7 Navy Ranks

Introduction to Navy Ranks
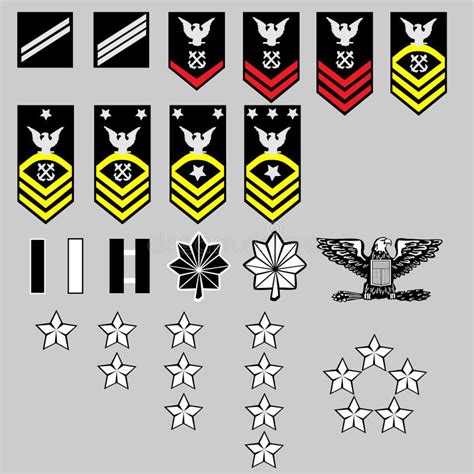

The Navy is a prestigious branch of the military, known for its bravery, sacrifice, and dedication to protecting the nation’s interests. With a rich history and a strong sense of camaraderie, the Navy has a well-defined ranking system that reflects the varying levels of responsibility, expertise, and leadership within its ranks. In this article, we will delve into the world of Navy ranks, exploring the different levels, their corresponding responsibilities, and the paths to advancement.
Understanding Navy Ranks
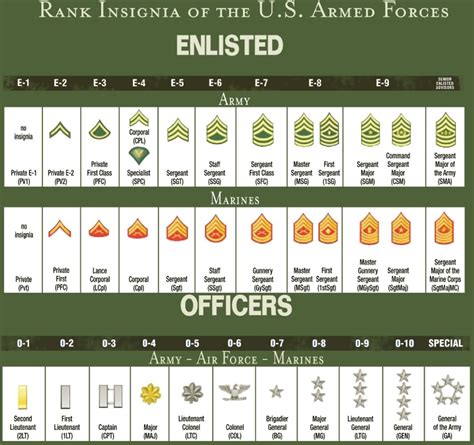
Navy ranks are divided into three main categories: Enlisted, Warrant Officer, and Commissioned Officer. Each category has its own set of ranks, with increasing levels of authority and responsibility. The ranks are denoted by a combination of stripes, chevrons, and insignia, which are worn on the uniform to indicate the individual’s rank and branch of service.
Enlisted Ranks

The Enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Navy, comprising the majority of personnel. These ranks are further divided into three sub-categories: Junior Enlisted, Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs), and Senior Enlisted. * Junior Enlisted: Seaman Recruit (E-1), Seaman Apprentice (E-2), Seaman (E-3) * Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs): Petty Officer Third Class (E-4), Petty Officer Second Class (E-5), Petty Officer First Class (E-6) * Senior Enlisted: Chief Petty Officer (E-7), Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8), Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9)
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant Officers are technical experts in their field, holding a unique position between Enlisted and Commissioned Officers. They are appointed by a warrant, rather than a commission, and are responsible for providing specialized guidance and support. * Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2) * Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3) * Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4) * Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5)
Commissioned Officer Ranks

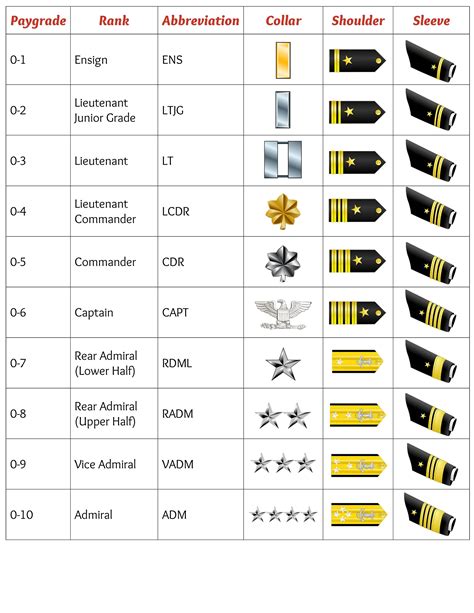
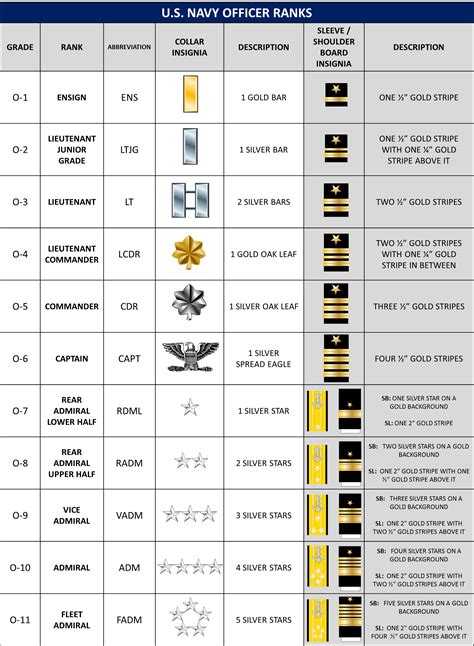
Commissioned Officers are the leaders of the Navy, responsible for making strategic decisions, commanding units, and overseeing operations. They are divided into two sub-categories: Junior Officers and Senior Officers. * Junior Officers: Ensign (O-1), Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2), Lieutenant (O-3) * Senior Officers: Lieutenant Commander (O-4), Commander (O-5), Captain (O-6)
Paths to Advancement
Advancement in the Navy is based on a combination of factors, including performance evaluations, time in service, and competitive exams. Enlisted personnel can advance through the ranks by completing training programs, gaining experience, and demonstrating leadership potential. Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers can also advance through the ranks, but require additional education, training, and experience.
Responsibilities and Specializations
Each rank has its unique set of responsibilities and specializations. For example: * Aviation: Pilots, Naval Flight Officers, and Aviation Maintenance personnel * Surface Warfare: Officers and Enlisted personnel responsible for operating and maintaining surface ships * Submarine Warfare: Officers and Enlisted personnel responsible for operating and maintaining submarines * Special Operations: SEALs, Special Warfare Combatant-Craft Crewmen, and other specialized units
Education and Training

The Navy provides a wide range of education and training programs to help personnel advance in their careers. These programs include: * Boot Camp: Basic training for new recruits * Rating Schools: Technical training for Enlisted personnel * Officer Candidate School: Training for Commissioned Officers * Warrant Officer Candidate School: Training for Warrant Officers * Advanced Training: Specialized training for personnel in specific fields, such as aviation or nuclear power
📝 Note: The Navy's ranking system is designed to recognize individual achievement and provide opportunities for advancement, but it also requires a strong commitment to service, sacrifice, and teamwork.
In the final analysis, the Navy’s ranking system is a complex and multifaceted structure that reflects the diverse range of roles, responsibilities, and specializations within the service. By understanding the different ranks, their corresponding responsibilities, and the paths to advancement, individuals can make informed decisions about their careers and strive for excellence in their chosen fields. The Navy’s emphasis on education, training, and leadership development provides a strong foundation for personal and professional growth, and its rich history and traditions inspire a sense of pride and purpose among its personnel. Ultimately, the Navy’s ranking system is a key component of its success, recognizing and rewarding individual achievement while fostering a sense of unity and cohesion among its members.
What are the main categories of Navy ranks?

+
The main categories of Navy ranks are Enlisted, Warrant Officer, and Commissioned Officer.
What is the highest Enlisted rank in the Navy?
+
The highest Enlisted rank in the Navy is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
What is the role of Warrant Officers in the Navy?

+
Warrant Officers are technical experts in their field, providing specialized guidance and support to other personnel.



