Oxidation Number Worksheet Answers: Simplify Your Chemistry Studies

In chemistry, understanding oxidation numbers (also known as oxidation states) is vital for grasping concepts like redox reactions, electrolysis, and other fundamental chemical processes. This detailed worksheet provides a comprehensive guide to help you master the art of determining and working with oxidation numbers.
What Are Oxidation Numbers?


Before diving into the worksheet, let’s clarify what oxidation numbers are. They are:
- Fictitious charges assigned to atoms in a compound.
- Tools to keep track of electrons in redox reactions.
- Numbers that help predict the behavior of elements in different chemical environments.
Basic Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers

Here are the fundamental rules you should follow:
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | In pure elements (like O2 or H2), the oxidation number is 0. |
| 2 | In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2. |
| 3 | Hydrogen’s oxidation number is +1 when bonded to non-metals, and -1 when bonded to metals. |
| 4 | The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound equals zero. In polyatomic ions, the sum equals the ion’s charge. |
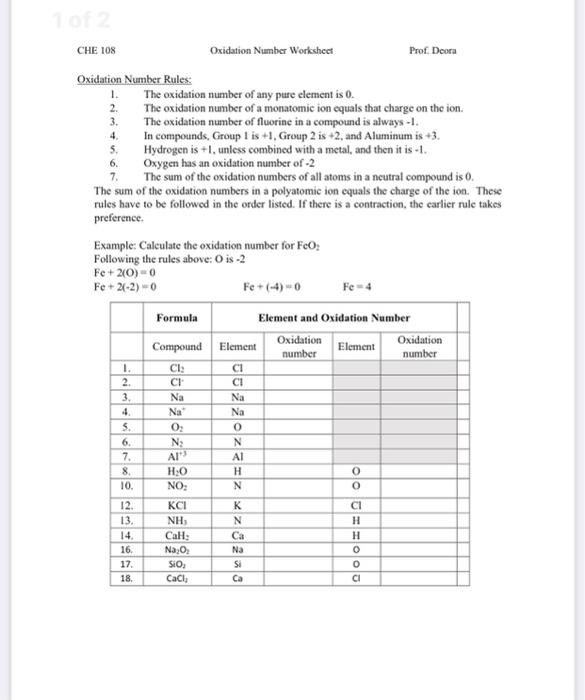
Worksheet Examples and Solutions

Example 1: Binary Compounds

- HCl
- H has an oxidation number of +1 (Rule 3).
- Cl must then be -1 to make the sum zero (Rule 4).
💡 Note: When dealing with binary compounds, ensure the sum of oxidation numbers is always zero.
Example 2: Polyatomic Ions
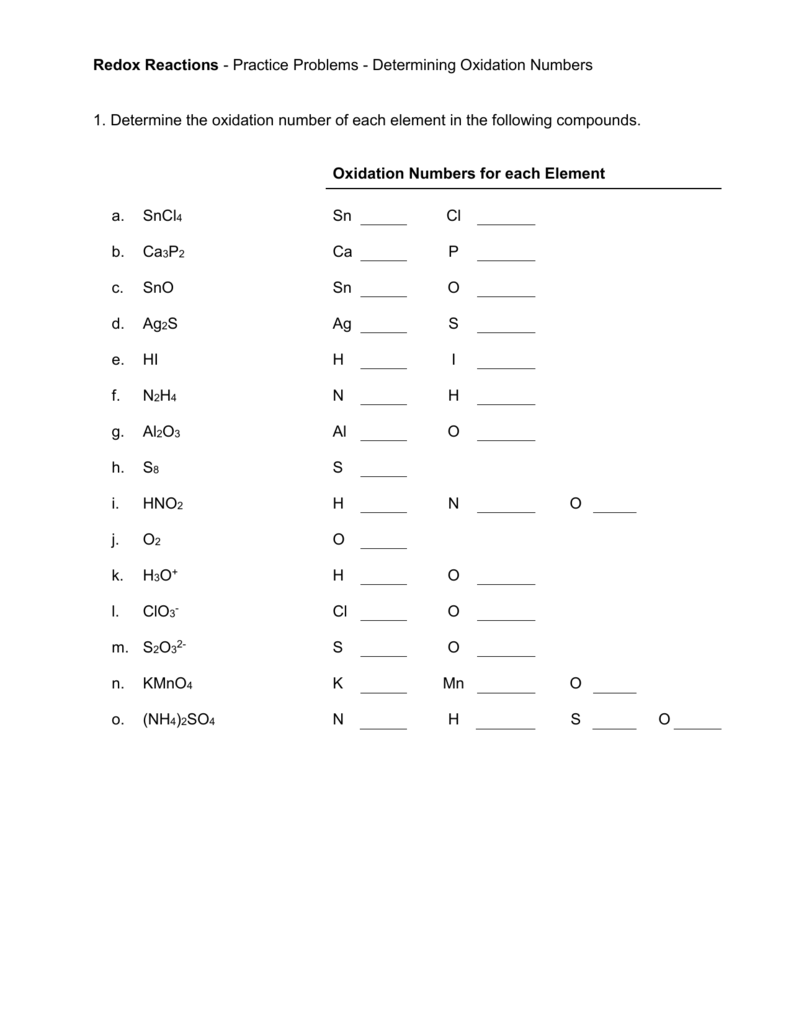
- SO42-
- Each O has -2 (Rule 2).
- 4 O atoms make -8.
- The ion’s total charge is -2, so S must be +6.
Example 3: Complex Ions

- [Fe(CN)6]3-
- CN- ion’s oxidation numbers are +2 for C and -3 for N.
- There are 6 CN ions, summing to a total charge of -6.
- Iron must then be +3 to balance the -3 charge (Rule 4).
To master oxidation numbers, practice is key. Below are some further examples to test your understanding:
Additional Practice Problems

Problem 1: Determine the oxidation numbers in AlCl3

- Al has an oxidation number of +3.
- Each Cl has -1.
Problem 2: Find the oxidation number of S in H2S

- H has an oxidation number of +1.
- There are two H, so they sum to +2.
- S must be -2 to balance.
Problem 3: Determine the oxidation number of Mn in MnO4-

- Each O has -2, summing to -8.
- The ion charge is -1, so Mn must be +7.
Final Thoughts on Oxidation Numbers

Understanding oxidation numbers not only simplifies the study of redox reactions but also provides insights into the chemical behavior of substances. By recognizing patterns in how elements behave, you can predict reactions more accurately and understand chemical equations more deeply.
Why are oxidation numbers important?

+
Oxidation numbers help in understanding the electron transfer in chemical reactions, which is key to analyzing and predicting redox reactions, balancing chemical equations, and understanding the reactivity of elements.
How do I know if an oxidation number is correct?

+
You can verify by ensuring the sum of oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion equals the charge of the ion or zero for a neutral compound. Also, you can check against common known oxidation states of elements.
Can an element have more than one oxidation number?

+
Yes, many elements, especially transition metals, can exhibit multiple oxidation states. For instance, iron can be +2, +3, or even +6 in some compounds.