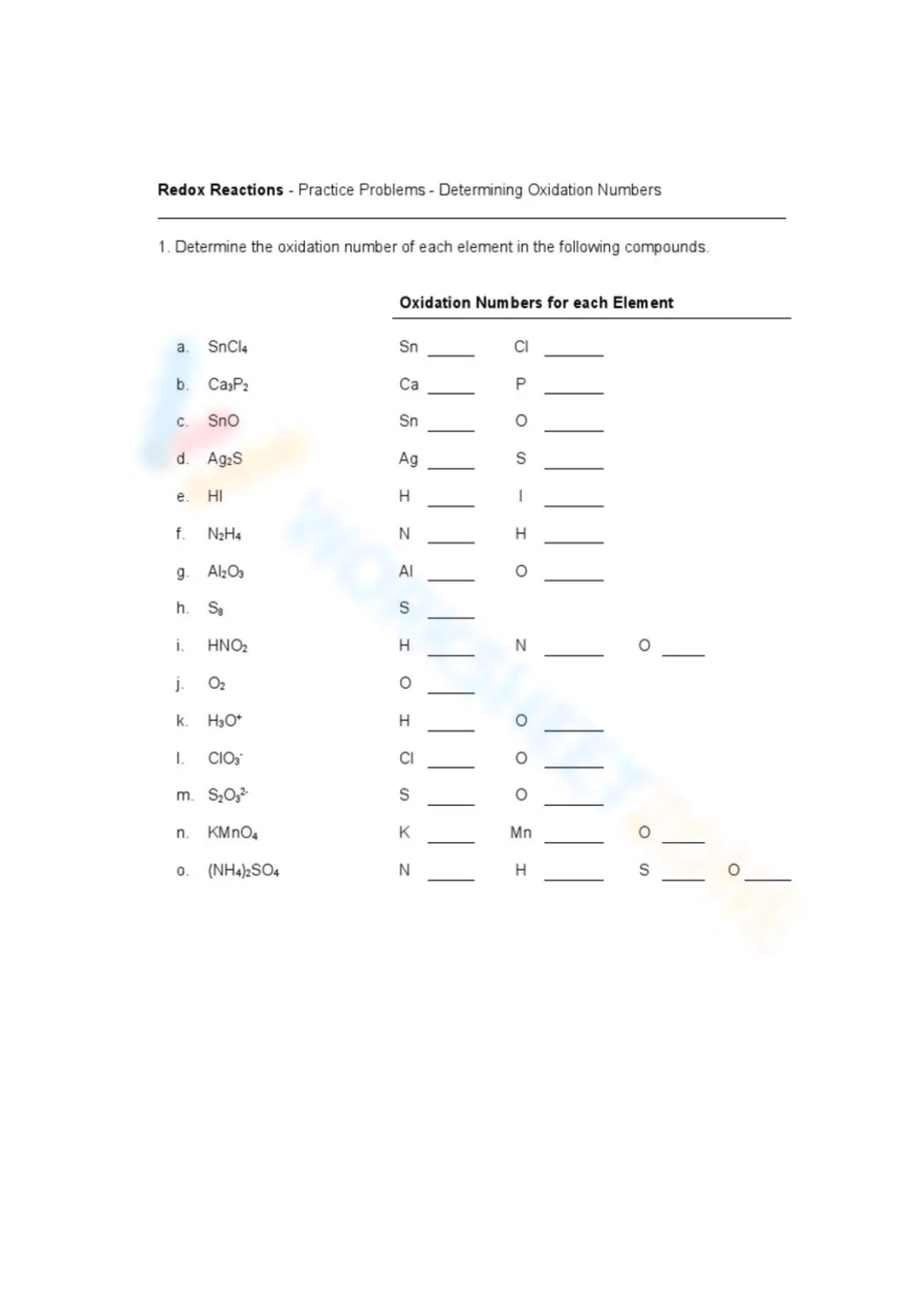
Master Oxidation Numbers with Our Worksheet Guide
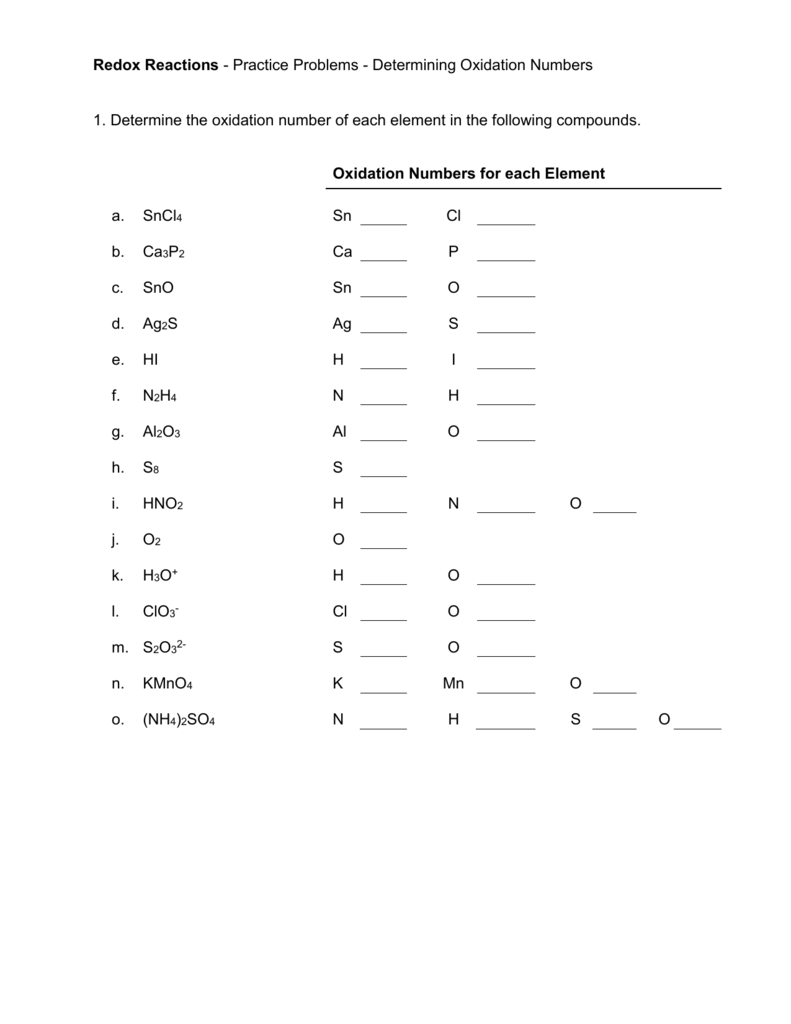
Understanding the concept of oxidation numbers, or oxidation states, is fundamental for anyone delving into chemistry. These numbers serve as a tool to understand how atoms might gain, lose, or share electrons, which is crucial in predicting the behavior of elements in chemical reactions. Today, we're not just talking about theory; we're providing you with a practical guide on how to master oxidation numbers through a comprehensive worksheet. This guide will not only boost your confidence but also enhance your analytical skills in chemistry.
What Are Oxidation Numbers?

