5 Plant Parts & Their Functions: Quick Guide
If you've ever been fascinated by the complexity and beauty of plant life, understanding the various parts of a plant and their functions is a great way to deepen that fascination. Plants are complex organisms that consist of multiple structures, each playing a vital role in their life cycle, growth, and survival. In this guide, we'll explore the essential parts of a plant: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits, along with what they do to make plants thrive in diverse environments.
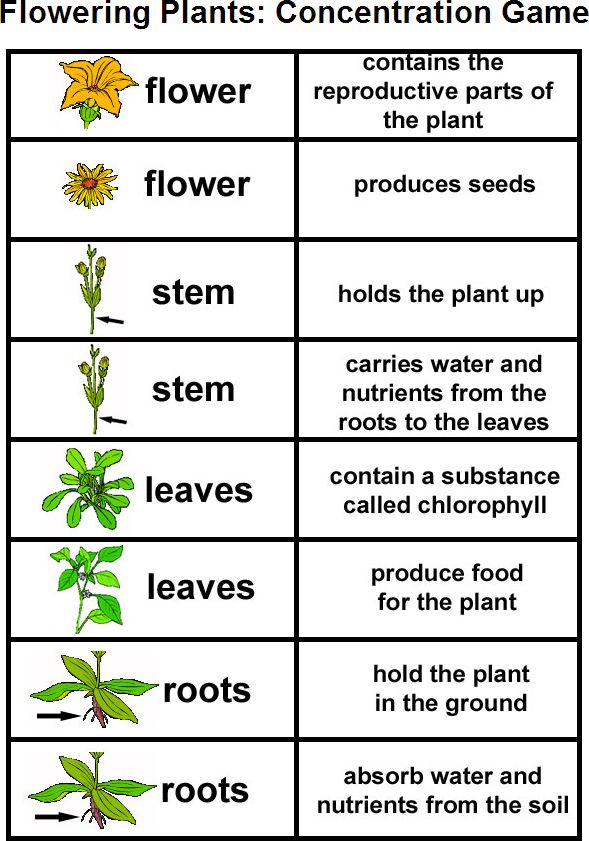
Roots


The roots serve as the base for plant support, water absorption, and nutrient uptake. Here’s a breakdown:
- Anchor the Plant: Roots hold the plant securely in the ground, preventing it from being uprooted by the wind or other natural forces.
- Water and Nutrient Absorption: They absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are crucial for plant growth.
- Storage: In some species, like carrots or potatoes, roots also store carbohydrates and other compounds for later use.
Stems


The stem’s primary roles include:
- Support: Stems hold leaves, flowers, and fruits up in the air to access sunlight.
- Transport: They facilitate the movement of water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots, leaves, and other parts through xylem and phloem.
- Vegetative Reproduction: Some plants can reproduce vegetatively through stems, like the strawberry plant with its runners.
🍃 Note: Stems vary significantly in structure, with trees having woody stems and herbaceous plants having softer, more flexible ones.
Leaves


Leaves are essentially the plant’s solar panels:
- Photosynthesis: This is where the magic happens. Through photosynthesis, leaves convert sunlight into chemical energy, producing glucose, which fuels the plant.
- Transpiration: They regulate water loss through their stomata, which also allows for gas exchange (CO2 in, O2 out).
- Food Storage: Leaves can temporarily store food, like in the case of spinach or lettuce.
Flowers

Flowers are the reproductive organs of many plants. Here’s what they do:
- Pollination: They attract pollinators like bees and birds, ensuring the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma, which can lead to fertilization.
- Fruit Formation: After pollination and fertilization, flowers can develop into fruits, which protect the seeds and help in their dispersal.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Flowers are often visually appealing, providing ecological services like attracting insects for pollination.
Fruits and Seeds


Fruits develop from fertilized ovules and have the following functions:
- Seed Dispersal: Fruits are often colorful and tasty to attract animals, which then disperse seeds after consuming the fruit.
- Nutrition: Some fruits are a source of nutrients for animals, while others, like berries, can protect seeds during digestion.
- Protection: Fruits protect seeds from environmental stress, predators, and diseases.
From the roots that anchor plants in the soil to the leaves that convert sunlight into energy, each part of a plant has evolved to perform specific roles that ensure the plant's survival and reproduction. This intricate system highlights the adaptability and resilience of plants, making them a fundamental component of Earth's ecosystem. By understanding these plant parts and their functions, we not only appreciate the beauty of nature but also gain insights into ecological balance, agriculture, and even potential medicinal uses.
FAQ Section
Can plants survive without roots?

+
While roots are crucial for anchoring plants and absorbing water, some plants like the Venus flytrap can absorb nutrients from their environment directly through their leaves. However, long-term survival without roots for water absorption would be challenging for most plants.
What is the role of leaves in water conservation?
+
Leaves regulate water loss through a process called transpiration. They control how much water is released through tiny pores called stomata, which open and close to balance water conservation with the need for CO2 for photosynthesis.
How do flowers contribute to plant reproduction?

+
Flowers facilitate sexual reproduction by attracting pollinators to transfer pollen from the male parts (anthers) to the female parts (stigmas), leading to fertilization and the development of seeds within fruits.
Why do some fruits not have seeds?

+
Seedless fruits like bananas or grapes are often the result of parthenocarpy, where fruits develop without fertilization. This can occur naturally or be induced through plant breeding techniques, providing consumers with seedless options.



