Name That Atom Worksheet: 10 Simple Answers

In the vast universe of chemistry, understanding the basic building blocks of matter is essential. Atoms are these fundamental units, and being able to identify them accurately is the first step to mastering chemical concepts. This blog post delves into the "Name That Atom Worksheet," offering ten straightforward answers to common queries about atomic structures. Whether you're a student grappling with chemistry basics or a teacher aiming to solidify your students' knowledge, this guide is crafted to illuminate the atomic landscape with clarity and precision.
Understanding the Atom

The atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms consist of three primary particles:
- Protons - Positively charged particles found in the nucleus, defining the atomic number of the element.
- Neutrons - Neutral particles in the nucleus that contribute to the mass of the atom but not to its chemical behavior.
- Electrons - Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus, playing a critical role in chemical reactions due to their attraction to protons.
🔎 Note: Electrons are arranged in shells around the nucleus, with each shell able to hold a specific number of electrons.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
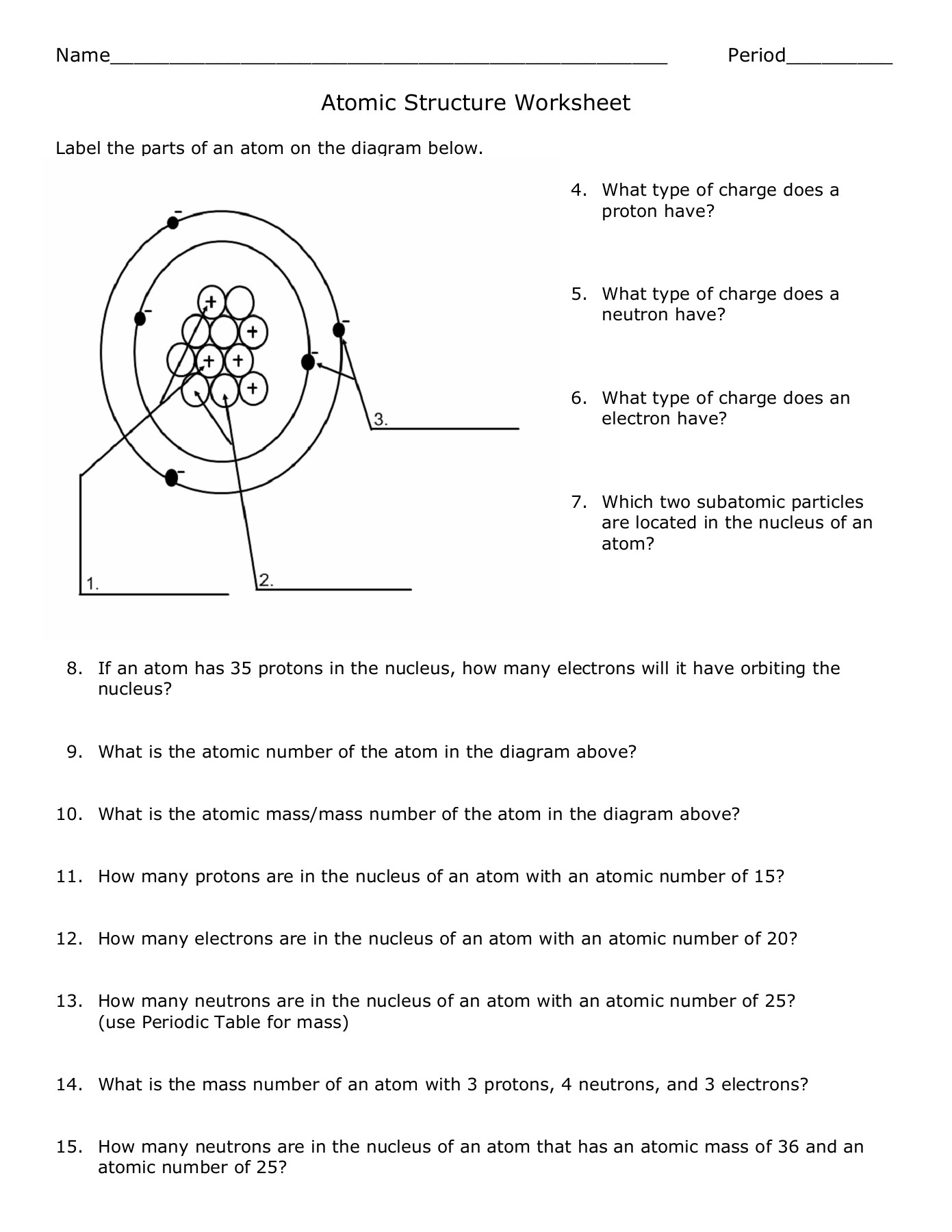
When it comes to naming atoms, two key numbers provide insight:
- Atomic Number - Represents the number of protons in the nucleus, uniquely identifying the element. This is fixed for each element.
- Mass Number - The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. This number can vary, creating isotopes of the same element.
Name That Atom: The Worksheet