Oxidation numbers are fictional charges assigned to atoms in compounds or ions, illustrating their hypothetical ionic state. These numbers:
- Help in identifying the oxidation state of elements.
- Indicate the distribution of electrons among atoms.
- Are essential in naming compounds, balancing redox reactions, and predicting chemical properties.
Let’s dive into how these numbers work in practice.
Why Master Oxidation Numbers?

Mastering oxidation numbers is vital because:
- Balancing Reactions: Redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions require understanding oxidation states to balance the equation correctly.
- Nomenclature: Properly naming compounds often requires knowing the oxidation state.
- Electrochemical Considerations: Oxidation states predict the behavior of elements in electrical cells.
- Understanding Bonding: Knowledge of oxidation states helps in predicting bond strengths and properties in molecules.
⚗️ Note: While atoms in their elemental form have an oxidation number of 0, elements can have different oxidation states when bonded in a compound.
Our Oxidation Number Worksheet Guide
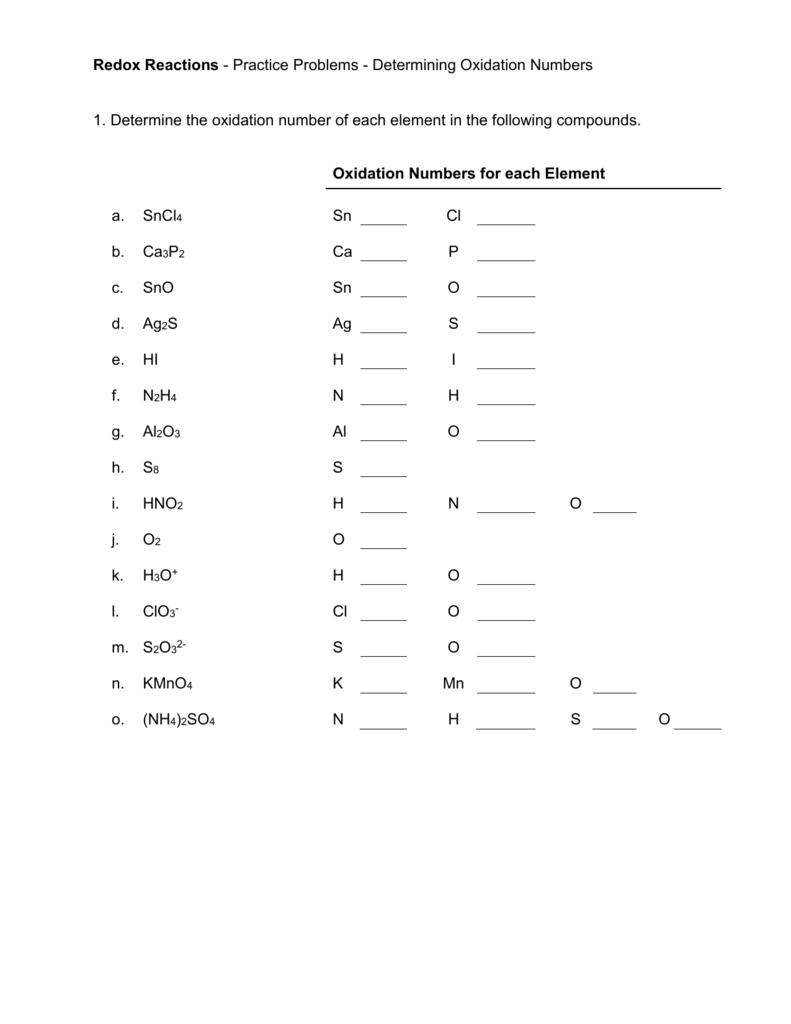
Here’s a step-by-step guide on using our worksheet to master oxidation numbers:
1. Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers

Start with learning the rules:
- Free elements have an oxidation number of 0.
- Monoatomic ions have oxidation numbers equal to their charge.
- Hydrogen’s oxidation state is usually +1, but it’s -1 when combined with elements less electronegative than itself.
- Oxygen’s oxidation state is typically -2, but it can be -1 in peroxides and -1⁄2 in superoxides.
- Fluorine always has an oxidation number of -1 in its compounds.
- The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is 0, while in an ion, it equals the ion’s charge.
2. Applying the Rules

Using the worksheet, apply these rules to different compounds:
- Try exercises like:
- What’s the oxidation number of S in H2SO4?
- Determine the oxidation states of C in C2H6 and C2H4.
- Practice with ions like:
- What are the oxidation states of each element in SO42-?
3. Identifying Redox Reactions

Next, your worksheet will ask you to:
- Identify oxidation and reduction in chemical reactions:
- Which element is oxidized in the reaction 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO?
- Determine the oxidizing and reducing agents.
4. Complex Molecules and Polyatomic Ions

