Orbital Diagram Worksheet Answers: Master Chemistry Easily

In the fascinating world of chemistry, mastering concepts like electron configurations can significantly bolster your understanding and proficiency. An essential tool in visualizing and understanding where electrons are placed within an atom is through Orbital Diagrams. This comprehensive blog post delves into the intricacies of orbital diagram worksheet answers, guiding you through the process of decoding these visual aids, enabling you to master chemistry with ease.
Understanding Orbital Diagrams

Before we jump into the answers, it’s vital to grasp what orbital diagrams are. These diagrams:
- Visualize electron placement within an atom’s energy levels.
- Represent each orbital with a line, and electrons within these orbitals are depicted by arrows.
- Use Hund’s Rule to show electrons in singly occupied orbitals before pairing up.
- Incorporate the Pauli Exclusion Principle to ensure no two electrons in the same orbital share all four quantum numbers.

How to Construct an Orbital Diagram
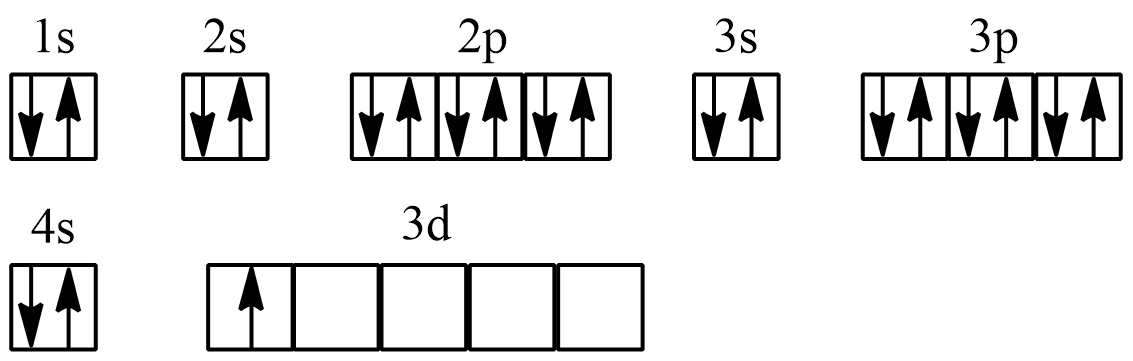
Here’s a step-by-step guide to constructing an orbital diagram:
- Identify the element: Determine the atomic number to know how many electrons are present.
- Write out electron configuration: Use the Aufbau Principle to determine the order of filling orbitals.
- Draw the orbitals: Each energy level is split into subshells - s, p, d, and f - with increasing levels of complexity.
- Fill electrons: Start filling from the lowest energy level up. Use arrows for electrons: one pointing up, the next down for pairs.
- Apply Hund’s Rule: Place electrons singly in each orbital before pairing them up.
Sample Orbital Diagram Worksheet Answers

Let’s look at some sample answers to common questions on an orbital diagram worksheet:
Example 1: Orbital Diagram for Nitrogen (N)
| Energy Level | Subshell | Orbital Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2 | p | ↑_ _ _ |

Nitrogen has 7 electrons. We start filling from the 1s orbital, move to 2s, and then place electrons in the 2p orbitals according to Hund’s Rule.
👀 Note: The 2p orbitals will be filled one electron at a time before pairing.
Example 2: Orbital Diagram for Phosphorus (P)

| Energy Level | Subshell | Orbital Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2 | p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 3 | s | ↑↓ |
| 3 | p | ↑_ ↑_ ↑_ |
Here, Phosphorus has 15 electrons. After filling the first three levels, we begin filling the 3p orbitals, adhering to Hund’s Rule.
📌 Note: Remember to follow the electron configuration correctly for each element.
Throughout this guide, we've explored the creation of orbital diagrams for different elements, emphasizing the importance of understanding electron configurations, Hund's Rule, and the Pauli Exclusion Principle. Whether you're studying for an exam, or just expanding your knowledge in chemistry, mastering orbital diagrams will provide a clear picture of electron placement in atoms.
Orbital diagrams not only help in visualizing the electron structure but also in understanding chemical reactions, bond formation, and the periodic trends in the elements. This knowledge is invaluable for anyone delving into the world of chemistry, making complex concepts much more approachable and manageable.
Why are orbital diagrams useful in chemistry?

+
Orbital diagrams visually represent the distribution of electrons in atomic orbitals, helping chemists understand the reactivity, stability, and properties of elements.
How do I know the order to fill the electrons in the orbitals?

+
Use the Aufbau principle to determine the order of filling. A mnemonic like ‘1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p’ can help remember this sequence.
What happens if an electron is unpaired in an orbital diagram?

+
An unpaired electron indicates an atom or ion’s ability to form bonds or participate in reactions. It suggests potential for further interaction or spin pairing.