7 Steps to Understand Naval Enlisted Rank Structure
Understanding the Naval Enlisted Rank Structure: A Comprehensive Guide
The naval enlisted rank structure can be complex and confusing for those who are new to the military or are considering a career in the Navy. With its unique hierarchy and ranking system, it’s essential to understand the different ranks and their responsibilities to navigate the naval environment effectively. In this article, we will break down the 7 steps to understand the naval enlisted rank structure, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you make sense of the Navy’s ranking system.
Step 1: Understanding the Enlisted Ranks

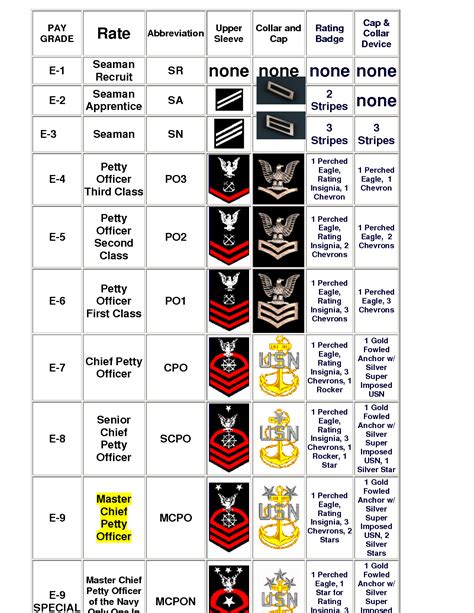
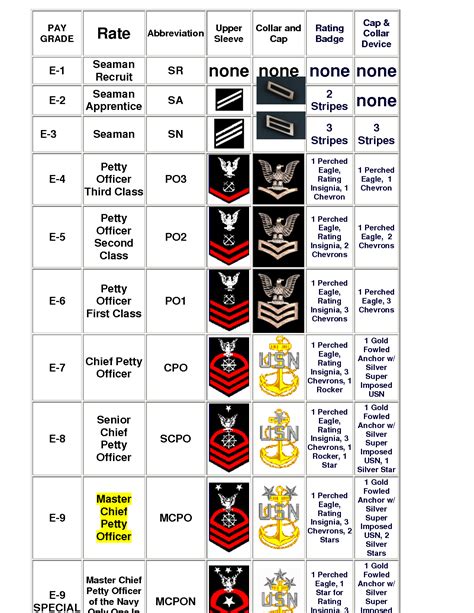
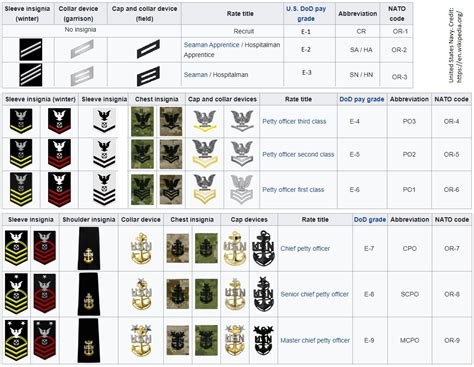
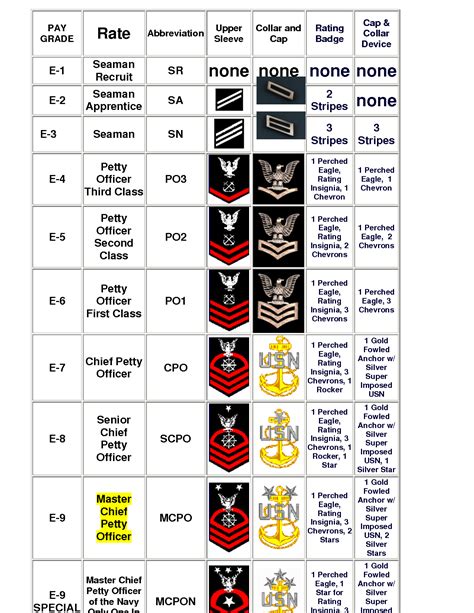
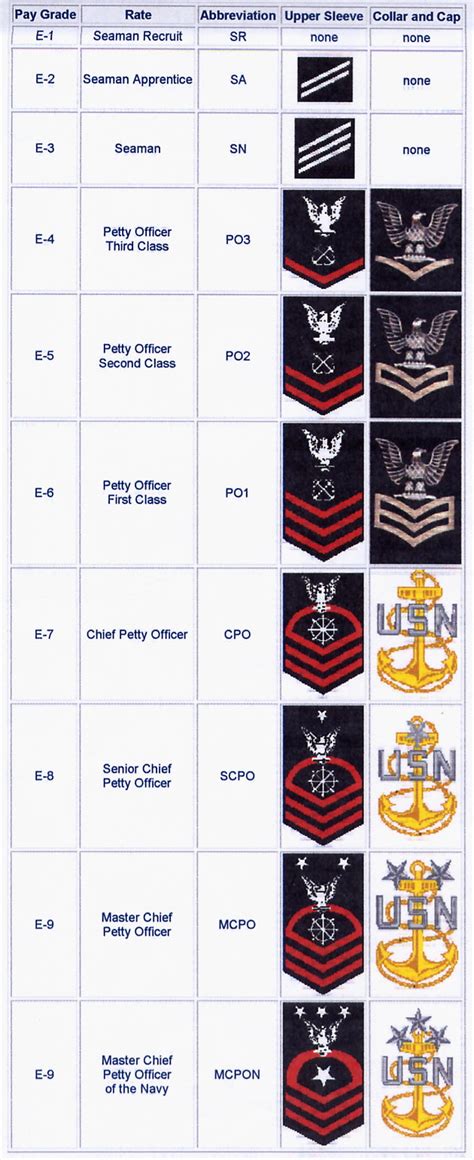
The naval enlisted rank structure is divided into nine pay grades, each with its unique rank and responsibilities. The ranks are as follows:
- E-1: Seaman Recruit (SR)
- E-2: Seaman Apprentice (SA)
- E-3: Seaman (SN)
- E-4: Petty Officer Third Class (PO3)
- E-5: Petty Officer Second Class (PO2)
- E-6: Petty Officer First Class (PO1)
- E-7: Chief Petty Officer (CPO)
- E-8: Senior Chief Petty Officer (SCPO)
- E-9: Master Chief Petty Officer (MCPO)
🚨 Note: The enlisted ranks are denoted by a combination of letters and numbers, with the letter "E" indicating enlisted and the number indicating the pay grade.
Step 2: Recognizing Rank Insignia
Each rank has its unique insignia, which is worn on the sleeve or collar of the uniform. The insignia consists of stripes, chevrons, and anchors, which indicate the rank and pay grade. For example:
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit (E-1) | No insignia |
| Seaman Apprentice (E-2) | 2 diagonal stripes |
| Seaman (E-3) | 3 diagonal stripes |
| Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) | 1 anchor and 2 stripes |
| Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) | 1 anchor and 3 stripes |

