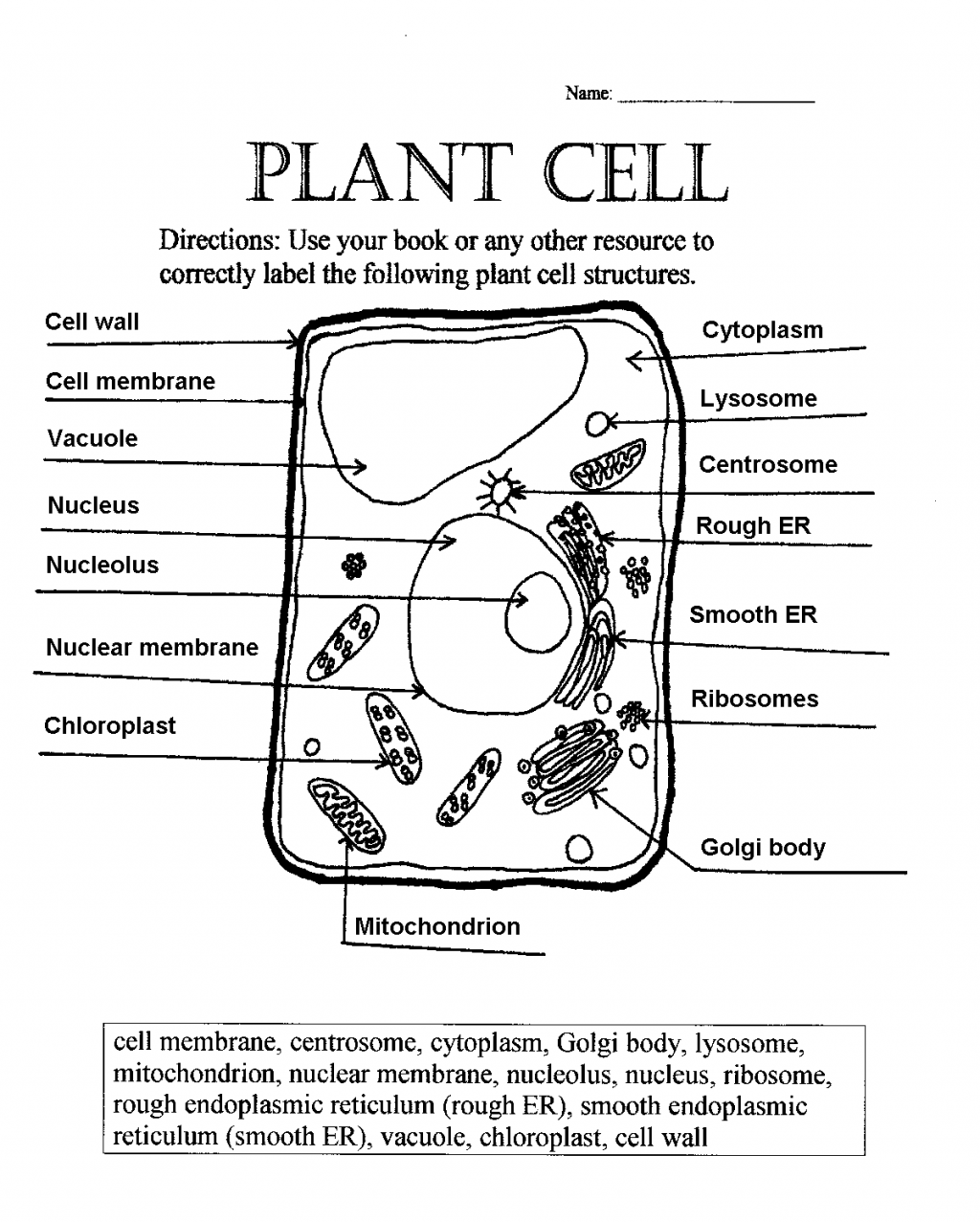
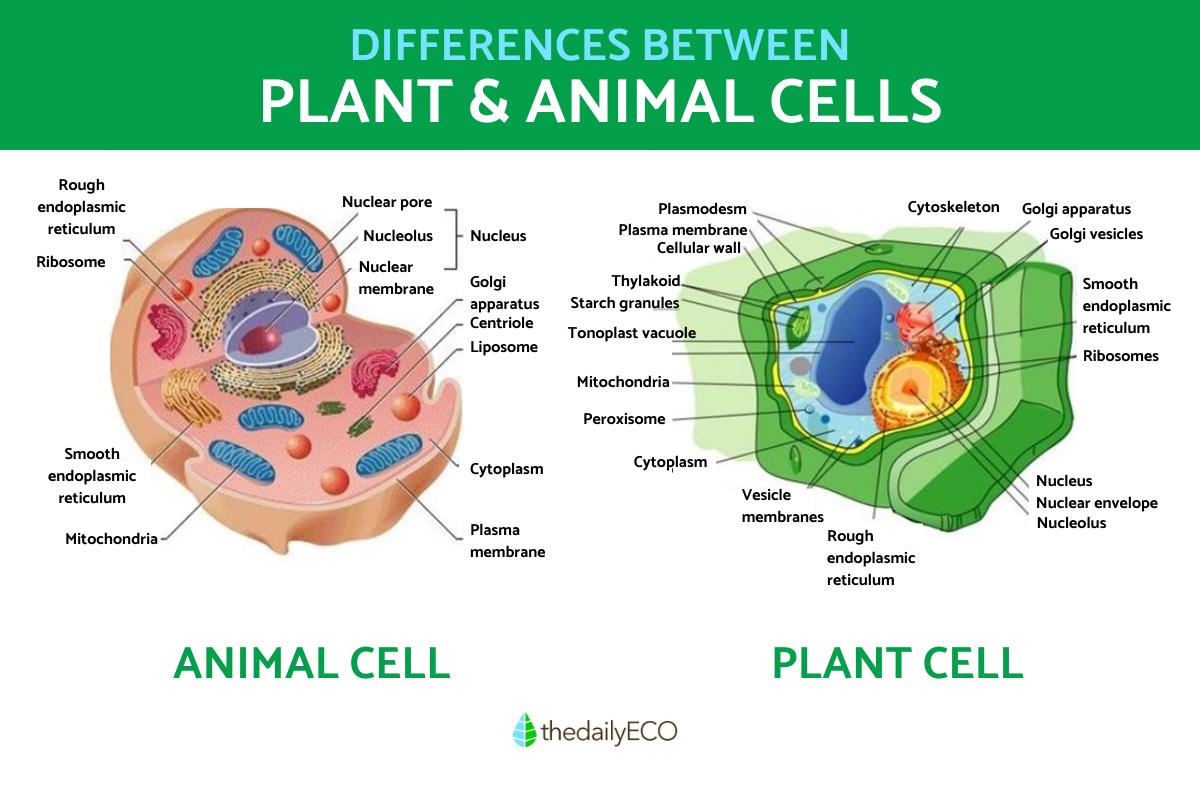
Discover the Key: Parts of a Plant Cell Worksheet
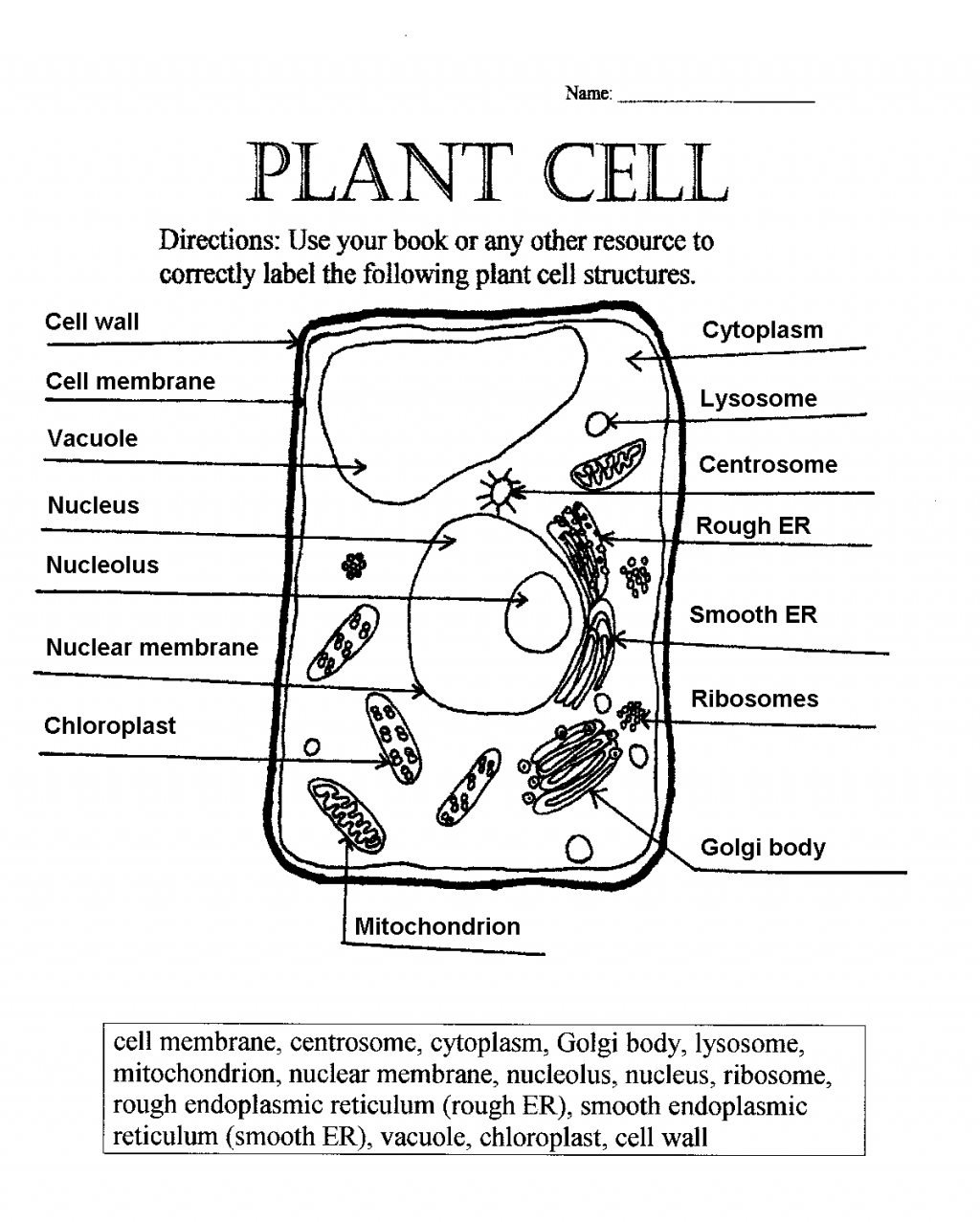
In the realm of biology, understanding the microscopic world can be both enlightening and essential for students. One of the foundational elements in plant biology is comprehending the various parts of a plant cell. A plant cell worksheet serves as an excellent tool to educate individuals about these cellular components. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate parts of a plant cell, their functions, and why understanding them is vital for any biology student.
Cell Wall: The Protective Shield

