5 Ways to Master Net Force Calculations Easily
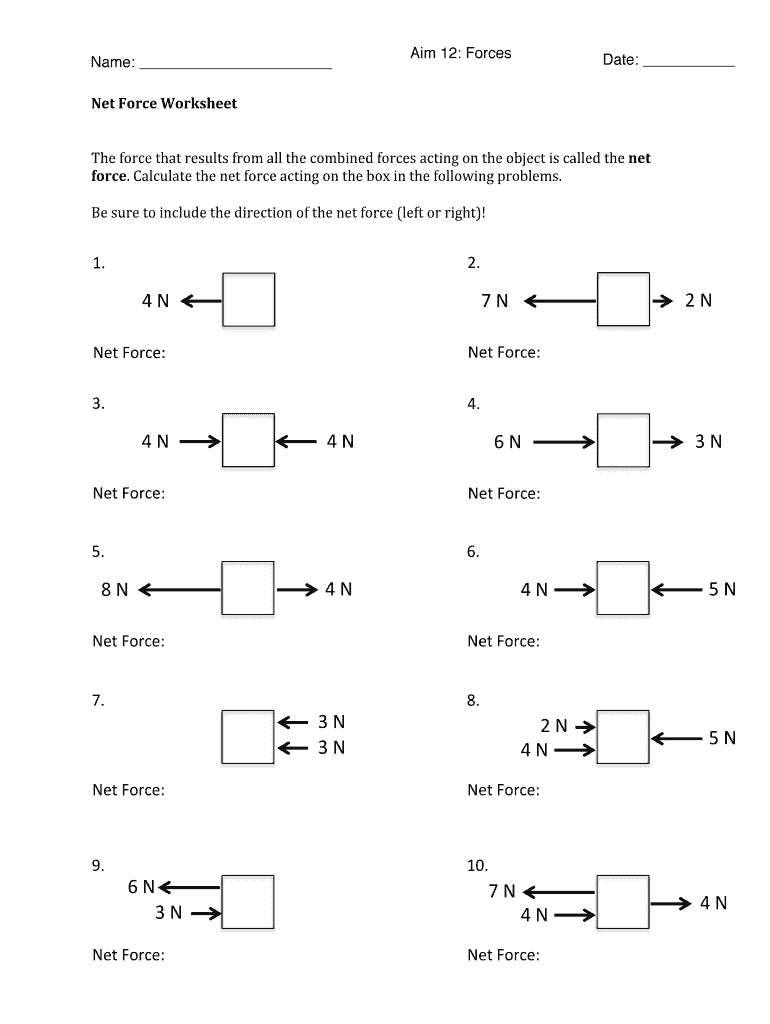
In the fascinating world of physics, understanding how forces interact with each other is crucial to solving many problems. One of the fundamental concepts you'll encounter is net force, which is the total force acting on an object when all individual forces are taken into account. Mastering net force calculations can be an engaging journey, and in this post, we'll explore five effective methods to make this complex topic seem simple and intuitive.
1. Conceptual Understanding

Before diving into numbers and equations, it's imperative to grasp the basic concept of forces. Forces can be thought of as pushes or pulls that act upon an object, trying to change its state of motion or rest.
Here are some key points:
- Vector Nature: Forces are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude and direction.
- Balance: Objects at rest or moving with constant velocity are subject to balanced forces where the net force is zero.
- Unbalanced: Acceleration occurs when forces are unbalanced, meaning the net force is not zero.

🔍 Note: Understanding vector components can significantly aid in determining the net force, especially when forces are not aligned in simple directions.
2. Free Body Diagrams

A free body diagram is a visual representation tool used to show all forces acting on an object. Here's how to master this method:
- Identify all forces acting on the object.
- Draw each force as an arrow pointing in its direction from the object's center of mass.
- Label each force with its magnitude and any known direction.
- Calculate the net force by summing up vectorially.
This diagrammatic approach allows you to visualize the forces and estimate their effects more intuitively.

✅ Note: Practicing free body diagrams can help in identifying hidden or less obvious forces like friction or air resistance.
3. Use of Newton's Second Law

Net force is directly related to acceleration through Newton's Second Law, F_{net} = ma, where F_{net} is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration of the object.
To leverage this for net force calculations:
- Choose the positive direction (often along the axis of motion).
- List all known forces and their directions.
- Apply Newton's Second Law to find the net force by substituting known values and solving for the unknowns.
This mathematical approach gives you a clear, straightforward way to calculate net force.
| Force | Direction | Magnitude (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (W) | Downwards | mg |
| Normal Force (N) | Upwards | Reaction force from surface |
| Applied Force (F) | Right or Left | Given value |
| Friction Force (f) | Opposite to motion | μN |

4. Break It Down into Components

When dealing with forces at angles, breaking them down into their components simplifies the calculation:
- Resolve each force into its horizontal and vertical components using trigonometry (sin, cos).
- Sum the components in each direction separately.
- Vectorially add these sums to find the net force.
This technique is particularly useful for forces not aligned along one axis or when dealing with forces on an inclined plane.
🧮 Note: Remember, only forces acting in the same direction can be directly added; forces at angles require resolution first.
5. Practice with Real-World Scenarios

Applying net force calculations to real-life scenarios helps reinforce your understanding:
- Pulling a Sled: Calculate the net force when someone pulls a sled at an angle with friction involved.
- Skydiving: Estimate the net force on a skydiver falling with air resistance.
- Traffic Flow: Analyze how forces balance when cars are stationary in traffic or accelerating.
By working through these scenarios, you'll not only sharpen your calculations but also develop an intuition for how forces interact in the physical world.
As you venture into the world of net forces, remember that understanding the physics principles, rather than just memorizing formulas, is the key to mastering this topic. These five methods provide a structured approach to simplify net force calculations, making what might seem like an abstract or mathematical endeavor into a practical, visual, and even enjoyable part of learning physics. Every time you solve a problem using these techniques, you're not just finding an answer; you're building your ability to think critically and predict outcomes in various physical scenarios.
How can I determine the direction of the net force?

+
The direction of the net force is determined by adding all the forces as vectors. The direction will be along the resultant vector of these forces.
What if two forces are equal but in opposite directions?

+
If two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, they cancel each other out, resulting in a net force of zero, and the object will either remain at rest or move with constant velocity if no other forces are acting.
Is net force only applicable in linear motion?

+
No, net force calculations can be applied to both linear and rotational motion. For rotational motion, net torque is considered.