traits are inherited together or independently. For example, crossing pea plants with different seed colors and shapes.
Why do some traits not follow Mendel’s laws?

+
Some traits don’t follow Mendel’s laws due to phenomena like incomplete dominance, co-dominance, or polygenic inheritance. These situations occur when the interaction of genes or the effects of multiple genes are more complex than simple dominance.