5 Steps to Master Net Force Particle Model Worksheets

Exploring the Fundamentals of Net Force Particle Model Worksheets

Understanding the net force particle model is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of physics, particularly when it comes to forces, motion, and equilibrium. Net force particle model worksheets are an excellent tool to help students visualize and solve force problems effectively. This blog post will guide you through five critical steps to master these worksheets, enhancing your ability to analyze and understand the forces acting on objects.
Step 1: Understanding the Concept of Net Force

The journey to mastering net force particle model worksheets begins with a solid understanding of what net force is. Net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object. If you imagine all forces as arrows pushing or pulling in different directions, the net force is the direction and magnitude of the remaining force after all opposing forces have canceled each other out.
- Vector Sum: Forces are vectors; they have both magnitude and direction.
- Opposing Forces: When forces are in opposite directions, they can either cancel each other or leave a residual force if they are not equal.
- Resultant Force: The remaining force after accounting for all forces is the net force.
🧠 Note: In physics, the term "net force" often refers to the resultant force or simply "the force" when discussing dynamics.

Step 2: Analyzing Forces Using Free-Body Diagrams

The next step involves drawing free-body diagrams (FBDs), which are simplified representations of an object with all the forces acting upon it. These diagrams help in visualizing the forces, making it easier to apply the net force particle model:
- Identify the Object: Isolate the object in question from its surroundings.
- List Forces: Identify all forces acting on the object, including gravitational force, normal force, friction, tension, and any applied forces.
- Draw FBD: Represent each force as an arrow, with the direction indicating the force's direction and the arrow's length indicating its magnitude.
- Balance the Forces: Use vector addition to determine the net force.

Step 3: Calculating Net Force
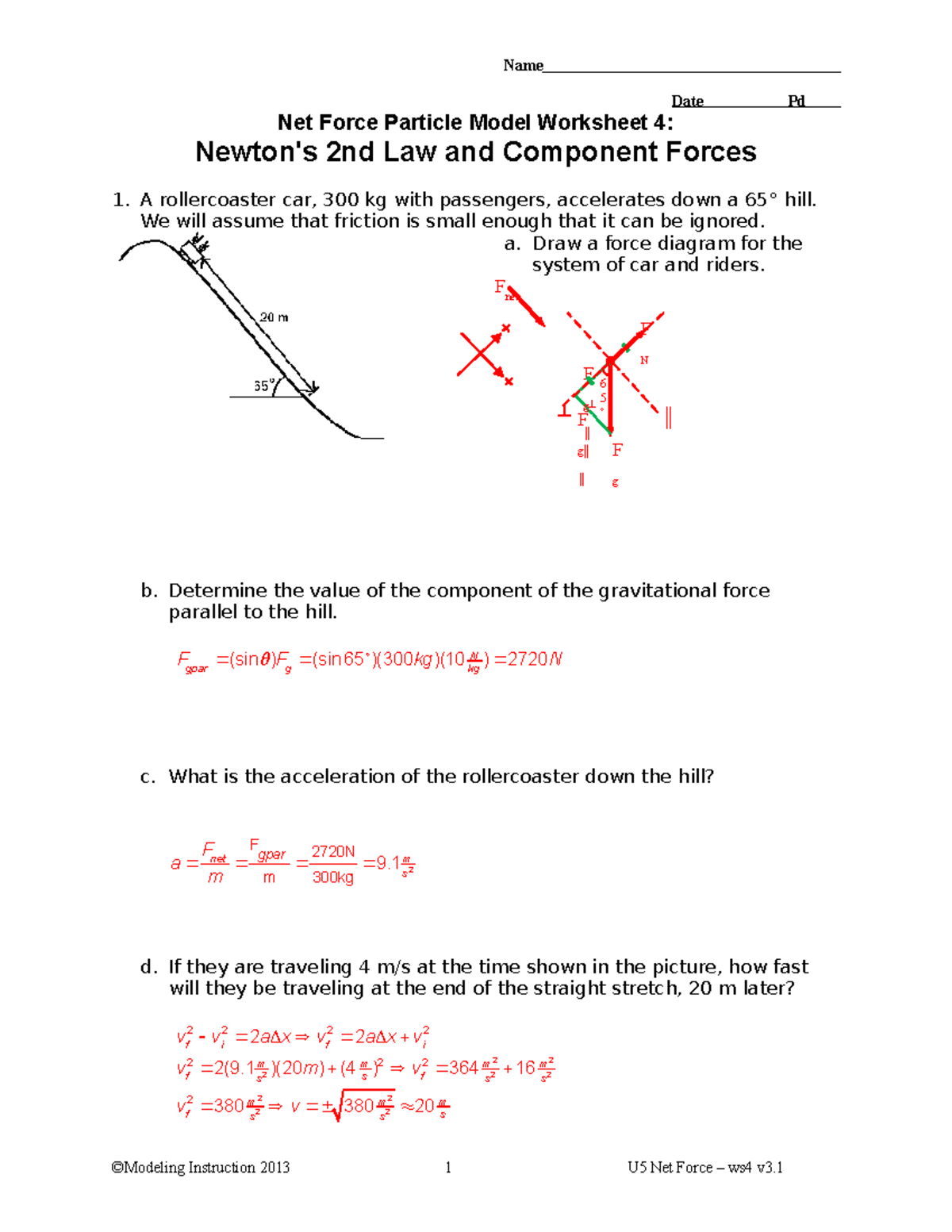
Once you have your free-body diagram, you can proceed to calculate the net force:
| Force | Direction | Magnitude (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Gravitational Force (Fg) | Downward | m * g |
| Normal Force (Fn) | Perpendicular to surface | N/A* |
| Applied Force (Fapp) | Direction of application | Varies |

