5 Fun Ways to Master Multiplication Using Arrays

Learning multiplication can sometimes be a daunting task for students, yet employing arrays as a visual aid can transform this often challenging skill into an engaging and memorable experience. Multiplication arrays provide a concrete way for children to see what the numbers are doing when they are multiplied, making abstract concepts tangible. Here are five fun, innovative ways to use arrays to master multiplication:
1. Building Blocks Array
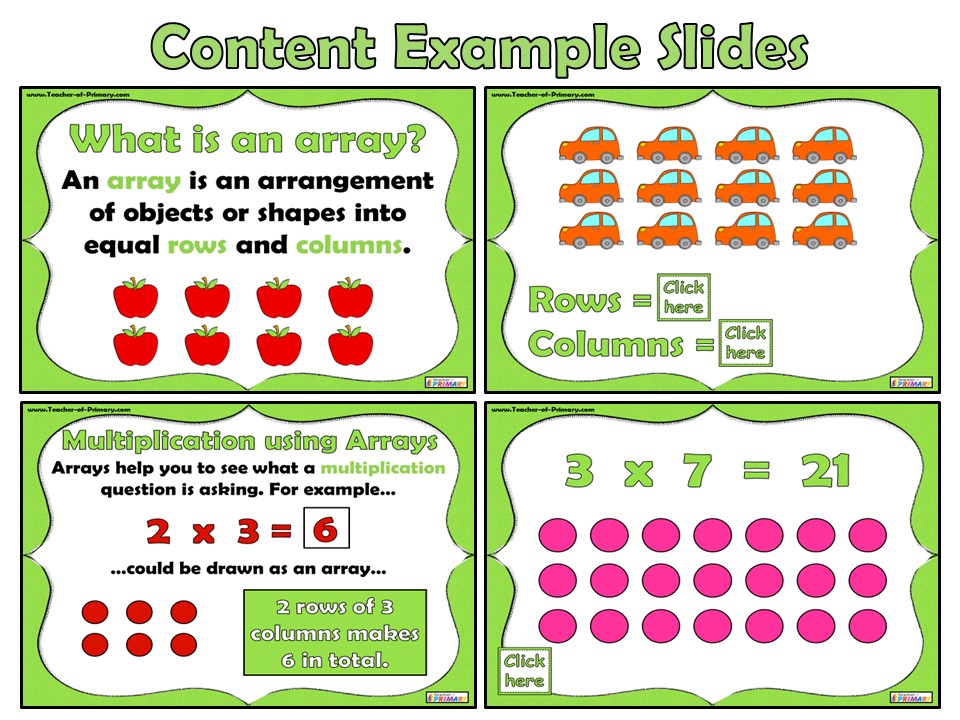

Start with basic building blocks or LEGO pieces. Let’s say you want to teach multiplication of 2 x 4. Arrange the blocks in two rows of four blocks each. This visual representation helps kids see the numbers as physical objects:
- Have children count the total number of blocks by rows.
- Switch the array to vertical columns to teach the commutative property (e.g., 4 x 2).
2. Hopscotch Grid


Create a hopscotch grid on the playground or indoor space with chalk or tape, labeling each square with a number. Here’s how to use it:
- Children can hop through the grid to physically represent the multiplication, for instance, hopping 3 x 4 would mean hopping three times forward and four hops to the side.
- This active learning method helps in understanding the multiplication visually and kinesthetically.
3. Candy Grid Game


This game turns learning into a treat:
- Make a grid using candy or small tokens where each row and column represent numbers to be multiplied.
- Children can pick a number from a row and another from a column, then count the candy to find the product.
🍬 Note: Ensure the candies are safe for consumption and consider nutritional guidelines when using this method.
4. Music and Rhythm Multiplication


Children often enjoy rhythm and music, and combining it with learning multiplication can be highly effective:
- Use musical notes or simple clapping patterns to represent arrays. For example, tapping out 3 x 4 could be done in three groups of four taps.
- Play a game where children create rhythms for different multiplication facts.
5. Interactive Digital Arrays


In today’s digital age, using technology can make learning multiplication a fun interactive experience:
- There are several apps and online tools that allow children to click or drag objects into arrays for visual representation of multiplication.
- Children can compete in virtual games where they build arrays to win points or solve puzzles.
In summary, mastering multiplication using arrays through these fun methods not only helps in understanding the concept but also makes it an enjoyable part of learning. Whether it's through building, physical activity, games, music, or technology, each approach reinforces the idea of multiplication as visual and tangible. This interactive way of learning helps in retaining the information better, making children more confident in their math skills.
Can arrays be used for any multiplication fact?
+
Yes, arrays can be used to visualize any multiplication fact, from simple single-digit problems to complex double-digit multiplication.
What age group is suitable for learning multiplication with arrays?
+
Arrays are most effective for children starting to learn multiplication, generally between the ages of 6 and 9, but can be adapted for older students as well.
How can parents or teachers introduce arrays to kids?
+
Begin with simple grid drawings, physical objects like blocks or candies, and gradually introduce more complex representations using games or interactive methods.