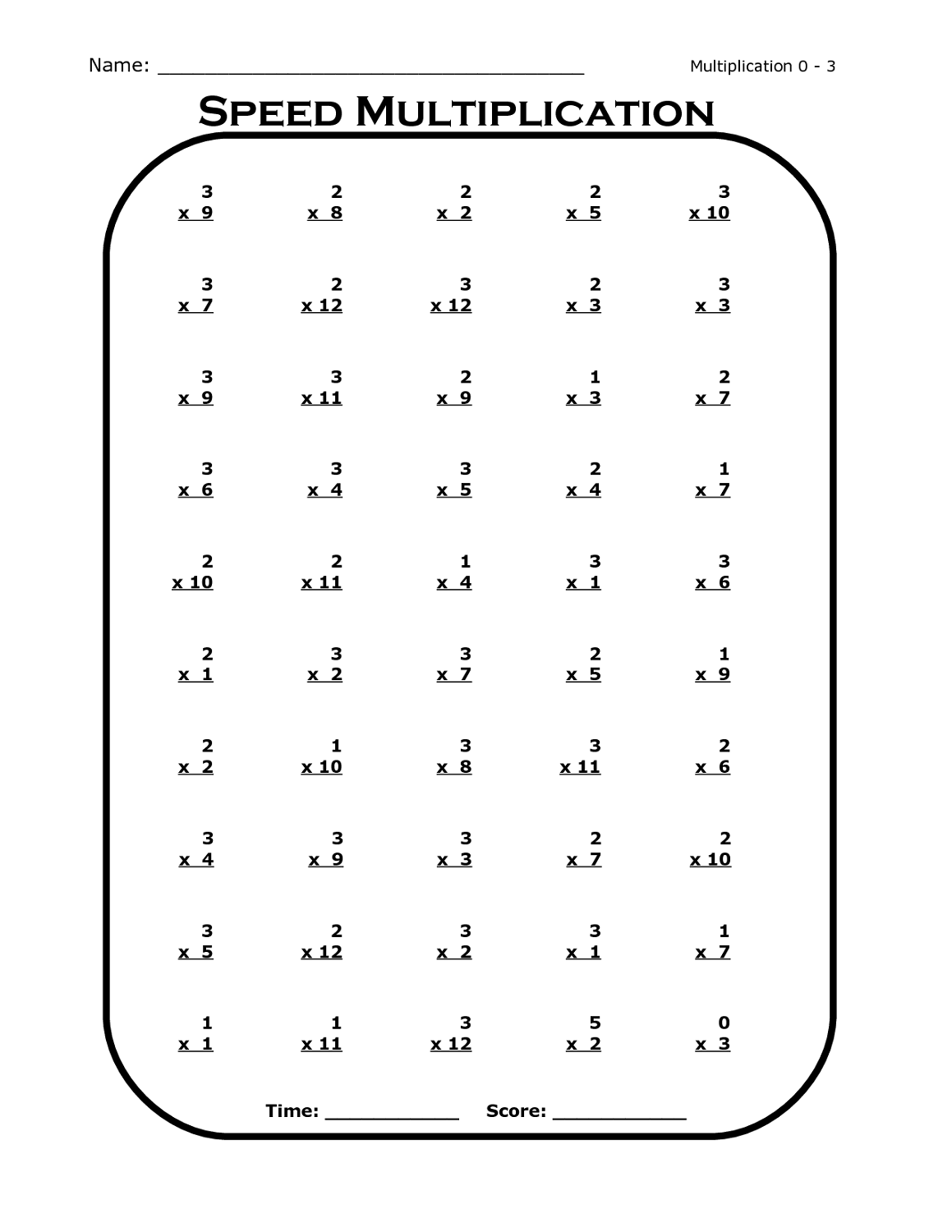
Particle Diagrams Answer Key: Simplified Solutions Guide

