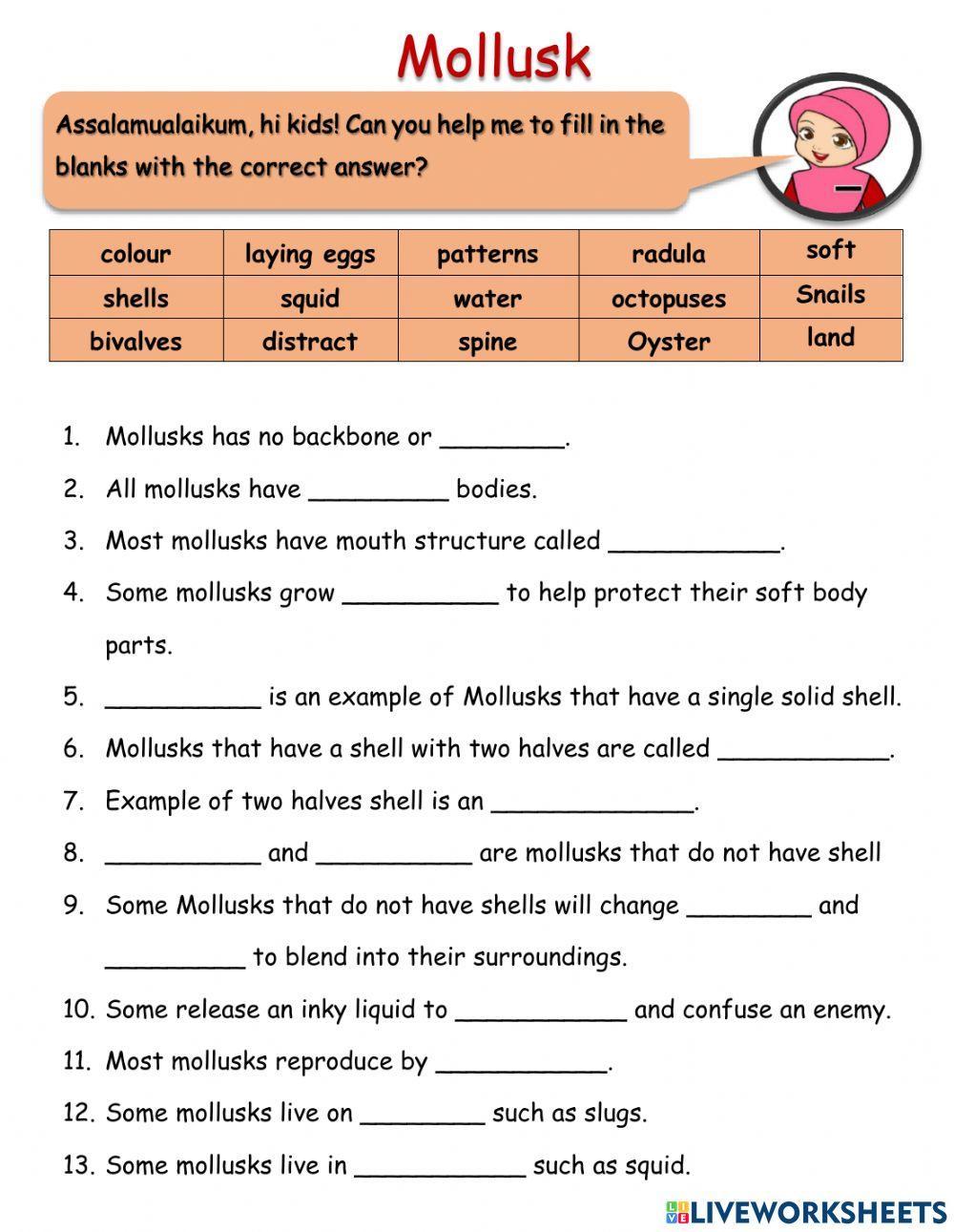
