5 Ohio Payroll Tips

Understanding Ohio Payroll: An Overview

Managing payroll in Ohio requires a thorough understanding of the state’s laws and regulations. From tax withholdings to employee benefits, there are several factors to consider when processing payroll. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of Ohio payroll, providing you with the necessary information to ensure compliance and accuracy.
Ohio Payroll Laws and Regulations
Ohio has its own set of payroll laws and regulations that employers must adhere to. Some of the key laws include: * Minimum Wage: Ohio’s minimum wage is 8.70 per hour for non-tipped employees and 4.35 per hour for tipped employees. * Overtime Pay: Employers must pay employees 1.5 times their regular rate for hours worked over 40 in a workweek. * Workers’ Compensation: Employers are required to provide workers’ compensation insurance to their employees. * Unemployment Insurance: Employers must pay unemployment insurance taxes to fund the state’s unemployment program.
5 Ohio Payroll Tips
To ensure compliance with Ohio payroll laws and regulations, follow these 5 tips: * Tip 1: Verify Employee Information: Ensure that all employee information, including names, addresses, and Social Security numbers, is accurate and up-to-date. * Tip 2: Calculate Taxes Correctly: Calculate federal, state, and local taxes correctly, taking into account Ohio’s tax withholding rates and any applicable deductions. * Tip 3: Comply with Overtime Pay Laws: Ensure that employees are paid correctly for overtime hours worked, including calculating the correct overtime rate and paying any required premiums. * Tip 4: Provide Required Benefits: Provide employees with required benefits, such as workers’ compensation insurance and unemployment insurance, and ensure that employees are aware of their rights and benefits. * Tip 5: Maintain Accurate Records: Maintain accurate and detailed payroll records, including employee information, pay rates, and tax withholdings, to ensure compliance with Ohio payroll laws and regulations.
Ohio Payroll Tax Rates

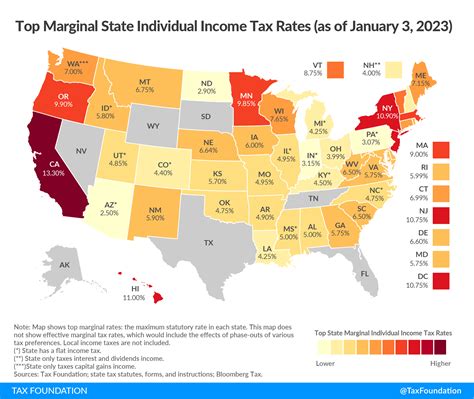
Ohio has a progressive income tax system, with tax rates ranging from 2.85% to 4.24%. The state also has a variety of local taxes, including municipal income taxes and school district taxes. Employers must withhold the correct amount of taxes from employee wages, taking into account the employee’s tax filing status, number of exemptions, and other factors.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $44,250 | 2.85% |
| $44,251 - $89,500 | 3.24% |
| $89,501 - $179,000 | 3.62% |
| $179,001 - $224,000 | 3.96% |
| $224,001 and above | 4.24% |

📝 Note: These tax rates are subject to change, and employers should consult the Ohio Department of Taxation for the most up-to-date information.
Ohio Payroll Processing

Processing payroll in Ohio requires careful attention to detail and compliance with state laws and regulations. Employers can use payroll software or outsource payroll processing to a third-party provider to ensure accuracy and compliance. Some key factors to consider when processing payroll include: * Payroll Frequency: Determine the payroll frequency, whether it be weekly, biweekly, or monthly. * Payroll Cut-Off Dates: Establish payroll cut-off dates to ensure that all employee hours and earnings are accurately recorded. * Payroll Taxes: Calculate and withhold the correct amount of payroll taxes, including federal, state, and local taxes.
In final consideration, managing payroll in Ohio requires a thorough understanding of the state’s laws and regulations. By following these 5 Ohio payroll tips and staying up-to-date on the latest tax rates and regulations, employers can ensure compliance and accuracy in their payroll processing.
What is the minimum wage in Ohio?
+
The minimum wage in Ohio is 8.70 per hour for non-tipped employees and 4.35 per hour for tipped employees.
How often must employers pay employees in Ohio?

+
Employers in Ohio must pay employees at least twice per month, on regular paydays designated in advance.
What are the tax withholding rates in Ohio?

+
Ohio has a progressive income tax system, with tax rates ranging from 2.85% to 4.24%. Employers must withhold the correct amount of taxes from employee wages, taking into account the employee’s tax filing status, number of exemptions, and other factors.



