Orthographic Drawing: Master Your Skills with This Worksheet

In the world of design, drafting, and engineering, one of the most fundamental skills to master is the creation of orthographic drawings. These drawings provide a clear, detailed representation of an object in a two-dimensional form, displaying its multiple sides in relation to each other. Whether you're an aspiring engineer, an architect, or a hobbyist looking to sharpen your technical drawing skills, this comprehensive worksheet on orthographic drawing will guide you through the process with step-by-step instructions, helpful tips, and practical exercises.
Understanding Orthographic Projection
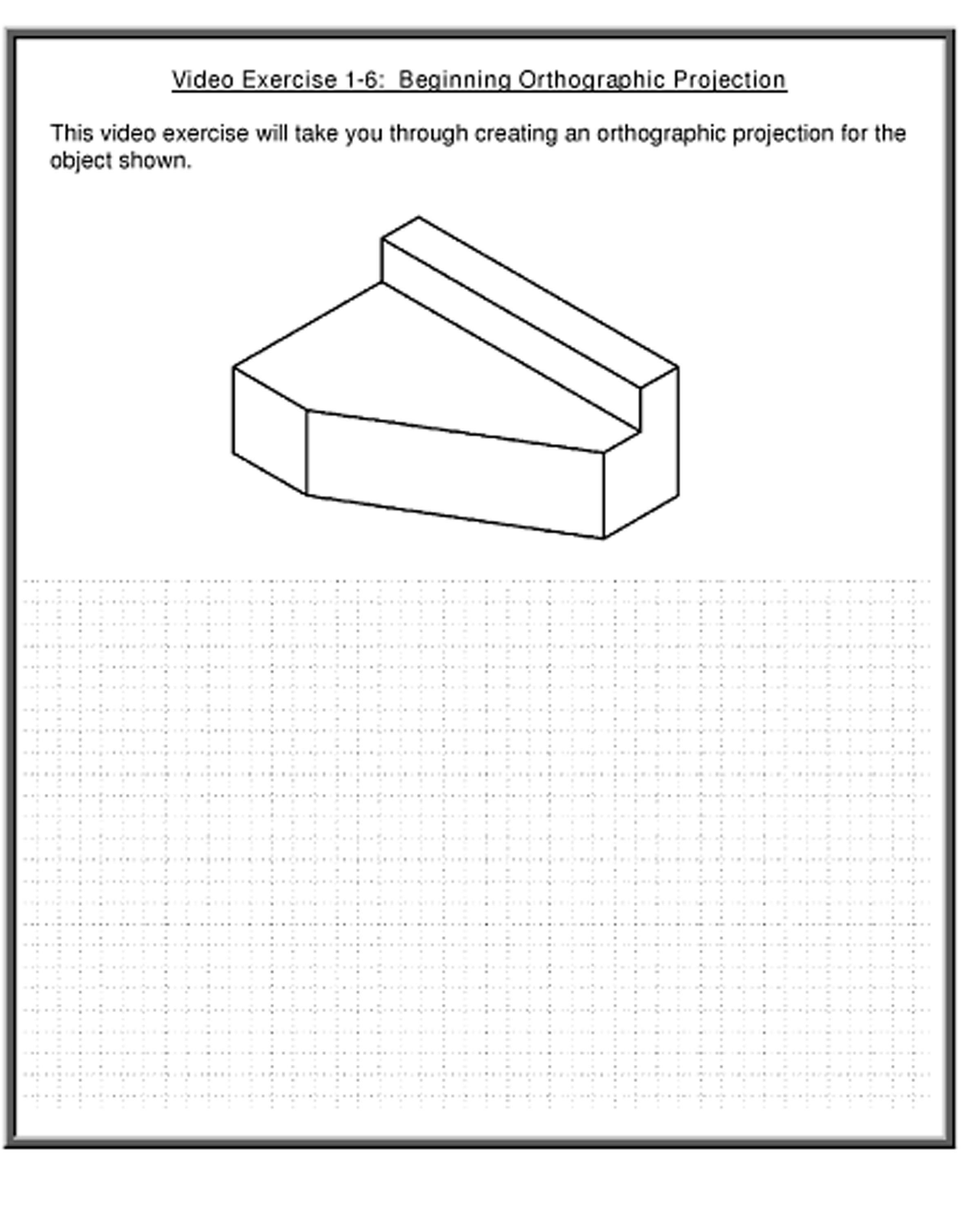
Orthographic projection, often referred to as multiview projection, is a technique used to represent a three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional plane. Here’s a basic rundown:
- Front View: Shows the front face of the object.
- Top View: Illustrates the top of the object.
- Side View: Displays the right or left side of the object.
Key Concepts

