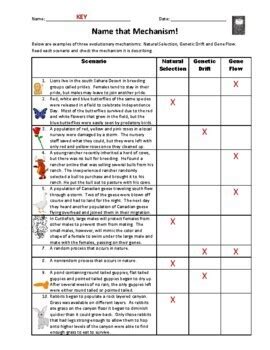
Worksheet
Natural Selection Scenarios

Introduction to Natural Selection

Natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology that explains how species adapt and evolve over time. It is the process by which individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits on to their offspring. This leads to the accumulation of adaptations that enable species to better fit their environment. In this blog post, we will explore various natural selection scenarios to understand how this process works in different contexts.
What is Natural Selection?

Natural selection is often referred to as the “survival of the fittest.” It is a key driver of evolution, as it allows species to adapt to changing environments and ecosystems. The process of natural selection involves several key components: * Variation: All individuals within a species exhibit genetic variation, which can result in different traits and characteristics. * Heritability: The traits and characteristics that are influenced by genetics can be passed on from parents to offspring. * Differential reproduction: Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, while those with unfavorable traits are more likely to die off or fail to reproduce. * Adaptation: Over time, the accumulation of favorable traits leads to the adaptation of the species to its environment.
Types of Natural Selection

There are several types of natural selection, including: * Directional selection: This type of selection occurs when one extreme of a trait is favored over the other extreme. For example, in a population of birds, individuals with larger beaks may be more likely to survive and reproduce because they are better able to crack open seeds. * Stabilizing selection: This type of selection occurs when the average value of a trait is favored over extreme values. For example, in a population of humans, individuals with average-sized feet may be more likely to survive and reproduce because they are better able to walk and run. * Disruptive selection: This type of selection occurs when both extremes of a trait are favored over the average value. For example, in a population of insects, individuals with either very large or very small wings may be more likely to survive and reproduce because they are better able to evade predators or migrate to new habitats.
Natural Selection Scenarios

Let’s consider some natural selection scenarios to illustrate how this process works in different contexts: * The peppered moth: Prior to the Industrial Revolution, the peppered moth had a light-colored, speckled appearance, allowing it to blend in with lichen-covered tree bark. However, with the increase in air pollution, the trees became darker, and a genetic variation in the moth population resulted in a dark-colored morph. The dark-colored moths were better camouflaged on the dark tree trunks and were more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to an increase in the frequency of the dark-colored morph. * The Galapagos finches: The Galapagos finches are a classic example of adaptive radiation, where a single species colonizes a new habitat and then diverges into multiple species. The finches have distinct beak shapes and sizes, which are adapted to different food sources. For example, the large ground finch has a large, powerful beak that allows it to crack open tough seeds, while the small tree finch has a small, pointed beak that allows it to eat insects and nectar. * The evolution of antibiotic resistance: The overuse of antibiotics has led to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In a population of bacteria, individuals that are susceptible to antibiotics will die off, while those that have developed resistance will survive and reproduce. Over time, the frequency of antibiotic-resistant bacteria will increase, making it more difficult to treat infections.
📝 Note: Natural selection is an ongoing process that occurs in all species, and it is not limited to the scenarios described above.
Factors that Influence Natural Selection

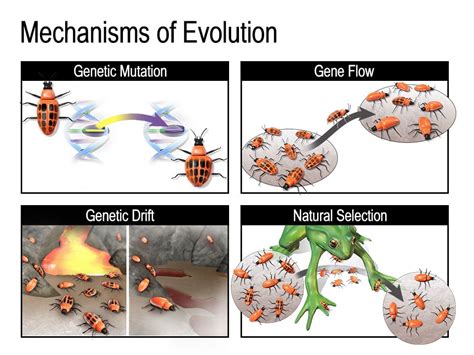
Several factors can influence the process of natural selection, including: * Genetic variation: The amount of genetic variation within a population can affect the rate and direction of natural selection. * Environmental change: Changes in the environment, such as climate change or the introduction of new predators, can lead to changes in the selective pressures acting on a population. * Population size: The size of a population can affect the rate of genetic drift and the effectiveness of natural selection. * Gene flow: The movement of individuals with different genotypes into a population can introduce new genetic variation and affect the process of natural selection.
Conclusion

In conclusion, natural selection is a fundamental process that drives the evolution of species. By understanding how natural selection works in different contexts, we can gain insights into the amazing diversity of life on Earth. From the peppered moth to the Galapagos finches, natural selection scenarios illustrate the power of this process to shape the characteristics of species over time.
What is the main driver of natural selection?

+
The main driver of natural selection is the differential reproduction of individuals with favorable traits, which allows them to pass those traits on to their offspring.
Can natural selection occur in a stable environment?
+
Yes, natural selection can occur in a stable environment, as long as there is genetic variation and differential reproduction within the population.
How does genetic variation affect natural selection?
+
Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon. The more genetic variation within a population, the greater the potential for natural selection to drive evolution.