Step 3: Understanding Rank Responsibilities
Each rank has its unique responsibilities and duties. As you move up the ranks, your responsibilities increase, and you are expected to take on more leadership roles. Here’s a brief overview of the responsibilities for each rank:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): Entry-level rank, responsible for learning and adapting to naval life.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): Assists in daily tasks and begins to develop specialized skills.
- Seaman (E-3): Performs specific tasks and begins to take on more responsibility.
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): Leads small teams and takes on more complex tasks.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): Supervises and mentors junior personnel.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): Leads larger teams and takes on more significant responsibilities.
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): Senior leadership role, responsible for mentoring and guiding junior personnel.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): Advanced leadership role, responsible for leading and managing teams.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): Senior-most enlisted rank, responsible for advising and guiding senior leadership.
Step 4: Understanding the Rating System

The Navy has a unique rating system, which categorizes enlisted personnel into specific job specialties. There are over 60 ratings in the Navy, ranging from aviation to healthcare. Each rating has its unique responsibilities and requirements.
Step 5: Advancement and Promotion
Advancement and promotion in the Navy are based on performance, experience, and education. Enlisted personnel can advance through the ranks by completing required training, gaining experience, and demonstrating leadership potential.
Step 6: Leadership and Responsibility
As you move up the ranks, you take on more leadership responsibilities and are expected to mentor and guide junior personnel. Leadership is a critical aspect of the naval enlisted rank structure, and personnel are expected to demonstrate leadership potential to advance.
Step 7: Staying Current and Adapting to Change

The naval enlisted rank structure is constantly evolving, and personnel must stay current with changes in policy, procedures, and technology. Adapting to change is essential in the Navy, and personnel must be able to adjust to new situations and challenges.
🚨 Note: The naval enlisted rank structure is complex, and it's essential to stay up-to-date with changes and developments to succeed in your career.
In conclusion, understanding the naval enlisted rank structure is critical for success in the Navy. By following these 7 steps, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the ranking system, including the different ranks, responsibilities, and requirements. Remember to stay current and adapt to change, as the Navy is constantly evolving.
What is the highest enlisted rank in the Navy?
+
The highest enlisted rank in the Navy is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
How do I advance through the ranks in the Navy?
+
Advancement and promotion in the Navy are based on performance, experience, and education. Enlisted personnel can advance through the ranks by completing required training, gaining experience, and demonstrating leadership potential.
What is the rating system in the Navy?

+
The Navy has a unique rating system, which categorizes enlisted personnel into specific job specialties. There are over 60 ratings in the Navy, ranging from aviation to healthcare.