- Parallel Projection: Lines of sight or projection are parallel and perpendicular to the plane of projection.
- Principal Planes: The six sides of the bounding box around an object, where views are typically taken.
- Hidden Lines: Represented by dashed lines, these indicate features or edges hidden from the view being shown.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Orthographic Drawings
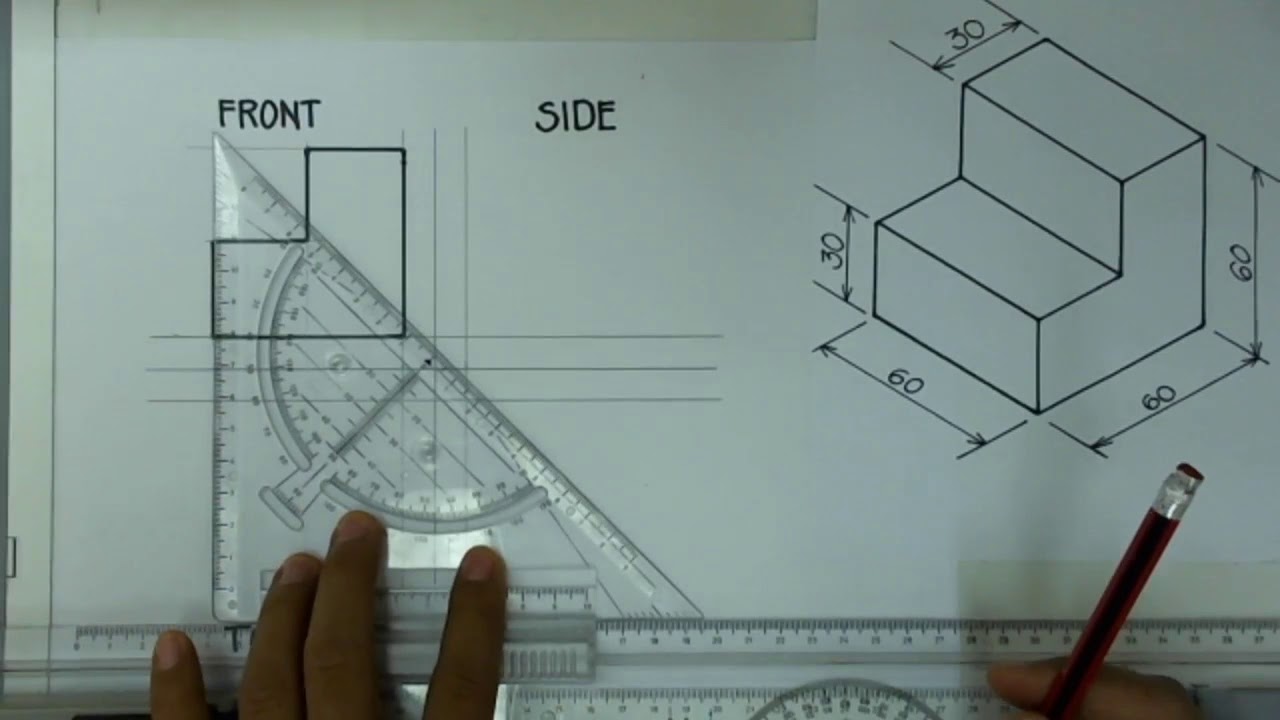
Follow these steps to practice creating your own orthographic drawings:
Choose Your Object
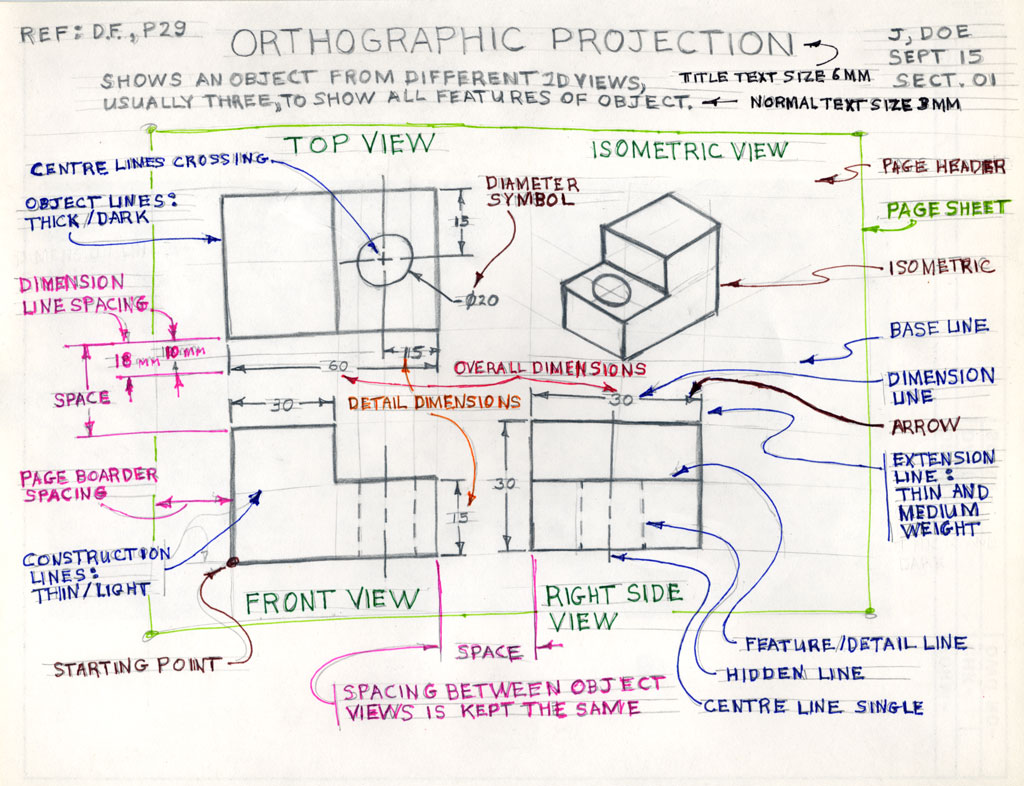
Select a simple object with clear, distinct sides. This could be a cube, a basic building, or any small object around your workspace.
Sketch the Object

