5 Ways Retired Pay Increases

Introduction to Retired Pay Increases
As individuals approach retirement, one of the most significant concerns is ensuring that their retirement income keeps pace with the rising cost of living. Retired pay increases are essential to maintaining the purchasing power of retirees, allowing them to enjoy their post-work life without financial stress. There are several mechanisms through which retired pay can increase, reflecting both economic conditions and policy adjustments. Understanding these methods is crucial for retirees and those planning for retirement to manage their expectations and financial planning effectively.
Cost of Living Adjustments (COLAs)

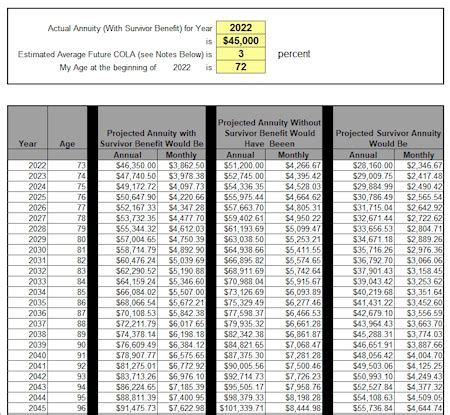
One of the primary ways retired pay increases is through Cost of Living Adjustments (COLAs). COLAs are adjustments made to the retirement benefits to counteract the effects of inflation, ensuring that the purchasing power of retirees is not eroded over time. These adjustments are typically based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the average change in prices of a basket of goods and services consumed by households. By linking retired pay to the CPI, retirees can maintain their standard of living even as prices rise due to inflation.
Legislative Increases
Another method through which retired pay can increase is through legislative actions. Governments or retirement plan administrators can enact laws or policies that increase retirement benefits. These increases can be across the board or targeted towards specific groups of retirees. Legislative increases are often implemented to address perceived shortcomings in retirement benefits, to reflect changes in the cost of living, or to adjust for discrepancies in the retirement system. For instance, a government might pass a law to increase the pension amount for all retirees by a certain percentage or to provide additional benefits to veterans or public servants.
Investment Returns

For retirees with retirement accounts that are invested in the market, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, the value of their retirement portfolio can increase based on investment returns. If the investments perform well, the overall value of the retirement account can grow, potentially leading to higher retirement income. This method of increase is more volatile, as it depends on market performance, which can fluctuate significantly. However, over the long term, investments can provide a substantial increase in retired pay, especially if managed wisely and diversified to mitigate risk.
Employer Contributions
In some cases, especially for those in defined benefit plans or certain types of retirement accounts, employer contributions can increase retired pay. Employers may contribute a certain amount each year to the retirement plan, which can accumulate over time and lead to a higher retirement benefit. Additionally, some employers may offer profit-sharing plans or matching contributions to retirement accounts, which can also boost the retiree’s income in retirement. These contributions can be a significant source of increase in retired pay, especially for employees who stay with the same employer for an extended period.
Catch-up Contributions

Finally, for individuals who are nearing retirement or already retired, catch-up contributions can be a way to increase their retirement savings and, consequently, their retired pay. The IRS allows individuals aged 50 and older to make catch-up contributions to their retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, beyond the standard contribution limits. By maximizing these contributions, individuals can quickly boost their retirement savings, potentially leading to a higher income in retirement. This strategy is particularly useful for those who may have started saving for retirement later in life or who wish to compensate for years of lower contributions.
💡 Note: Understanding the specifics of each method of increase, including any eligibility requirements or limitations, is crucial for maximizing retired pay.
When considering the impact of these increases on retired pay, it’s essential to look at the broader economic context and the specific rules governing each type of retirement plan. Factors such as inflation rates, legislative changes, investment performance, and employer contribution policies can all influence the extent to which retired pay increases over time. By staying informed and making proactive decisions about retirement savings and investments, individuals can better position themselves for a secure and comfortable retirement.
In essence, retired pay increases are multifaceted and can be influenced by a variety of economic, legislative, and personal factors. Whether through COLAs, legislative actions, investment returns, employer contributions, or catch-up contributions, understanding these mechanisms is key to navigating the retirement landscape effectively. By leveraging these methods and staying adaptable, retirees can work towards maintaining their standard of living and enjoying their post-work life with financial confidence.
What are COLAs, and how do they affect retired pay?
+
COLAs, or Cost of Living Adjustments, are increases made to retirement benefits to offset the effects of inflation, ensuring that retirees can maintain their purchasing power over time.
How can investment returns impact retired pay?
+
Investment returns can significantly impact retired pay for those with market-based retirement accounts. Positive returns can increase the value of the retirement portfolio, potentially leading to higher retirement income.
What are catch-up contributions, and who is eligible?
+
Catch-up contributions are additional contributions allowed by the IRS for individuals aged 50 and older to certain retirement accounts, enabling them to save more for retirement and potentially increase their retired pay.