Partial Sums Worksheet: Simplify Learning for Students

Understanding partial sums is fundamental in mathematics, providing students with the tools to tackle more complex calculations. It's a method where you sum numbers by place value, making addition easier and more intuitive. This approach not only simplifies large computations but also aids in developing number sense.
Why Use Partial Sums in Education?

The traditional method of addition, although essential, can sometimes confuse students, especially when they move from single-digit to multi-digit numbers. Here’s where partial sums shine:
- Decomposition and Organization: It breaks down numbers into more manageable pieces.
- Understand Place Value: Students grasp how each digit’s value changes based on its position.
- Reducibility: Large sums become less intimidating when viewed as smaller, easier-to-handle parts.
- Flexibility: The strategy promotes mental math and adaptability in number manipulation.
Steps to Teach Partial Sums

Here’s a straightforward approach to teaching partial sums:
- Introduction to Place Value: Ensure students understand the significance of each digit’s place in numbers.
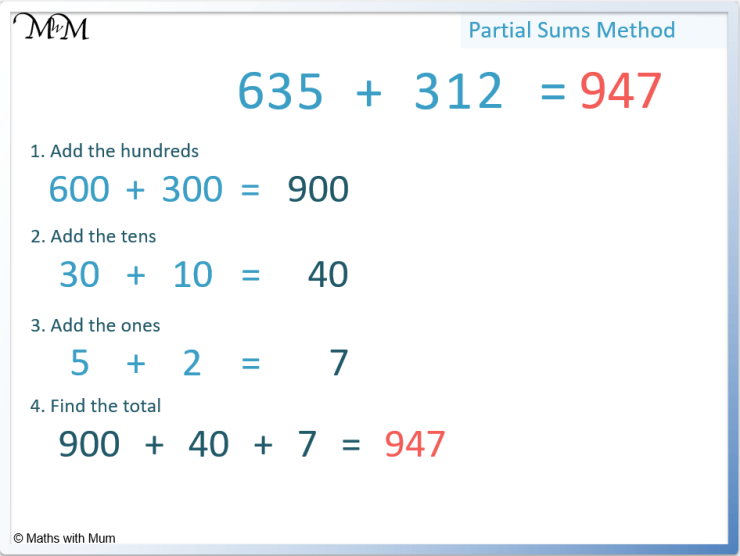
- Breaking Down Numbers: Teach them to break down each number by place value. For example, 245 becomes 200 + 40 + 5.
-
Summing Each Place: Have students add all the hundreds, then the tens, and finally the ones.
- For example, in the sum of 245 + 387:
- 200 + 300 = 500 (Hundreds)
- 40 + 80 = 120 (Tens)
- 5 + 7 = 12 (Ones)
- Combine the Sums: Students combine these sums to get the final answer.
- Example: 500 + 120 + 12 = 632

💡 Note: This visual representation helps students understand how numbers can be broken down for easier computation.
Benefits of Using Partial Sums

Here are the key benefits of adopting the partial sums method:
- Mental Math Skills: Students learn to manipulate numbers in their minds.
- Flexibility: Encourages alternative thinking strategies in math.
- Error Checking: Easier to spot errors because you’re working with simpler sums.
When to Introduce Partial Sums

Here’s a guide on when to introduce this strategy:
- After students have a solid understanding of place value.
- When transitioning from single-digit to multi-digit addition.
- As an alternative method for students struggling with traditional addition.
Visual Aids and Manipulatives

Using visual aids can make learning partial sums more engaging:
- Base Ten Blocks: Use these to represent each place value visually.
- Number Lines: Show addition steps in a number line context.
- Place Value Charts: Enhance understanding of where numbers belong.

Practice and Reinforcement

Here’s how to ensure students retain this learning:
- Use worksheets with increasing complexity to provide ample practice.
- Create real-life scenarios where partial sums are beneficial.
- Encourage students to explain their process to others.
- Incorporate games and interactive activities involving partial sums.
In summary, introducing students to partial sums not only makes math more intuitive but also equips them with a powerful tool for handling arithmetic. With its emphasis on understanding and mental flexibility, this strategy fosters not just computational ability but also a deeper mathematical mindset.
What are partial sums in math?

+
Partial sums are a method of addition where each digit’s place value is added separately before combining for the final answer.
How does partial sums help students?

+
Partial sums simplify larger numbers into easier-to-add parts, promote understanding of place value, and foster mental flexibility in calculations.
Can partial sums be used for all addition problems?
+
Yes, it can be applied to all multi-digit addition problems, though it’s particularly useful for sums with larger numbers or for students learning place value.