Army Reserve Pay Scale: 7 Ranks Explained
Understanding the Army Reserve Pay Scale: A Comprehensive Guide
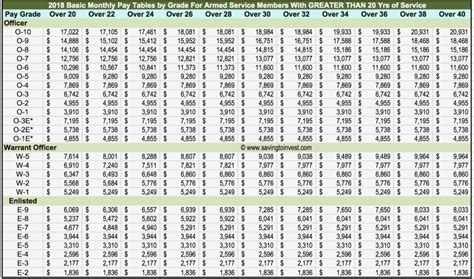
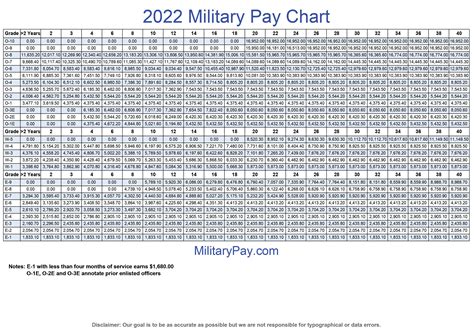
The Army Reserve is a vital component of the United States Armed Forces, providing critical support to the nation’s defense and humanitarian efforts. One of the most important aspects of serving in the Army Reserve is understanding the pay scale. In this article, we will delve into the Army Reserve pay scale, explaining the different ranks and their corresponding salaries.
What Determines Army Reserve Pay?

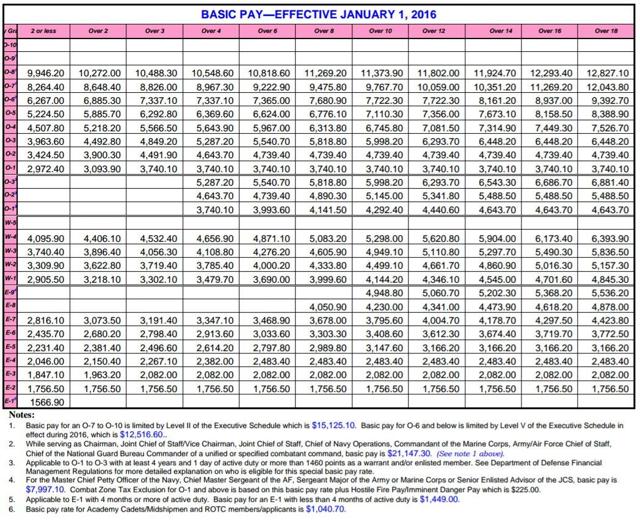
The Army Reserve pay scale is determined by two main factors: rank and time in service. The more time you serve and the higher your rank, the more you can expect to earn. Additionally, Army Reserve members receive a drill pay, which is a monthly stipend for attending training exercises and other mandatory events.
7 Army Reserve Ranks Explained

Below, we will explore seven Army Reserve ranks, from lowest to highest, and their corresponding pay scales.
1. Private (PVT) - E-1
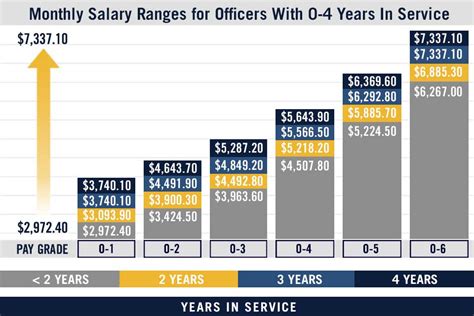
- Basic pay: 1,733.10 per month (drill pay: 172.33 per drill)
- Time in service: 0-2 years
- Description: The lowest rank in the Army Reserve, privates are entry-level soldiers who have just completed basic training.
2. Private Second Class (PV2) - E-2
- Basic pay: 1,942.50 per month (drill pay: 194.25 per drill)
- Time in service: 1-3 years
- Description: Privates second class have gained some experience and have demonstrated a higher level of responsibility.
3. Private First Class (PFC) - E-3

- Basic pay: 2,043.70 per month (drill pay: 204.37 per drill)
- Time in service: 2-4 years
- Description: Private first class soldiers have shown significant improvement and are often given more responsibilities.
4. Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - E-4

- Basic pay: 2,356.10 per month (drill pay: 235.61 per drill)
- Time in service: 3-6 years
- Description: Specialists and corporals are non-commissioned officers who have gained significant experience and leadership skills.
5. Sergeant (SGT) - E-5

- Basic pay: 2,857.40 per month (drill pay: 285.74 per drill)
- Time in service: 5-8 years
- Description: Sergeants are senior non-commissioned officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills.
6. Staff Sergeant (SSG) - E-6
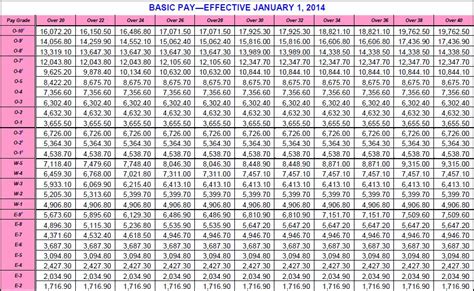
- Basic pay: 3,321.60 per month (drill pay: 332.16 per drill)
- Time in service: 7-10 years
- Description: Staff sergeants are experienced non-commissioned officers who have shown strong leadership and mentoring skills.
7. Sergeant First Class (SFC) - E-7

- Basic pay: 3,864.10 per month (drill pay: 386.41 per drill)
- Time in service: 9-12 years
- Description: Sergeant first class soldiers are senior non-commissioned officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership, technical skills, and mentoring abilities.
Additional Forms of Compensation

In addition to basic pay and drill pay, Army Reserve members may also receive:
- Special duty pay: Additional pay for specialized duties, such as drill instructor or recruiter.
- Hazardous duty pay: Additional pay for performing hazardous duties, such as parachuting or diving.
- Subsistence allowance: A monthly stipend for food and other living expenses.
- Education benefits: Eligibility for education assistance programs, such as the Montgomery GI Bill.
📝 Note: Pay scales are subject to change and may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Conclusion

Understanding the Army Reserve pay scale is essential for anyone considering a career in the military. By knowing the different ranks and their corresponding salaries, you can make informed decisions about your service and plan for your financial future. Remember to also consider additional forms of compensation, such as special duty pay and education benefits, which can enhance your overall compensation package.
How often do Army Reserve members receive pay?

+
Army Reserve members typically receive pay once a month, on the 1st and 15th of each month.
Do Army Reserve members receive benefits in addition to pay?

+
Yes, Army Reserve members are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, medical coverage, and access to base facilities.
How do Army Reserve members advance in rank?

+
Army Reserve members can advance in rank through a combination of time in service, performance evaluations, and completion of training and education courses.
Related Terms:
- Army Reserve monthly pay
- Navy Reserve pay per month
- Army Reserves pay
- Army Reserve pay calculator
- Air Force Reserves Pay Chart
- Navy Reserve Pay Chart



