Ohm's Law: Simple Worksheet for Mastering Electrical Basics

In the world of electrical engineering, Ohm's Law stands as one of the most fundamental principles. It's a simple yet powerful equation that helps us understand how voltage, current, and resistance interact within an electrical circuit. Whether you're an aspiring electrical engineer, a hobbyist, or a student of science, mastering Ohm's Law is crucial. This blog post will guide you through creating a simple worksheet that can serve as a tool for mastering the basic concepts of electricity using Ohm's Law.
Understanding Ohm’s Law

Before diving into the worksheet creation, let’s ensure we understand what Ohm’s Law is:
- Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. This relationship is expressed in the equation:
Where:
- V represents voltage, measured in Volts (V).
- I represents current, measured in Amperes (A).
- R represents resistance, measured in Ohms (Ω).
📝 Note: In practical applications, sometimes the voltage (V) or current (I) might be known, and you’ll need to calculate the other values based on Ohm’s Law.
Creating Your Ohm’s Law Worksheet
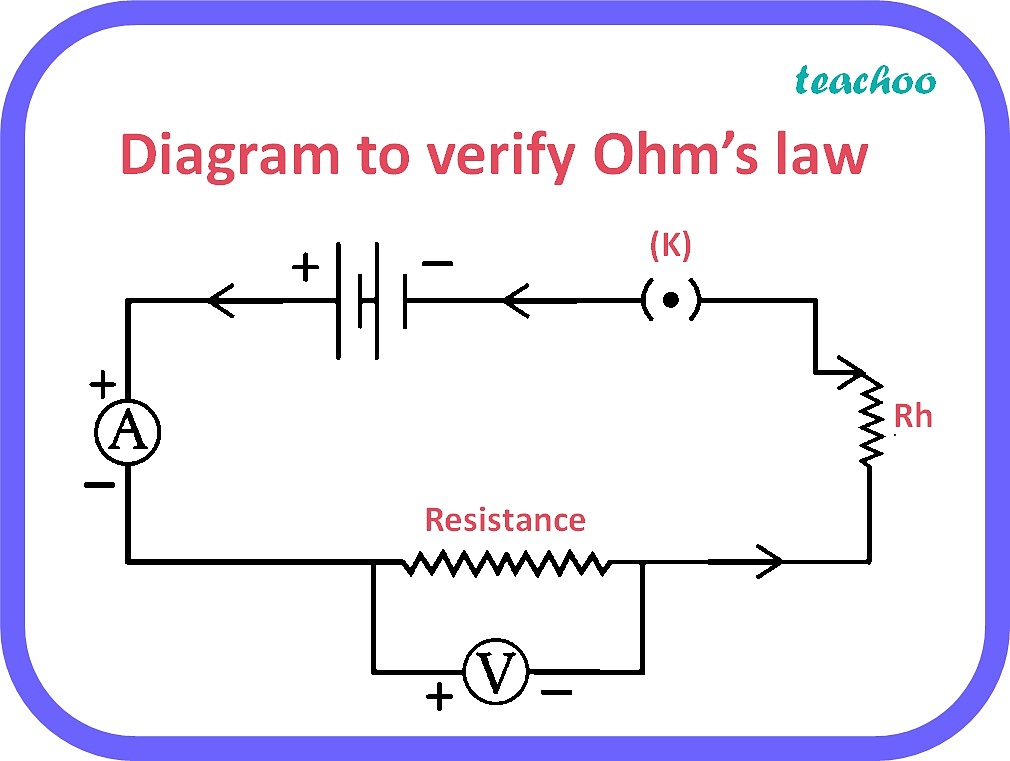
Here’s how you can design an effective worksheet to practice Ohm’s Law:
Step 1: Objective Setting

Begin by setting clear learning objectives. These might include:
- Understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
- Calculate missing values in the Ohm’s Law triangle.
- Solve for one variable when the other two are known.
Step 2: Basic Exercises

Start with basic exercises where:
- Voltage (V) is given, and students calculate current (I) or resistance ®.
- Current (I) is given, and students calculate voltage (V) or resistance ®.
- Resistance ® is given, and students calculate voltage (V) or current (I).
| Given Values | Find |
|---|---|
| V = 12V, R = 6Ω | Current (I) |
| I = 2A, V = 10V | Resistance ® |
| R = 5Ω, I = 1A | Voltage (V) |

Step 3: Multiple Choice Questions

Include multiple choice questions to test conceptual understanding:
- If you increase the voltage while keeping resistance constant, what happens to the current?
- It increases.
- It decreases.
- It remains the same.
Step 4: Practical Applications

Provide real-world scenarios where students apply Ohm’s Law:
- Calculate the power dissipation of a resistor in an LED circuit.
- Determine the necessary resistor value to limit current to a safe level in an electronic device.
Step 5: Challenge Questions

Include more complex problems to challenge advanced learners:
- Find the total resistance in a circuit with parallel and series resistors.
- Calculate the voltage drop across multiple resistors in a complex circuit.
💡 Note: Ensure your worksheet includes both theoretical questions and practical, scenario-based problems to cater to different learning styles.
Summing Up

We’ve walked through a comprehensive approach to creating a worksheet that not only teaches Ohm’s Law but also engages students in practical applications. By focusing on the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, this worksheet aims to solidify understanding and promote critical thinking in electrical engineering. Regular practice with such materials can transform beginners into proficient circuit designers, fostering a deeper appreciation for electrical principles.
What is Ohm’s Law?

+
Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance ® in an electrical circuit with the formula V = I * R.
Why is it important to understand Ohm’s Law?

+
Understanding Ohm’s Law is fundamental for anyone working with electricity as it allows for the calculation of safe and efficient circuit design, preventing damage to electronic components.
How can I use Ohm’s Law in real-life applications?

+
Ohm’s Law is used in designing and troubleshooting electrical systems, from household appliances to complex electronic devices, ensuring proper power management and safety.