5 Key Answers: Net Force Particle Model Worksheet
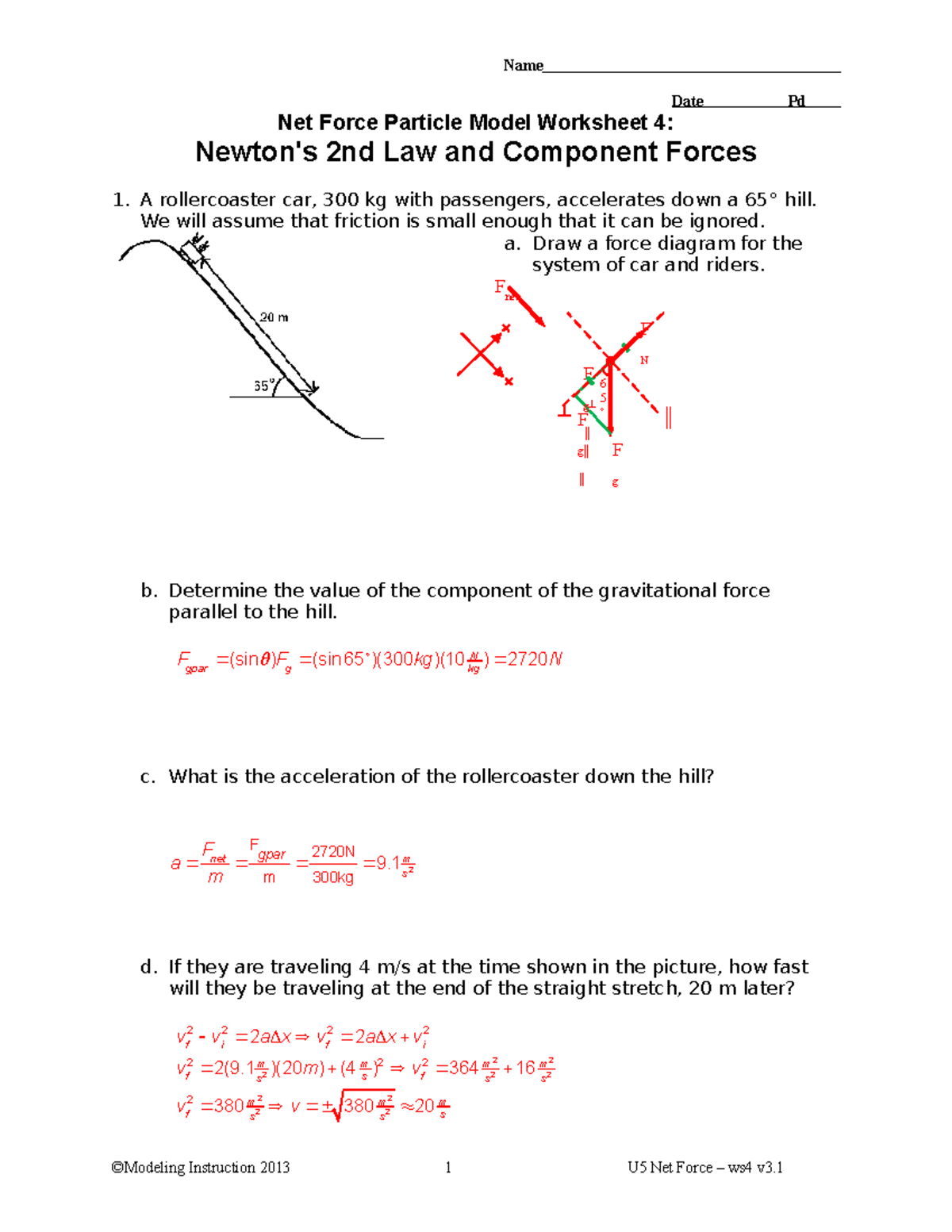
Understanding the net force particle model is essential for grasping how forces interact within systems, particularly in physics. This model simplifies complex interactions by focusing on the net forces acting on an individual particle. Here's a comprehensive exploration of five key answers to common questions surrounding the net force particle model:
1. What is the Net Force?

The net force on an object is the total vector sum of all the forces acting on it. To find the net force:
- Identify all forces acting on the object, including gravity, friction, normal force, applied force, etc.
- Add these forces vectorially, considering both magnitude and direction.
- Remember that forces in opposite directions cancel each other out, while forces in the same direction add up.
2. How Does Net Force Determine Motion?

The direction and magnitude of the net force directly influence an object’s acceleration according to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, which states:
- Fnet = ma, where Fnet is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration.
- If the net force is zero, the object is either at rest or moving with a constant velocity (constant speed in a straight line).
- Non-zero net forces result in acceleration, changing either the speed or direction of the object’s motion.

3. The Role of Equilibrium in the Net Force Model

Equilibrium occurs when the net force on an object is zero:
- In static equilibrium, the object remains at rest.
- In dynamic equilibrium, the object moves at a constant velocity.
- Equilibrium requires that all forces balance out. If they don’t, the object accelerates in the direction of the net force.
4. Applications of the Net Force Model in Real Life

The net force model is not just theoretical; it has practical applications:
- Aircraft and Vehicles: Engineers calculate the net forces acting on vehicles to ensure safe operation under different conditions.
- Construction: Ensuring structures remain in static equilibrium by balancing forces like load and tension.
- Sports: Understanding how forces affect ball trajectory or athlete movement.
| Scenario | Net Force Effect |
|---|---|
| Car Accelerating | Forward force from engine overcomes backward friction force. |
| Book on Table | Normal force equals gravitational force, resulting in zero net force. |
⚠️ Note: Remember that net force acts on the center of mass of an object or system.
5. How to Visualize Net Forces Using Free-Body Diagrams

Free-body diagrams (FBD) are crucial for understanding net forces:
- Draw an isolated object and represent each force with a vector starting from the center of mass.
- Label each force clearly and indicate its magnitude and direction.
- Sum the vectors to find the net force; arrows can be drawn to show the resultant force.
Final Thoughts

Mastery of the net force particle model is essential for understanding physical phenomena. By recognizing and calculating the net forces, one can predict an object’s motion, stability, and interaction within its environment. This model simplifies complex real-world scenarios by breaking down the forces at play, making it a fundamental tool in physics education and practical engineering applications.
What if there are multiple forces in different directions?

+
Resolve all forces into horizontal and vertical components. Then sum the components separately to find the net force in each direction.
Can an object be in equilibrium while moving?
+
Yes, if the net force is zero, the object can be moving with a constant velocity, which is known as dynamic equilibrium.
How does friction affect net force?

+
Friction acts opposite to the direction of motion, reducing the net force if it opposes the applied force, or contributing to the net force if it’s in the same direction (like when an object slides down an incline).