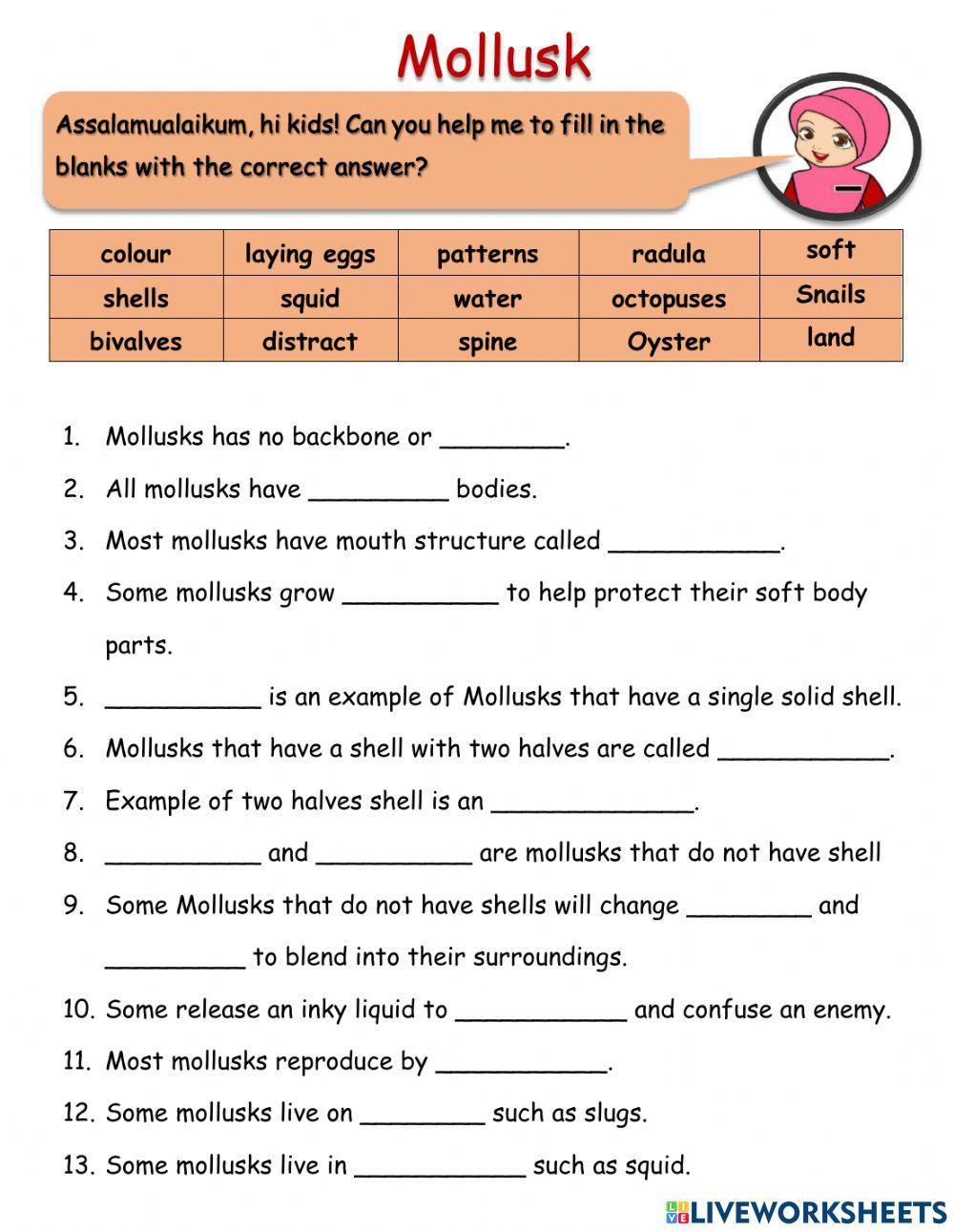
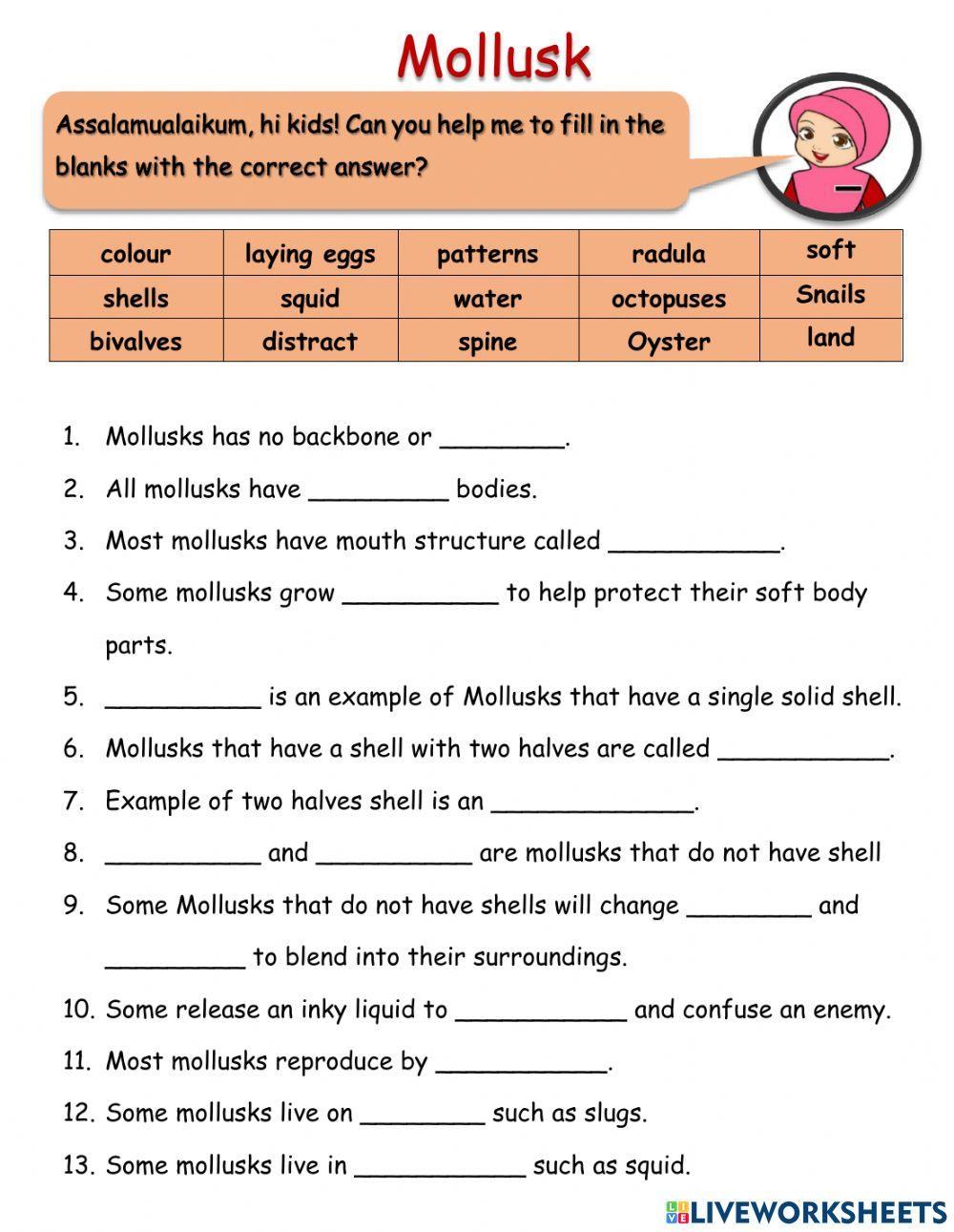
5 Essential Facts About Mollusks: Worksheet Answers