Before you dive into detailed drawing:
- Lightly sketch your object in 3D to get a sense of its volume and orientation.
- Establish the orientation of your object with respect to the north.
Set Up Your Views

Using a pencil, lightly draw the guidelines for the front, top, and side views:
Front View Top View Side View [Sketch a rectangle here] [Sketch a rectangle here] [Sketch a rectangle here] 
Transfer Measurements

Measure the object or use the sketch:
- Transfer measurements from your 3D sketch or real object to the front view.
- Use a ruler for precision to ensure all dimensions are accurate.
Draw Each View
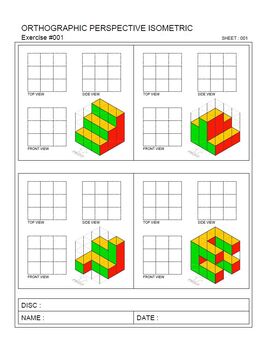
Draw each view based on the measurements:
- Ensure each view aligns with the others. Use construction lines if necessary.
- Add hidden lines where features are obscured in certain views.
- Label dimensions, if required, using standard drafting notation.
Review and Refine

Check your drawing for consistency:
- Compare views to ensure they logically match up.
- Correct any discrepancies, ensuring all lines are parallel where they should be.
- Use an eraser to clean up construction lines, leaving only the final drawing.
👉 Note: Remember, the key to mastering orthographic drawing lies in consistency. Pay attention to alignment, ensure all lines are parallel to their respective planes, and always review your work for accuracy.
Practical Exercises

Now that you understand the basic principles, let’s put that knowledge into practice:
Exercise 1: Simple Cube

Draw an orthographic projection of a simple cube with all sides equal.
Exercise 2: Box with Protrusions

Draw a box with various protrusions, like cylinders or smaller cubes protruding from its sides.
Exercise 3: Everyday Object

Pick an object around you (e.g., a mug, a laptop, or a book) and create its orthographic drawing.
👉 Note: Remember to approach each exercise with patience. Start with simple shapes and gradually increase complexity as you gain confidence in your skills.
Tips for Perfecting Your Drawings

- Use a Grid: For complex objects, grid paper can help maintain proportions.
- Reference Points: Use points on your object to align views accurately.
- Rotate Your Paper: Sometimes, rotating your paper can help visualize different views.
- Practice Hidden Lines: This aspect can be challenging. Pay attention to how objects relate in space.
👉 Note: Mastery in orthographic drawing requires practice. Don't be discouraged by initial mistakes; they are part of the learning curve.
Why Master Orthographic Drawing?

Orthographic drawing is not just a skill for those in technical fields:
- It enhances spatial visualization and problem-solving capabilities.
- It is essential for clear communication in manufacturing, architecture, and product design.
- It can be a fun way to dissect and understand objects from all angles.
By now, you've equipped yourself with the knowledge to create accurate and informative orthographic drawings. Whether you're pursuing a career that demands technical precision or you're an enthusiast looking to master a new skill, the practice of orthographic projection will undoubtedly enhance your understanding of spatial relationships, enhance your attention to detail, and improve your ability to visualize and communicate complex ideas effectively.
What are the benefits of learning orthographic drawing?
+
Orthographic drawing enhances your spatial reasoning, helps in manufacturing, and improves your ability to visualize objects from various angles, fostering better communication in technical fields.
How do you align views in an orthographic drawing?
+
Align views by ensuring that corresponding dimensions and features match up correctly between views. Use construction lines or reference points to maintain alignment.
What role do hidden lines play in orthographic projection?
+
Hidden lines indicate features or edges of an object that are not visible from the view being shown, helping to clarify the object’s three-dimensional shape.
Can orthographic drawing be done digitally?
+
Yes, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is widely used for creating accurate orthographic projections digitally, offering tools for precision and easy revisions.
What are some common mistakes in orthographic drawing?
+
Common mistakes include inconsistent dimensions across views, neglecting hidden lines, and not aligning views correctly, which can distort the object’s representation.