*Note: The normal force depends on the contact surface and the object's weight.
- Sum all forces in the x and y directions separately.
- Use vector addition to find the resultant force.
🧮 Note: Remember to use Newton's second law (F = ma) to find acceleration if needed.
Step 4: Solving Net Force Problems

Now that you have the tools, let's dive into how to solve problems:
- Read the Problem Carefully: Identify known and unknown variables.
- Draw a Free-Body Diagram: Visualize the forces acting on the object.
- Choose a Coordinate System: Select the direction of positive x and y.
- Set Up Equations: Write equations for the net force in each direction.
- Solve the Equations: Use algebra to solve for unknowns.
💡 Note: Sometimes, you might need to consider forces resolved into components along the chosen axes.
Step 5: Applying the Net Force Particle Model in Context

Finally, apply what you've learned in real-world or textbook problems:
- Statics: When an object is at rest, the net force is zero.
- Dynamics: When an object is accelerating, use Newton's second law to relate force, mass, and acceleration.
- Friction: Include frictional forces in your analysis where applicable.
By following these steps, you're not just solving problems; you're developing a deeper understanding of the physical world around you. The mastery of the net force particle model provides a foundation for understanding complex motion and forces in various scenarios, from simple dynamics to intricate engineering challenges.
In the end, working through net force particle model worksheets not only sharpens your problem-solving skills but also enhances your ability to visualize and analyze forces in real-life situations. By breaking down problems into these structured steps, you'll find yourself tackling even the most challenging problems with ease, making you well-equipped for any physics-related endeavor or course.
Why is drawing free-body diagrams important?
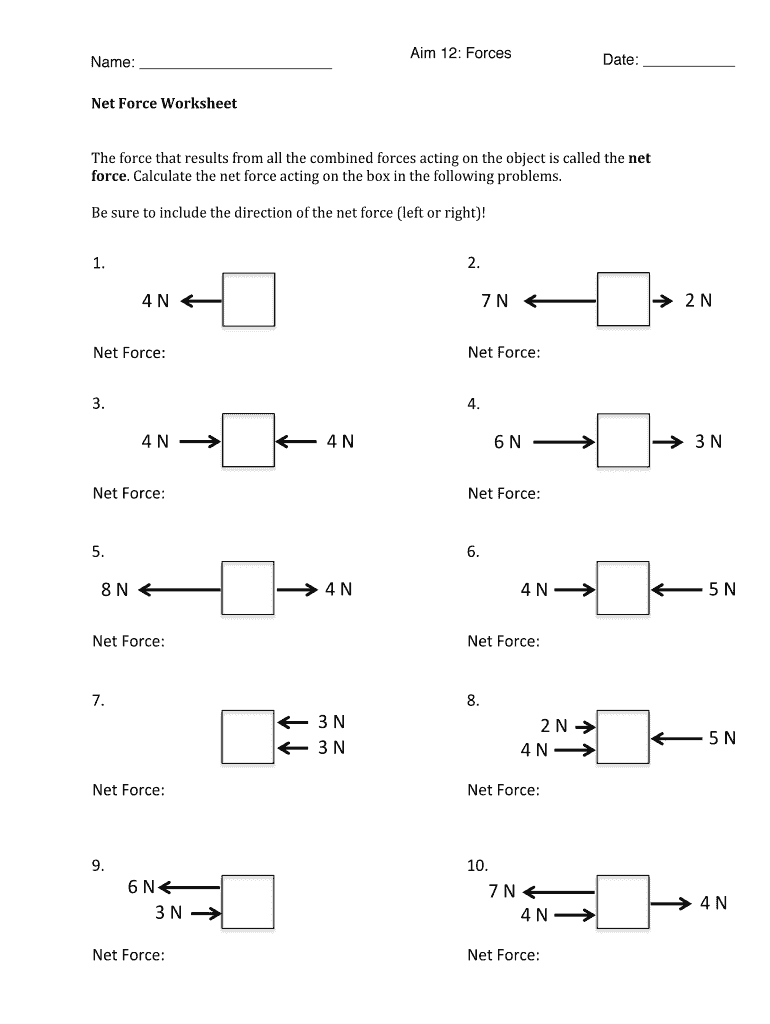
+
Free-body diagrams provide a visual representation of all the forces acting on an object, which helps in understanding and solving force problems by identifying all relevant forces, their directions, and magnitudes.
How can I check if my calculation of net force is correct?

+
One effective way to verify your net force calculations is to use Newton’s second law (F = ma). If the object is accelerating, the calculated net force should result in the correct acceleration when divided by the object’s mass.
What should I do if the forces in my problem don’t balance out to zero?

+
If the forces don’t balance out to zero, this indicates that the object is accelerating. Check your calculations, ensure all forces are correctly identified, and use Newton’s second law to find the acceleration.