Mastering Operant Conditioning: Worksheet Answers Revealed

Exploring Operant Conditioning


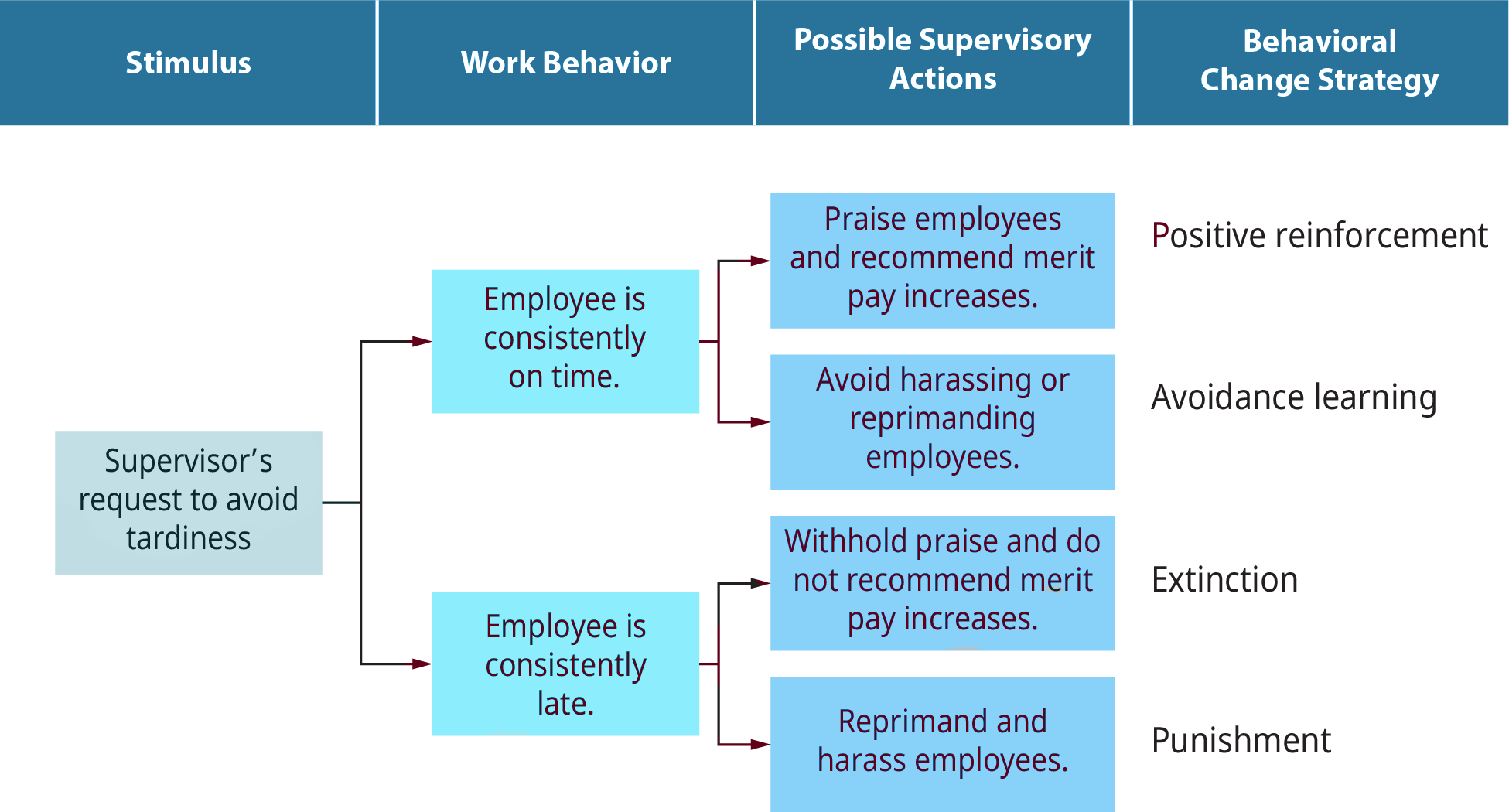
Operant conditioning is a learning process through which behavior is shaped by its consequences. This technique, pioneered by B.F. Skinner, involves reinforcement or punishment, which increase or decrease the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. Understanding how operant conditioning works can provide insights into both human and animal behavior, offering strategies for behavior modification in various settings like education, therapy, and personal growth.
Key Components of Operant Conditioning