When delving into the fascinating world of mollusks, it's beneficial to arm yourself with knowledge that will enhance your understanding and appreciation of these diverse organisms. Whether you're a student looking to ace your science quiz, a hobbyist keen on expanding your biology knowledge, or just someone intrigued by marine life, understanding some essential facts about mollusks can be highly rewarding. Here are five key aspects of mollusks along with worksheet answers to deepen your insight:
Diversity of Mollusks


The world of mollusks is remarkably diverse, comprising over 85,000 species. Here’s a look at some of the classes:
- Gastropods: Snails, slugs, and sea slugs.
- Bivalves: Clams, oysters, mussels, and scallops.
- Cephalopods: Squid, octopuses, cuttlefish, and nautiluses.
- Chitons: Also known as polyplacophora, with eight articulated shells.
- Scaphopods: Also called tusk shells, because of their unique shape.
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| Gastropods | Snails, Slugs |
| Bivalves | Clams, Mussels |
| Cephalopods | Squid, Octopuses |

Anatomy and Physiology

Mollusks have a unique body structure which includes:
- Soft Body: Enclosed in a shell in most species, although some, like slugs, lack this external covering.
- Mantle: A layer of tissue that usually produces the shell.
- Foot: A muscular organ used for movement, digging, or adhesion.
- Radula: A tongue-like structure with teeth for feeding in many species.
Additionally, some mollusks exhibit the ability to change color and texture for protection or communication, a trait especially prominent in cephalopods.
Ecological Significance


Mollusks play several vital roles in ecosystems:
- Filter Feeders: Many bivalves filter water, improving water quality and cycling nutrients.
- Keystone Species: Some mollusks like certain snails can control algae levels, maintaining balance in ecosystems.
- Predators: Cephalopods are apex predators in the ocean, controlling other species populations.
💡 Note: Mollusks are indicators of environmental health, as they can accumulate pollutants in their bodies.
Reproduction and Life Cycle

Mollusks display varied reproductive strategies:
- Sexual Reproduction: Most species have separate sexes with external fertilization for marine mollusks and internal for terrestrial ones.
- Life Cycle: From eggs to larvae, then to juveniles, and finally to adults. Some have larval stages that are crucial for dispersal.
Notably, some species, like the sea hares, lay egg masses that resemble ribbons, which can be quite fascinating to observe.
Mollusks and Humans

Humans have interacted with mollusks in numerous ways:
- Food Source: Mollusks like clams, oysters, and squids are culinary delights worldwide.
- Ornamental Use: Shells are used for jewelry, decoration, and cultural artifacts.
- Scientific Research: Their nervous systems, especially of cephalopods, provide insights into complex animal behavior.
However, overexploitation and habitat destruction by humans pose threats to mollusk populations. Responsible harvesting practices are crucial to ensure their survival.
In summary, understanding mollusks enriches our knowledge of biodiversity, ecological processes, and even human history. Each class and species has unique adaptations that contribute to their survival and our fascination with them. Whether through their diverse forms, ecological roles, or cultural significance, mollusks offer a microcosm of the vast and intricate tapestry of life on Earth.
What is the difference between a mollusk and a crustacean?

+
Mollusks and crustaceans belong to different phyla. Mollusks have soft bodies often covered by a shell, while crustaceans have a hard exoskeleton and jointed limbs. Additionally, crustaceans like crabs and lobsters, belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
Why are cephalopods considered the most intelligent invertebrates?

+
Cephalopods like octopuses and squids possess the most complex nervous systems of all invertebrates, with well-developed brains, enabling them to exhibit advanced behaviors such as problem-solving, tool use, and even play.
How do mollusks impact water quality?

+
Many bivalve mollusks are filter feeders, filtering out particles from the water, including pollutants, thus improving water quality. However, they can also concentrate these pollutants in their tissues, which can serve as bioindicators of environmental pollution.