5 Essential Tips for Mastering Motion Graphs With Answers

Understanding motion graphs is a fundamental aspect of physics education. These graphs serve as a visual representation of how objects move, describing their position, velocity, and acceleration over time. Mastering the interpretation and creation of these graphs can significantly enhance one's grasp of kinematics. Here are five essential tips to help you excel in handling motion graphs effectively:
1. Understand the Basics
Before diving into complex graphs, make sure you have a solid understanding of what each type of graph represents:
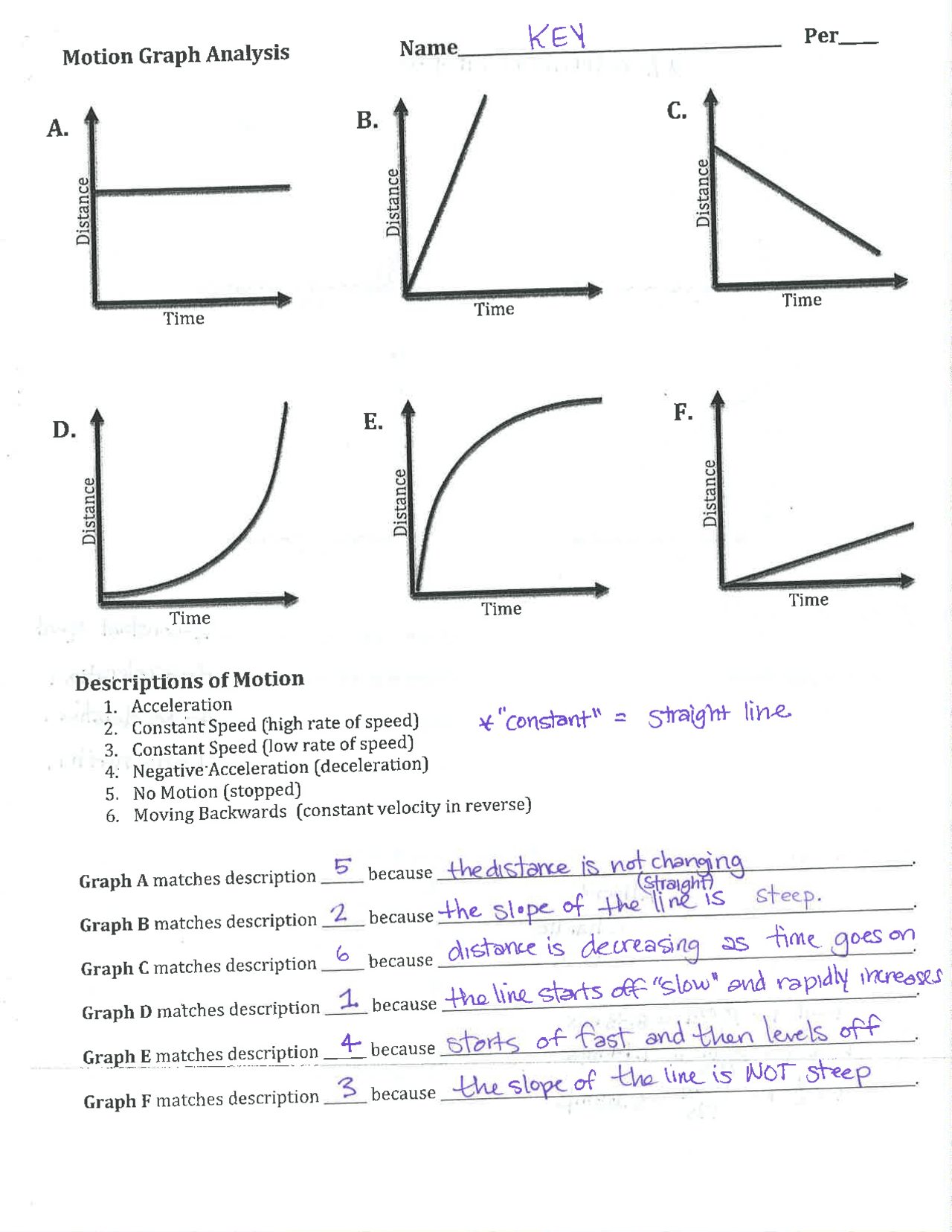
- Position vs. Time Graph: Shows how an object’s position changes over time. The slope of this graph indicates velocity. A straight line with a positive slope represents constant positive velocity, while a horizontal line means the object is at rest.
- Velocity vs. Time Graph: Illustrates how velocity changes over time. The slope here represents acceleration, and the area under the curve gives the displacement.
- Acceleration vs. Time Graph: This graph shows acceleration as a function of time. Here, the area under the curve represents the change in velocity.
2. Identify Key Points and Features

When analyzing motion graphs:
- Slopes and Areas: Understand that slopes in a position-time graph represent velocity, while areas under the curve in a velocity-time graph represent displacement. Conversely, slopes in a velocity-time graph indicate acceleration, and areas represent changes in velocity.
- Curvature and Shape: A straight line implies constant acceleration or velocity, while a curved line suggests changing acceleration or velocity. Recognize inflection points where the curve changes direction, indicating a change in the nature of motion.
📝 Note: Pay special attention to the sign of the slope. Positive slopes indicate motion in the positive direction, and negative slopes signify motion in the negative direction.
3. Practice Sketching Graphs

Sketching graphs from verbal or mathematical descriptions of motion:
- Position from Velocity: If you know how an object’s velocity changes with time, you can determine its position by integrating (or graphically adding up) the areas under the velocity-time curve.
- Velocity from Acceleration: Similarly, velocity can be deduced from acceleration-time graphs by integrating the area under the curve.
Here’s an example of how to sketch a position vs. time graph from a given acceleration:
| Time (s) | Velocity (m/s) | Position (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 3 | 6 | 9 |

💡 Note: Always label your axes with units to keep your graphs meaningful and scientific.
4. Connect the Graphs

Learn how the different types of motion graphs relate:
- Position to Velocity: The slope at any point on a position-time graph equals the velocity at that instant.
- Velocity to Acceleration: The slope of a velocity-time graph at any point gives you the acceleration at that moment.
- Acceleration to Velocity: Integrate acceleration over time to find velocity, which essentially means finding the area under the acceleration graph.
5. Solve Problems Using Graphs

Using graphs to solve motion problems can be incredibly powerful:
- Tangent Lines: For instantaneous quantities like velocity or acceleration at a point, draw tangent lines and find their slopes.
- Area Analysis: Use the area under the curve for finding changes in position or velocity over an interval.
- Graphical Methods: Sometimes, graphing data can make a problem simpler to solve than using equations alone.
By mastering these graphical techniques, you'll not only understand the physical principles better but also approach problems with a strategic mindset.
In closing, understanding and mastering motion graphs can provide a visual insight into the dynamics of motion, making complex concepts like acceleration, velocity, and position much more intuitive. Remember to identify key elements like slopes, areas, and shapes, practice sketching, connect different types of graphs, and use graphical methods for problem-solving. These tips will not only help in academic settings but also enrich your appreciation of physical motion in the real world.
What does the slope of a position-time graph represent?

+
The slope of a position-time graph represents the object’s velocity. A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a zero slope implies the object is at rest.
How can I convert a velocity-time graph to an acceleration-time graph?

+
To convert a velocity-time graph to an acceleration-time graph, you take the slope of the velocity-time graph at each instant. This slope is the acceleration at that time.
Why are the areas under velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs significant?

+
The area under a velocity-time graph gives the displacement or change in position, while the area under an acceleration-time graph gives the change in velocity. This direct relationship allows for quick calculations and visual interpretations of motion problems.