5 Tips for Multiplying by 2-Digit Numbers Easily

5 Tips for Multiplying by 2-Digit Numbers Easily
Multiplying two-digit numbers can seem like a daunting task, but with some strategic thinking and practice, it can become much simpler. Here, we'll explore five techniques that make multiplying two-digit numbers a breeze. These methods not only speed up your calculations but also enhance your mental math skills, making everyday arithmetic less of a chore and more of a fun challenge.
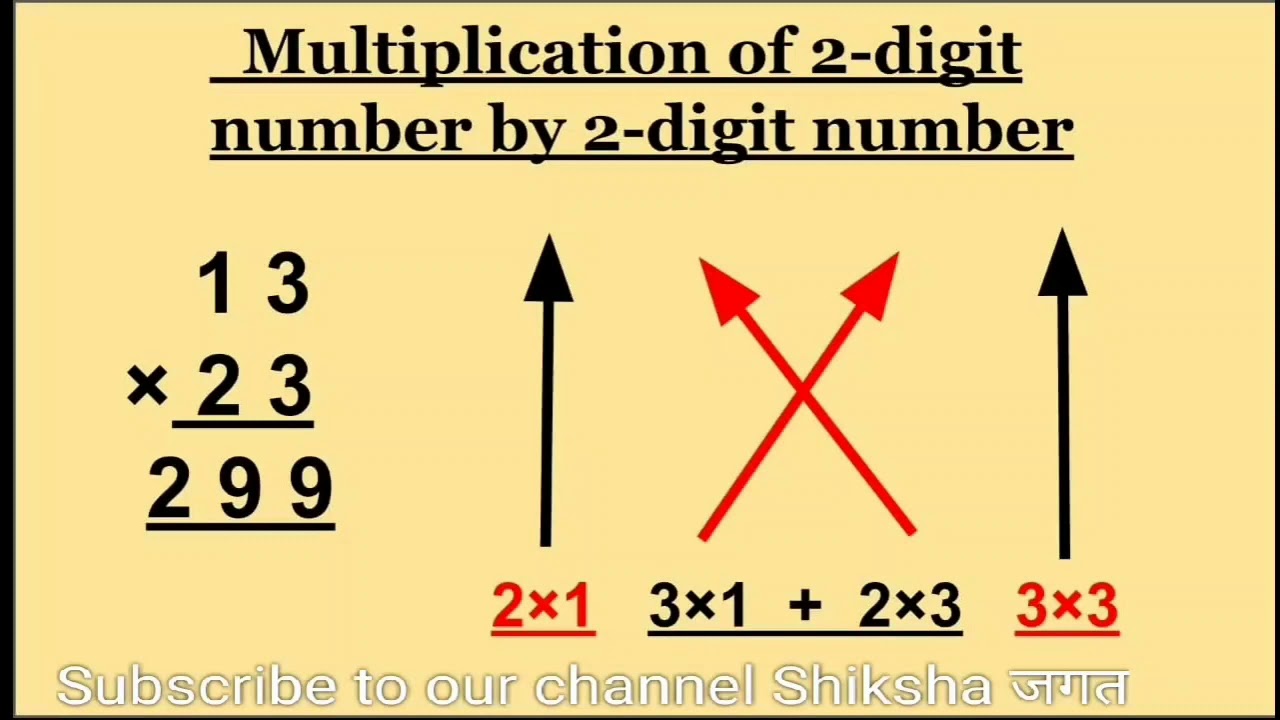
Tip #1: Use the Cross Multiplication Method

Cross multiplication is an effective technique for multiplying two-digit numbers. Here’s how to do it:
- Step 1: Take the first digits of both numbers and multiply them together to get the first digit of the result.
- Step 2: Add the product of the first digit of the first number and the second digit of the second number to the product of the second digit of the first number and the first digit of the second number. This gives you the middle digit or digits of your result.
- Step 3: Finally, multiply the last digits of both numbers to find the last digit of the result.
For example, let's multiply 34 by 12:
- 3 x 1 = 3 (First part of the answer)
- (3 x 2) + (4 x 1) = 10 (Middle digits, carry over 1)
- 4 x 2 = 8
The result is 318.
Tip #2: Apply the Difference of Squares
This method works particularly well when one of the numbers is close to a power of 10. Here’s the process:
- Identify which number is close to a power of 10 (10, 100, etc.).
- Consider the formula: (a + b)(a - b) = a2 - b2
- Example: Multiply 49 x 51:
- 49 is close to 50, so let a = 50, b = 1.
- (50 + 1)(50 - 1) = 502 - 12
- 2500 - 1 = 2499
Tip #3: Double-and-Halve Technique

This method is excellent for multiplication where one of the numbers is even:
- Double one number and halve the other.
- Continue halving and doubling until you reach a multiplication table that you’re familiar with.
- Example: Multiply 32 x 18:
- Halve 18 to get 9, double 32 to get 64
- 32 x 18 = (32 x 2) x (18 ÷ 2) = 64 x 9
- 64 x 9 = 576
Tip #4: Utilize Known Patterns

Recognizing patterns can drastically reduce the complexity of multiplication:
- Patterns involving 9s:
- Multiplying any number by 9 is the same as multiplying by 10 and subtracting the original number.
- Patterns involving squares:
- Numbers ending in 5 when squared always end in 25, so just square the number before the 5, add 25, and place the decimal point appropriately.
- Example: To calculate 35 x 35:
- (3 x 3) = 9, so 35 x 35 = 925
Tip #5: Practice with Vedic Math

Vedic Mathematics offers a set of unique strategies that can make multiplication more intuitive:
- The Nikhilam method for numbers close to powers of 10:
- Subtract each number from the nearest power of 10 to find the difference.
- Multiply these differences together to get the last part of your answer.
- Add back the sum of the original numbers and the nearest power of 10 to get the final product.
- Example: 93 x 98:
- 100 - 93 = 7, 100 - 98 = 2
- 7 x 2 = 14 (last two digits)
- 93 + 98 - 2 = 189 (first digits)
- Thus, 93 x 98 = 18914
In closing, mastering multiplication with two-digit numbers opens up a world of quick calculations and enhanced mental math prowess. Each technique discussed here, from cross multiplication to Vedic math, provides a unique approach to tackle different scenarios. By incorporating these methods into your routine, you'll not only boost your calculation speed but also develop a deeper understanding of numbers and their relationships. The joy of mastering these techniques lies in the newfound confidence and efficiency they bring to everyday arithmetic tasks.
Can these methods work for larger numbers?

+
These methods are designed primarily for two-digit numbers, but some can be adapted for larger numbers with practice, especially Vedic math techniques.
Is there a method that always works?

+
The traditional long multiplication is always accurate, but for mental math, these tips provide shortcuts that are situationally effective.
How can I remember which method to use?
+
Practice and familiarity with each method help in deciding which one suits different numbers. Consider the structure of the numbers and use the method that simplifies the problem the most.