Understanding particle diagrams in chemistry can be both fascinating and complex. Whether you are a student, an educator, or a curious enthusiast, particle diagrams provide a visual representation of molecular or atomic structures. These diagrams are crucial for understanding chemical reactions, states of matter, and the behavior of particles at an atomic level. This post offers a comprehensive guide to interpreting and creating particle diagrams, ensuring you're equipped to tackle any problem with ease.
What Are Particle Diagrams?
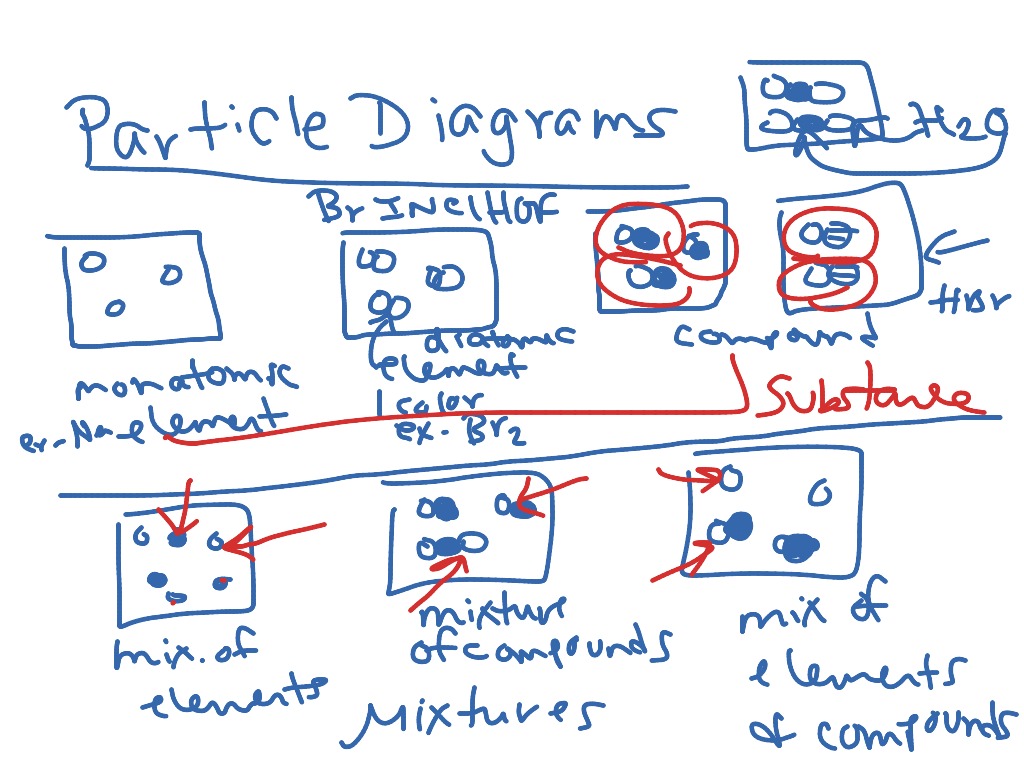
Particle diagrams are visual tools used in chemistry to illustrate the arrangement and interaction of atoms, ions, or molecules. They help in:
- Understanding the composition of substances
- Visualizing chemical reactions
- Identifying states of matter (solid, liquid, gas)
- Depicting the movement of particles
Here’s an example of how a particle diagram for ice might look:
| State of Matter | Particle Diagram |
|---|---|
| Ice (Solid) | [Ice Particle Diagram Image Here] |

Creating Your Own Particle Diagrams

Here are the steps to create a basic particle diagram:
- Identify the substance: Know what compound or element you are dealing with.
- Determine the scale: Decide whether you are drawing individual atoms, molecules, or larger structures.
- Choose the state of matter: Whether it’s a solid, liquid, or gas, this will dictate particle arrangement.
- Draw particles: Use circles or spheres to represent atoms or molecules. Different sizes or colors can indicate different elements.
- Arrange particles:
- Solids: Packed closely with minimal movement.
- Liquids: Particles are close but can move past each other.
- Gases: Widely spaced with free movement.
- Label: Use labels or a legend to clarify what each particle represents.
⚠️ Note: When representing compounds, ensure that each particle's bonding is accurately portrayed.
Interpreting Particle Diagrams

When you encounter a particle diagram:
- Identify the type of particle: Look for keys or legends for element or molecule representation.
- Analyze spacing and arrangement: The closeness and pattern of particles tell about the state of matter.
- Note any bonds: Check for connections or lack thereof between particles indicating chemical or ionic bonds.
- Observe particle size and shape: Sometimes, this can denote different atoms or phases.
Interpreting diagrams of chemical reactions, for instance:
- Reactants will often be shown on one side with products on the other, illustrating the transformation.
- Energy changes might be depicted with arrows or changes in particle arrangement.
Practical Applications

Particle diagrams aren’t just academic exercises; they have practical applications:
- Chemical Engineering: Understanding how to control reaction conditions.
- Material Science: Designing new materials with desired properties based on particle behavior.
- Environmental Science: Studying pollutant particle behavior in air and water.
- Medical Research: Examining the behavior of particles in drug delivery systems.
In summary, particle diagrams are more than mere representations. They are essential for visualizing the invisible world of chemistry. They not only aid in understanding fundamental concepts but also apply directly to real-world scientific and industrial challenges. By mastering the interpretation and creation of these diagrams, you unlock deeper insights into the intricate dance of atoms and molecules, bridging the gap between the microscopic and macroscopic realms.
How do I know if a diagram represents a solid, liquid, or gas?

+
Solid diagrams show particles in a fixed pattern with little to no space between them. Liquids have particles close but with room for movement, and gases have particles widely spaced, indicating free motion.
What does the size of a particle in a diagram indicate?

+
Generally, the size of a particle can signify different atoms, molecules, or even phases. However, consistency within a diagram is key; uniform size typically represents atoms or molecules of the same type.
Why are particle diagrams useful in chemical education?

+
They provide a tangible visualization of abstract concepts, allowing students to see how particles interact and behave in different states and reactions, thus enhancing comprehension and retention.