9 Officer Ranks in the US Air Force
Understanding the Hierarchy of Officer Ranks in the US Air Force

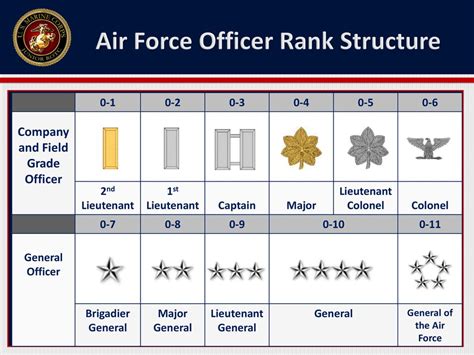
The United States Air Force is one of the most technologically advanced air forces in the world, with a large and complex organizational structure. At the heart of this structure are the officer ranks, which form the backbone of the Air Force’s leadership and command structure. In this article, we will delve into the nine officer ranks of the US Air Force, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and requirements.
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers are the leaders of the Air Force, responsible for making key decisions and overseeing the enlisted personnel and operations. There are nine commissioned officer ranks in the US Air Force, ranging from Second Lieutenant to General.
1. Second Lieutenant (2d Lt)
The Second Lieutenant is the lowest commissioned officer rank in the US Air Force. Typically, new officers hold this rank after completing Officer Training School (OTS) or the United States Air Force Academy. Second Lieutenants are usually in their early 20s and are fresh out of college or the academy.
- Responsibilities: Second Lieutenants typically serve as platoon leaders or assistants in operational and support units.
- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, and a commission from the President.
2. First Lieutenant (1st Lt)
The First Lieutenant rank is typically held by officers with one to three years of service. They are more experienced and confident than Second Lieutenants and take on more responsibilities.
- Responsibilities: First Lieutenants may serve as executive officers, flight commanders, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of one year of service, and a strong performance record.
3. Captain (Capt)
Captains have significant responsibilities and are often squadron section commanders or executive officers. They typically have five to eight years of service and have gained a reputation as leaders and experts in their field.
- Responsibilities: Captains may serve as squadron operations officers, flight commanders, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of five years of service, and a strong performance record.
4. Major (Maj)
Majors are senior officers with significant experience and responsibility. They often serve as squadron commanders or executive officers and have typically served for 10 to 15 years.
- Responsibilities: Majors may serve as squadron commanders, executive officers, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 10 years of service, and a strong performance record.
5. Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col)
Lieutenant Colonels are highly experienced officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise. They often serve as wing or group commanders and have typically served for 15 to 20 years.
- Responsibilities: Lieutenant Colonels may serve as wing or group commanders, executive officers, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 15 years of service, and a strong performance record.
6. Colonel (Col)
Colonels are senior officers with significant responsibility and experience. They often serve as wing or group commanders and have typically served for 20 to 25 years.
- Responsibilities: Colonels may serve as wing or group commanders, executive officers, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 20 years of service, and a strong performance record.
7. Brigadier General (Brig Gen)
Brigadier Generals are one-star generals who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise. They often serve as wing or group commanders and have typically served for 25 to 30 years.
- Responsibilities: Brigadier Generals may serve as wing or group commanders, executive officers, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 25 years of service, and a strong performance record.
8. Major General (Maj Gen)
Major Generals are two-star generals who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise. They often serve as wing or group commanders and have typically served for 30 to 35 years.
- Responsibilities: Major Generals may serve as wing or group commanders, executive officers, or section leaders.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 30 years of service, and a strong performance record.
9. General (Gen)
Generals are four-star generals who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise. They often serve as Chief of Staff of the Air Force or commanders of major commands.
- Responsibilities: Generals may serve as Chief of Staff of the Air Force, commanders of major commands, or executive officers.
- Requirements: Completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, a minimum of 35 years of service, and a strong performance record.
👮 Note: The ranks and responsibilities of Air Force officers can vary depending on the specific job and location.
In conclusion, the nine officer ranks of the US Air Force form a complex hierarchy of leadership and command. Each rank has its own unique responsibilities and requirements, and officers must demonstrate exceptional leadership and expertise to advance through the ranks. Understanding these ranks and responsibilities is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in the Air Force.
What is the lowest commissioned officer rank in the US Air Force?

+
The lowest commissioned officer rank in the US Air Force is Second Lieutenant (2d Lt).
What are the requirements for becoming a commissioned officer in the US Air Force?

+
To become a commissioned officer in the US Air Force, you must complete Officer Training School (OTS) or the United States Air Force Academy, have a bachelor’s degree, and receive a commission from the President.
How many years of service are typically required to reach the rank of Brigadier General?

+
Brigadier Generals typically have 25 to 30 years of service.