5 Tips for Mastering Decimal Number Lines

The Basics of Decimal Number Lines

 Understanding the fundamentals of decimal number lines is crucial when mastering mathematical concepts, especially those related to real numbers and their representation. Decimal number lines are linear scales that help visualize numbers, including whole numbers, decimals, and fractions, providing a visual aid for arithmetic operations and conceptual understanding.
Understanding the fundamentals of decimal number lines is crucial when mastering mathematical concepts, especially those related to real numbers and their representation. Decimal number lines are linear scales that help visualize numbers, including whole numbers, decimals, and fractions, providing a visual aid for arithmetic operations and conceptual understanding.
- Place Value: Every segment between whole numbers represents a decimal place value.
- Direction: Numbers increase as you move to the right, decrease to the left.
- Units of Distance: The distance between each whole number equals 1.0, while the segments between whole numbers are further divided into tenths, hundredths, etc.
Tip 1: Understand the Scale of Decimal Number Lines

 Grasping the scale of decimal number lines is vital for effective use:
Grasping the scale of decimal number lines is vital for effective use:
- Divide Segments: Each segment is typically divided into ten equal parts for decimals.
- Read Intervals: Practice reading the scale from 0 to 1 in tenths, hundredths, and even thousandths.
- Size and Proportion: Use proportionate markers or reference points to visually represent the decimal values accurately.
📏 Note: Always ensure that the scale of your number line correlates with the problem at hand. For example, if you're dealing with tenths, make sure the number line reflects this scale.
Tip 2: Plotting Points on a Decimal Number Line

 Learning to accurately plot decimal points on a number line is a skill:
Learning to accurately plot decimal points on a number line is a skill:
- Identify Whole Number: Start by finding the whole number closest to your point.
- Subdivide Segment: Divide the space between whole numbers into tenths, and if needed, into smaller parts.
- Estimate Position: Use proportion to estimate the exact location of the decimal on the segment.
- Label: Clearly label the points for clarity and later reference.
Tip 3: Ordering and Comparing Decimals
 To compare and order decimals, use number lines:
To compare and order decimals, use number lines:
- Visualize Each Decimal: Plot each decimal to be compared on the number line.
- Position Comparison: Determine which point is furthest to the right, indicating a larger value.
- Equality: Points that align exactly on the same vertical line are equal.
- Order: Read from left to right to establish the order of numbers.
Tip 4: Adding and Subtracting with Decimal Number Lines

 Number lines are an excellent tool for adding and subtracting decimals:
Number lines are an excellent tool for adding and subtracting decimals:
- Start Point: Locate the first number on the number line.
- Addition: Move to the right for addition, counting each segment as you go.
- Subtraction: Move left to subtract, keeping track of the segments passed.
- Exact Point: Find the exact point on the line that represents the result.
🔍 Note: When dealing with subtraction, it's often easier to find the distance between the points and then proceed in the opposite direction.
Tip 5: Using Number Lines for Real-World Applications

 Decimal number lines have practical applications:
Decimal number lines have practical applications:
- Measurements: For measurements that require precision, like in construction or sewing.
- Finance: Understanding currency, stock prices, or financial growth charts.
- Statistics: Visualizing statistical data, such as growth rates or probabilities.
- Time: Timekeeping and scheduling when dealing with fractions of hours or seconds.
Mastering decimal number lines allows one to approach real numbers with a visual and intuitive understanding, facilitating problem-solving and conceptual mastery. By using these tips, you can enhance your numerical literacy and tackle complex mathematical problems with ease. Whether it's visualizing fractions, comparing numbers, performing basic arithmetic, or applying the concepts in real-life scenarios, decimal number lines are an invaluable tool for learning and understanding mathematics.
Why are decimal number lines useful in education?

+
Decimal number lines are useful because they provide a visual representation of numbers, which aids in understanding the concept of place value, comparing magnitudes, and visualizing operations like addition and subtraction.
How can I help my child understand decimal number lines?

+
Practice plotting simple decimals on a number line. Use everyday objects or measurements to link the abstract concept to real-world applications, and encourage them to estimate and verify decimal positions.
Can decimal number lines be used beyond basic arithmetic?

+
Yes, decimal number lines can be extended for more complex concepts like algebra, understanding functions, rates of change, and even data analysis in statistics.
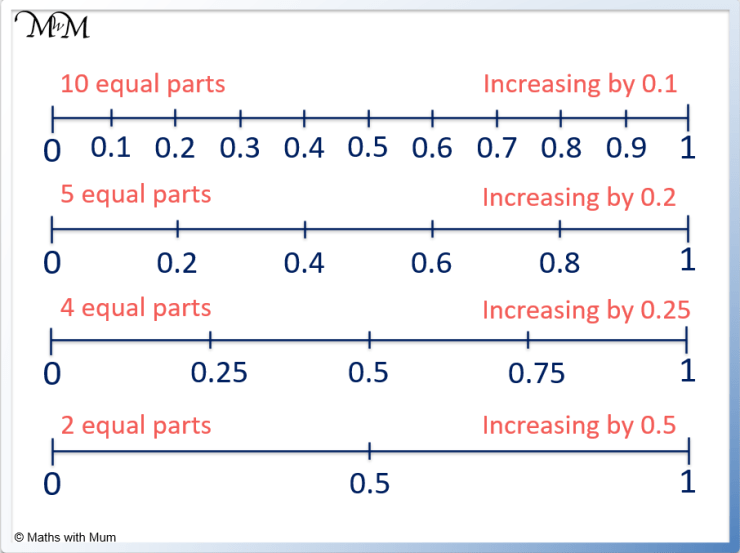
What’s the difference between a regular number line and a decimal number line?
+
A decimal number line focuses on the intervals between whole numbers, subdividing them to represent decimal places, while a regular number line may only show whole numbers or larger intervals.
Is there any software or tool that can simulate decimal number lines?

+
Yes, there are educational software programs and apps that allow for interactive decimal number line simulations, aiding in teaching and learning.