The first part we’ll explore is the cell wall. Distinct from animal cells, plant cells are surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Here’s what makes it significant:
- Protection: It serves as the cell’s first line of defense against physical damage.
- Shape Maintenance: The cell wall gives the plant cell its shape, preventing it from bursting under osmotic pressure.
- Intercellular Communication: Cell walls facilitate communication between adjacent cells through plasmodesmata.
Cell Membrane: The Gatekeeper


Just inside the cell wall, you’ll find the cell membrane, which is akin to the skin of the plant cell. Here’s how it functions:
- Selective Permeability: It controls what enters and exits the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis: Facilitates the transport of larger molecules in and out of the cell.
- Signal Reception: Membrane receptors receive signals from the environment or other cells, triggering cellular responses.
Cytoplasm: The Stage for Life


The cytoplasm encompasses all the contents within the cell membrane excluding the nucleus:
- Biosynthesis: It’s where most of the cell’s biochemical processes occur, including protein synthesis.
- Cytoskeleton Support: The cytoplasm holds the cytoskeleton, providing structure and assisting in movement.
- Storage: It contains granules and vacuoles, serving as storage for nutrients or waste products.
Nucleus: The Command Center


The nucleus is the control center of the cell, housing:
- Genetic Material: It contains DNA, the blueprint for life, within the chromatin fibers.
- Nuclear Envelope: This double-membrane structure regulates what goes in and out of the nucleus.
- Nucleolus: A dense region where ribosomal RNA is synthesized, crucial for protein assembly.
Vacuole: The Plant’s Reservoir


Vacuoles in plant cells are often large and perform several functions:
- Storage: They store water, nutrients, and waste products. As cells age, these can take up as much as 90% of the cell’s volume.
- Maintenance of Turgor Pressure: By taking up water, vacuoles provide the pressure needed for plant cells to maintain their shape and rigidity.
- Detoxification: They can also store toxins to keep them away from the rest of the cell.
Chloroplasts: The Energy Converters


Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and are critical for photosynthesis:
- Chlorophyll: This pigment captures light energy, converting it into chemical energy.
- Photosynthesis: Inside chloroplasts, the process occurs where carbon dioxide is fixed, and oxygen is released.
- Starch Storage: Chloroplasts can store the glucose they produce in the form of starch.
Mitochondria: The Energy Factories


Though they share mitochondria with animal cells, in plants, they provide:
- ATP Production: Through cellular respiration, mitochondria generate ATP, the cell’s energy currency.
- Link to Chloroplasts: They work in tandem with chloroplasts, managing energy needs during photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- Inheritance: Mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited, which can have implications in plant genetics.
Golgi Apparatus: The Cellular Sorting Hub


The Golgi apparatus in plant cells is involved in:
- Modifying and Sorting: It processes proteins and lipids, modifying them for different destinations within or outside the cell.
- Secretion: It packages these molecules into vesicles for secretion or lysosomal function.
- Cell Wall Formation: Plays a crucial role in the synthesis and secretion of cell wall materials.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Protein Manufacturer


The endoplasmic reticulum in plant cells is essential for:
- Rough ER: Where ribosomes attach and synthesize proteins for secretion or membrane insertion.
- Smooth ER: Involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
- Quality Control: Ensures proper folding of proteins before their transport or degradation.
💡 Note: A helpful mnemonic to remember key cell parts is "CCW CNV MEET" for Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, and Mitochondria.
Understanding the intricate components of a plant cell is not just an academic exercise; it opens doors to advanced botanical studies, genetic engineering, and agricultural improvements. Every part of the cell, from the protective cell wall to the energy-generating chloroplasts, plays a vital role in the life of a plant. By providing students with a structured plant cell worksheet, educators can foster a deeper appreciation for the complexity of plant biology.
Why are plant cells different from animal cells?
+
Plant cells differ from animal cells primarily because they have additional structures like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles, which are absent in animal cells.
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells?
+
The cell wall provides structural support, prevents the cell from over-expanding, and serves as a barrier against pathogens and mechanical stress.
Can plants live without chloroplasts?
+
Plants can live without chloroplasts in some specialized cells or in parasitic plants, which rely on other organisms for food, but they could not produce energy through photosynthesis.