5 Past Tense Verb Tips

Understanding the Past Tense: A Comprehensive Guide
The past tense is a fundamental aspect of language, used to describe actions, events, or situations that occurred in the past. Mastering the past tense is essential for effective communication, as it helps to convey when something happened, how long it lasted, and whether it has any relevance to the present. In this article, we will delve into the world of past tense verbs, exploring their usage, irregularities, and common mistakes to avoid.
Tip 1: Regular Past Tense Verbs

Regular past tense verbs are formed by adding -ed to the base form of the verb. For example, walk becomes walked, run becomes ran is an exception, and jump becomes jumped. This rule applies to most verbs in English, making it a straightforward process to convert them into the past tense. However, it’s essential to note that some verbs have different pronunciation when the -ed ending is added. For instance, the verb hug becomes hugged, with the emphasis on the first syllable.
Tip 2: Irregular Past Tense Verbs
Irregular past tense verbs, on the other hand, do not follow the -ed rule. These verbs have unique past tense forms that must be memorized. Examples of irregular past tense verbs include: * go -> went * take -> took * see -> saw * eat -> ate * give -> gave It’s crucial to learn these irregular forms, as they are commonly used in everyday conversations and writing.
Tip 3: Past Tense Verb Forms with -ing

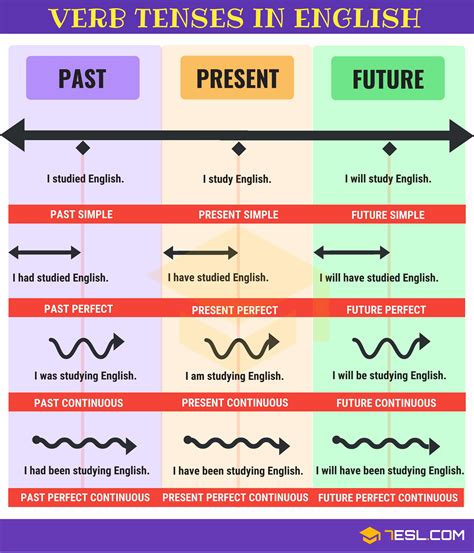
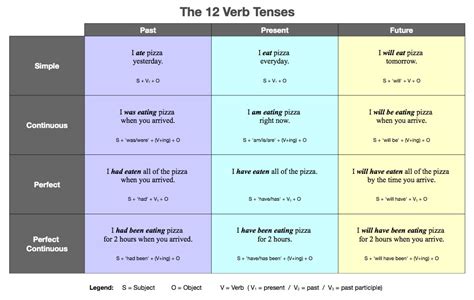
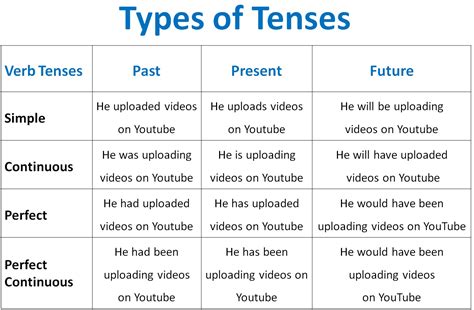
The past continuous tense is formed using the auxiliary verb was/were + the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb. This tense describes an action that was ongoing at a specific point in the past. For example: * I was walking to the store when I saw my friend. * They were studying for their exams all night. The past perfect tense, formed using had + the past participle, describes an action that occurred before another action in the past. For instance: * I had eaten breakfast before I went to the gym. * They had studied English for three years before moving to the US.
Tip 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid

When using past tense verbs, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can change the meaning of a sentence or make it unclear. Some common errors include: * Using the wrong verb form: I go to the store yesterday (should be I went) * Forgetting to use the auxiliary verb: I walking to the store (should be I was walking) * Using the present perfect instead of the past simple: I have eaten breakfast (should be I ate breakfast)
Tip 5: Practice Makes Perfect

To become proficient in using past tense verbs, practice is key. Try to incorporate past tense verbs into your daily conversations, writing, and reading. Read books, articles, and news in English to see how past tense verbs are used in context. Practice speaking and writing in the past tense, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes – it’s all part of the learning process.
📝 Note: Consistency is crucial when using past tense verbs. Make sure to use the correct verb form throughout a sentence or paragraph to avoid confusion.
To summarize, mastering the past tense is vital for effective communication in English. By understanding the rules for regular and irregular past tense verbs, using the correct verb forms, and practicing consistently, you can improve your language skills and convey your ideas with clarity and precision. The key to success lies in dedication and practice, so keep working on your past tense skills, and you’ll see improvement over time.
What is the difference between regular and irregular past tense verbs?
+
Regular past tense verbs are formed by adding -ed to the base form of the verb, while irregular past tense verbs have unique past tense forms that must be memorized.
How do I form the past continuous tense?
+
The past continuous tense is formed using the auxiliary verb was/were + the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
What is the difference between the past simple and past perfect tenses?

+
The past simple tense describes a completed action in the past, while the past perfect tense describes an action that occurred before another action in the past.