Transition Metals Naming Compounds Worksheet Answers

Introduction to Transition Metals

Transition metals are a group of metals that are found in the d-block of the periodic table. They are known for their ability to form ions with different charges, and for their catalytic properties. The naming of compounds containing transition metals can be complex, but it follows a set of rules that will be outlined in this post.
Naming Monatomic Ions

When naming monatomic ions, the charge of the ion must be specified. For example, Fe2+ is named iron(II) ion, and Fe3+ is named iron(III) ion. The charge of the ion is indicated by a Roman numeral in parentheses.
Naming Polyatomic Ions

Polyatomic ions are ions that contain more than one atom. When naming polyatomic ions, the name of the ion is used, followed by the name of the metal. For example, chromate is a polyatomic ion that contains chromium, oxygen, and a charge of -2. The name of the compound K2CrO4 is potassium chromate.
Naming Compounds with Transition Metals

When naming compounds that contain transition metals, the name of the metal is used, followed by the name of the nonmetal. The charge of the metal must be specified, unless the metal only has one possible charge. For example, CuCl is named copper(I) chloride, and CuCl2 is named copper(II) chloride.
Prefixes and Suffixes

Prefixes and suffixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound. The prefixes are: * mono- (1 atom) * di- (2 atoms) * tri- (3 atoms) * tetra- (4 atoms) * penta- (5 atoms) * hexa- (6 atoms)
The suffixes are: * -ide (for nonmetals) * -ate (for oxyanions with a charge of -2) * -ite (for oxyanions with a charge of -1)
For example, Cu2O is named dicopper(I) oxide, and Na2Cr2O7 is named sodium dichromate.
Examples of Naming Compounds with Transition Metals
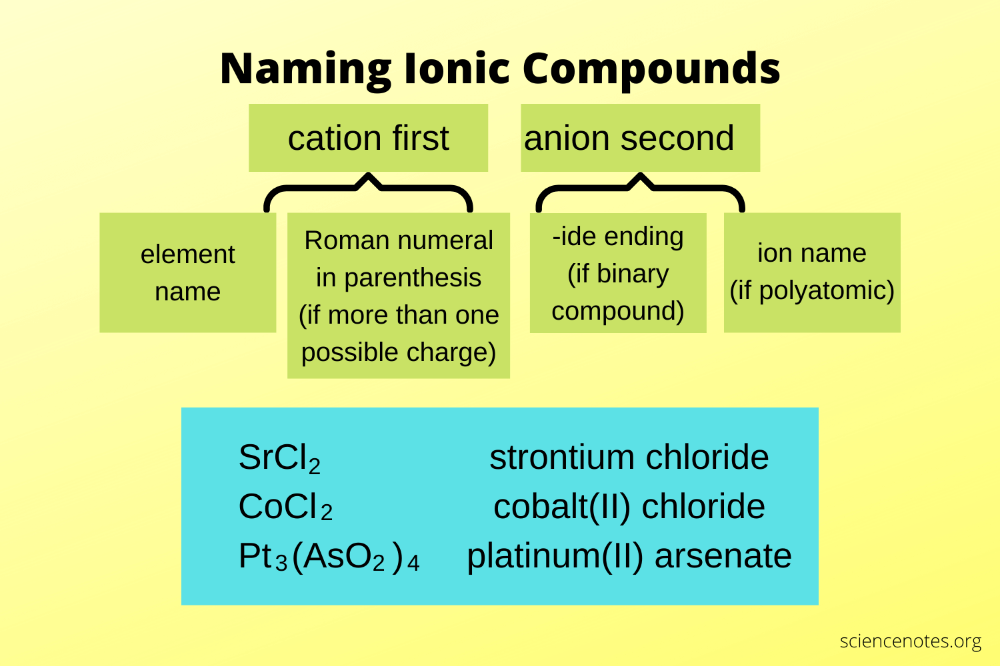
Here are some examples of naming compounds with transition metals: * Fe2O3: iron(III) oxide * CoCl2: cobalt(II) chloride * Ni(CO)4: tetracarbonylnickel(0) * KMnO4: potassium permanganate
📝 Note: The naming of compounds with transition metals can be complex, and it's essential to understand the rules and exceptions to name them correctly.
Table of Common Transition Metals and Their Ions

| Metal | Ions |
|---|---|
| Scandium (Sc) | Sc3+ |
| Titanium (Ti) | Ti2+, Ti3+, Ti4+ |
| Vanadium (V) | V2+, V3+, V4+, V5+ |
| Chromium (Cr) | Cr2+, Cr3+, Cr6+ |
| Manganese (Mn) | Mn2+, Mn3+, Mn4+, Mn6+, Mn7+ |
| Iron (Fe) | Fe2+, Fe3+ |
| Cobalt (Co) | Co2+, Co3+ |
| Nickel (Ni) | Ni2+ |
| Copper (Cu) | Cu+, Cu2+ |
| Zinc (Zn) | Zn2+ |
In summary, the naming of compounds with transition metals requires an understanding of the rules and exceptions. By following these rules, you can correctly name compounds with transition metals.
To finalize, the key points to remember are: * The charge of the metal must be specified, unless the metal only has one possible charge. * Prefixes and suffixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound. * The naming of compounds with transition metals can be complex, and it’s essential to understand the rules and exceptions to name them correctly.
What is the difference between the names of monatomic and polyatomic ions?

+
Monatomic ions are named with a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge, while polyatomic ions are named with a suffix (-ate, -ite) to indicate the charge.
How do you name compounds with transition metals and nonmetals?

+
The name of the metal is used, followed by the name of the nonmetal, with the charge of the metal specified unless it only has one possible charge.
What are the prefixes and suffixes used in naming compounds with transition metals?

+
The prefixes (mono-, di-, tri-, etc.) indicate the number of atoms of each element, while the suffixes (-ide, -ate, -ite) indicate the charge of the ion.