Here's a closer look at ten simple answers related to the "Name That Atom Worksheet":
The Atom with 1 Proton

This atom is Hydrogen. With only one proton, hydrogen has the lowest atomic number (1) on the periodic table. It’s vital for life, being a key component of water and organic molecules.
💡 Note: Hydrogen often exists in molecular form (H2) because it forms covalent bonds to achieve stability.
The Atom with 6 Protons

This is Carbon, a fundamental element in organic chemistry. Carbon’s ability to form stable bonds with other elements is central to the diversity of life on Earth.
The Atom with 7 Protons

Nitrogen is the answer here. Nitrogen gas (N2) constitutes about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere, and nitrogen is an essential component of amino acids, proteins, and DNA.
The Atom with 8 Protons

The element is Oxygen. Critical for respiration in most living organisms, oxygen is highly reactive and forms compounds easily due to its electron configuration.
The Atom with 12 Protons

This is Magnesium, an alkaline earth metal known for its role in photosynthesis and its presence in many enzymes in biological systems.
The Atom with 16 Protons

Sulfur falls into this category. It’s important in biology for the structure of amino acids and is used in various industrial applications due to its unique chemical properties.
The Atom with 17 Protons

The answer is Chlorine. With its strong electronegativity, chlorine forms chloride ions readily, playing a key role in salt production, water purification, and as a disinfectant.
The Atom with 20 Protons

This atom is Calcium. Calcium is crucial for bones, teeth, and numerous physiological processes, including nerve signaling and muscle contractions.
The Atom with 26 Protons

Iron is the element with this atomic number. Iron’s ability to exist in multiple oxidation states makes it vital for processes like oxygen transport in the blood.
The Atom with 35 Protons

The element here is Bromine, which is unusual because it’s one of the only two elements that are liquid at room temperature. Bromine is used in pharmaceuticals, flame retardants, and as a dye precursor.
Understanding the atomic structure and the unique properties of each element provides a solid foundation for further exploration in chemistry. This worksheet not only aids in remembering atomic numbers but also highlights the significance of these atoms in everyday life.
🔍 Note: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, leading to different mass numbers but the same chemical properties.
In this exploration of the "Name That Atom Worksheet," we've touched upon the essentials of atomic structure, the significance of atomic and mass numbers, and the everyday relevance of these elements. From hydrogen's role in water to iron's function in our blood, these building blocks shape our world in fundamental ways. As you delve deeper into chemistry, remember that each atom carries a unique story, and understanding them enriches our knowledge of the universe at its most basic level.
How do I find the atomic number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. You can find it in the periodic table as the top or bottom number associated with each element.
What is the significance of the atomic mass?
+Atomic mass or mass number reflects the total number of protons and neutrons, indicating an isotope’s mass. It’s critical for identifying isotopes and understanding an element’s properties.
Why are some elements important in life?
+Elements like hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, calcium, and iron play roles in biological processes. They form the molecular building blocks of life, participating in crucial functions from energy transfer to structural support.