At its core, operant conditioning revolves around four primary methods:
- Positive Reinforcement: Adding something desirable to encourage a behavior (e.g., receiving praise for completing a task).
- Negative Reinforcement: Removing an unpleasant stimulus to encourage behavior (e.g., turning off a loud alarm to stop the noise).
- Positive Punishment: Adding an aversive stimulus to decrease behavior (e.g., reprimanding a child for breaking a rule).
- Negative Punishment: Removing a desirable stimulus to decrease behavior (e.g., removing privileges like screen time).
Worksheet Scenario Analysis

Let’s analyze some common scenarios found in educational or training settings where operant conditioning principles are applied:
| Scenario | Method Applied | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Teacher gives stickers for correctly answered questions | Positive Reinforcement | Encourages students to answer questions correctly |
| A parent removes TV time for bad behavior | Negative Punishment | Decreases the occurrence of unwanted behavior |
| Employee receives a bonus for meeting sales goals | Positive Reinforcement | Increases motivation to exceed sales targets |

How to Apply Operant Conditioning

Applying operant conditioning effectively involves understanding the following steps:
- Identify the Behavior: Determine which behavior you want to modify.
- Choose the Correct Method: Decide if you need to reinforce or punish the behavior, and whether it should be positive or negative.
- Implement Consistently: Apply the method consistently to ensure predictability, which is key in conditioning.
- Monitor and Adjust: Observe the behavior’s change and adjust the reinforcement or punishment as necessary.
Ethical Considerations

⚠️ Note: When using operant conditioning, especially in human behavior modification, ethical considerations must be at the forefront:
- Respect Autonomy: Ensure that individuals have control over their environment and behaviors to some degree.
- Minimize Harm: Use methods that aim to foster growth, not harm or overly restrict the person or animal.
- Consent: In human settings, especially in therapy or educational contexts, consent should be obtained wherever possible.
Consequences of Misapplication

Improperly applied operant conditioning can lead to several issues:
- Learned Helplessness: If punishments or negative reinforcements are too harsh or if positive reinforcement is inconsistent, individuals might feel unable to influence their environment.
- Misbehavior: Overuse of negative consequences can foster resentment or rebellion, especially in children or subordinates.
- Dependency: Over-reliance on external rewards can hinder intrinsic motivation, leading to behaviors only occurring in the presence of a reward.
To foster an environment of learning and personal development through operant conditioning, one must balance encouragement with guidance, always with the goal of promoting autonomy and self-regulation. This journey of understanding operant conditioning not only illuminates the mechanics of behavior modification but also underscores the importance of empathy, understanding, and ethical consideration in any behavioral intervention strategy.
In summary, operant conditioning provides a framework for understanding and shaping behavior. By recognizing the power of consequences, we can encourage positive changes and discourage negative behaviors in educational, therapeutic, or personal contexts. However, careful implementation, ethical mindfulness, and continuous monitoring are crucial to prevent unintended consequences and promote a positive learning environment.
What is the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement?

+
Positive reinforcement involves adding a desirable stimulus to encourage a behavior, whereas negative reinforcement involves removing an aversive or undesirable stimulus to encourage behavior.
Can punishment be a part of positive parenting?
+
Yes, punishment can be part of positive parenting when used correctly. Positive punishment should not be overly harsh and should aim to teach and guide rather than merely punish. It’s important to balance punishments with positive reinforcement to foster a nurturing environment.
How can operant conditioning be applied in the workplace?

+
In the workplace, operant conditioning can be used through bonuses, promotions (positive reinforcement), providing additional responsibilities, or recognition to encourage productivity. Conversely, warnings, demotions, or removal of privileges (negative punishment) can discourage undesirable behaviors like tardiness or poor work quality.