Test your understanding with complex molecules and ions:
- Assign oxidation numbers to the elements in ClO3-.
- Figure out the oxidation state of Mn in KMnO4.
5. Tips and Tricks
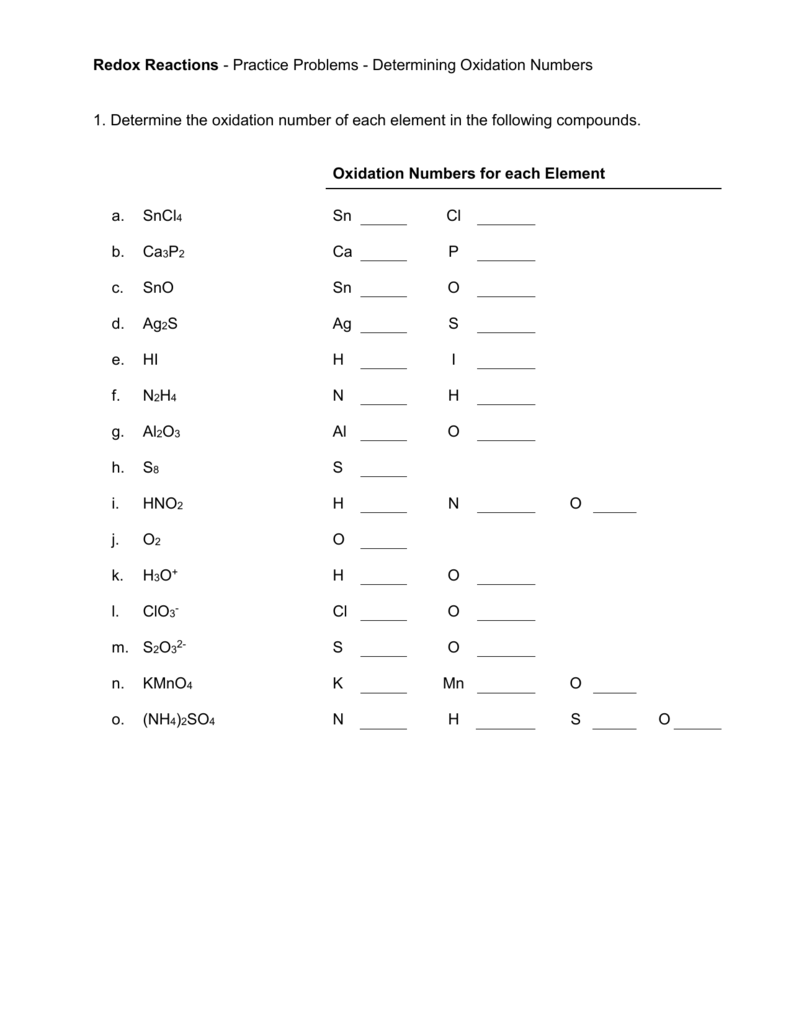
- Know Your Element Charges: Memorize common ion charges to quickly determine oxidation states.
- Break It Down: For complex molecules, break them down into known groups or ions.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you practice, the more familiar you become with common oxidation states.
💡 Note: Some elements have fixed oxidation states in certain compounds, which can serve as shortcuts when determining unknown states.
Benefits of Using Our Worksheet

- Reinforce Knowledge: Active application helps cement theoretical knowledge.
- Identify Weaknesses: You’ll quickly see areas where you might need more study.
- Prepare for Exams: Get ready for chemistry assessments with confidence.
- Enhance Analytical Skills: Understand the bigger picture of chemical reactions.
Mastering oxidation numbers through this structured approach will significantly enhance your chemical intuition. By working through our worksheet, you'll gain not only a theoretical understanding but also the practical skills to apply this knowledge in real-world chemical problems. Remember, like any skill in chemistry, mastering oxidation numbers requires consistent practice and engagement with the material. As you progress, you'll find that your ability to predict, understand, and manipulate chemical reactions will improve, offering you a competitive edge in both academic and professional settings.
Why are oxidation numbers important in chemistry?
+
Oxidation numbers help chemists understand the behavior of elements in compounds, determine the oxidation state for nomenclature, balance redox reactions, and predict properties and reactivity in chemical reactions.
Can an element have multiple oxidation states?

+
Yes, many elements, particularly transition metals, can exhibit multiple oxidation states depending on the compound they’re in. For example, iron can be Fe+2 or Fe+3.
How do I use a worksheet to master oxidation numbers?

+
A worksheet provides practice problems where you apply rules to determine oxidation numbers in different compounds and reactions. Through repetition and practice, you’ll get better at recognizing patterns and applying rules quickly and accurately.
What if my calculated oxidation number doesn’t match the element’s group?

+
Oxidation states can differ from an element’s group number, especially in compounds. This discrepancy often occurs when elements form multiple bonds or when the compound has a net charge, like in polyatomic ions.