5 Ways to Master Mole Calculations Easily

When you dive into the world of chemistry, understanding mole calculations becomes crucial. Whether you're an undergrad student, preparing for an exam, or just a hobbyist chemist, mastering mole calculations can make the difference between feeling overwhelmed and feeling in control. Here, we'll explore five straightforward strategies to simplify your journey through mole calculations.
1. Understand the Basics of the Mole

Before you can master mole calculations, it's vital to grasp what a mole is. The mole (mol) is a fundamental unit in chemistry, similar to how a dozen or a score represents quantity in everyday life. Here's how you can think about it:
- A mole is 6.022 x 10^23 entities, often atoms, molecules, or ions.
- This number is known as Avogadro's number in honor of Amedeo Avogadro.
- A mole provides a bridge between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and our macroscopic world where we measure and count larger quantities.
💡 Note: Avogadro's number is just a constant. Understanding its significance can help you in other areas like solution concentration or gas volume calculations.
2. Master the Conversion Factors

Mole calculations often require conversions. To make this easier:
- Memorize or have a reference for molar mass of common elements and compounds. This is the mass in grams of one mole of substance.
- Familiarize yourself with Avogadro's number. Remember, 1 mol = 6.022 x 10^23 entities.
- Know the volume of a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) - 1 mol of any ideal gas occupies 22.4 liters at STP.
| Conversions | Formula |
|---|---|
| From moles to grams | Mass (g) = Moles (mol) × Molar mass (g/mol) |
| From grams to moles | Moles (mol) = Mass (g) ÷ Molar mass (g/mol) |
| From moles to particles | Number of particles = Moles (mol) × Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23) |
| From particles to moles | Moles (mol) = Number of particles ÷ Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23) |
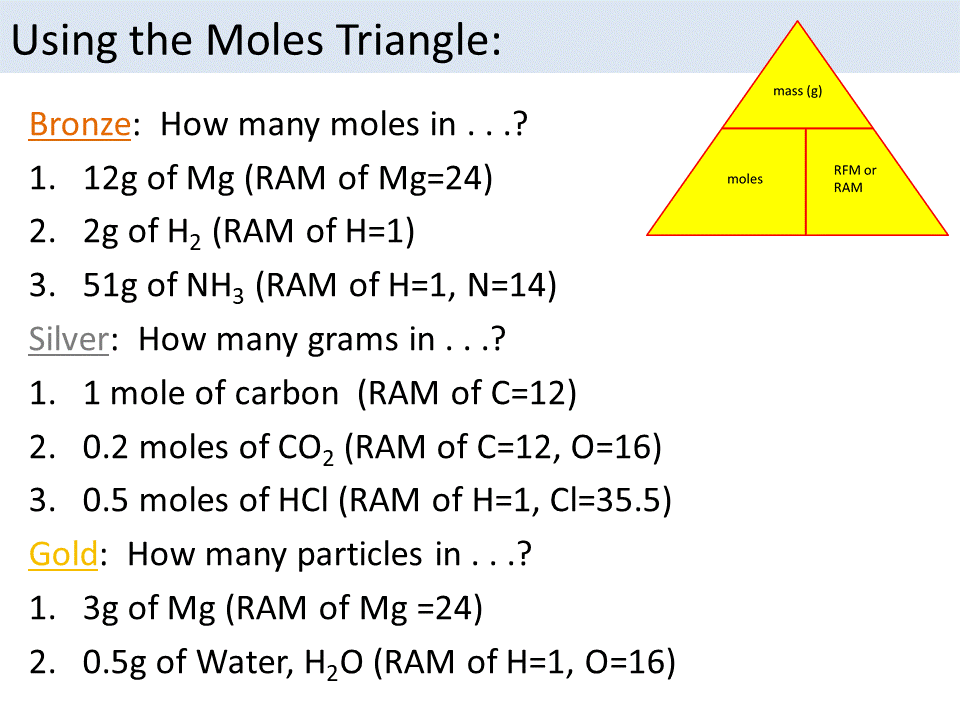
🔍 Note: The periodic table is your best friend. Keep it handy for quick reference to molar masses.
3. Use Dimensional Analysis for Problem-Solving

Dimensional analysis, or the factor-label method, allows you to convert between units while solving problems:
- Start with the unit you have.
- Set up conversion factors so that the units cancel out.
- Multiply through to find your answer.
This method is particularly useful because it:
- Helps with unit conversion.
- Keeps track of units, ensuring your calculations are correct.
- Can simplify complex calculations by breaking them into understandable steps.
4. Practice with a Variety of Problems

The saying 'practice makes perfect' holds true here. Here are types of problems you should solve:
- Simple mole-mass calculations: Convert from moles to mass and vice versa.
- Gas volume calculations: Use Avogadro's principle to find volumes at STP.
- Solution concentration: Understand how to calculate molarity, which involves moles of solute per liter of solution.
- Empirical and molecular formula determination: These require mole calculations to find the simplest whole number ratio of elements.
📘 Note: Textbooks and online resources offer a wealth of practice problems. Engage with them to solidify your understanding.
5. Integrate Technology and Tools

Today's world offers various tools to ease the learning process:
- Calculator apps: Many advanced calculators have built-in functions for mole conversions or molecular weight calculations.
- Chemistry simulation software: These tools allow you to visualize chemical reactions and understand mole relationships better.
- Online calculators: There are numerous websites with mole calculation tools. Use them to check your work.
- Educational platforms: Platforms like Khan Academy or Coursera provide video tutorials that can help with tricky concepts.
While technology is helpful, always ensure you understand the underlying concepts and not just rely on the tools for answers.
In the dynamic realm of chemistry, mastering mole calculations is not just about passing exams; it’s about understanding the fundamental principles that govern matter. By internalizing the key points outlined above, such as understanding the mole, mastering conversion factors, employing dimensional analysis, engaging with varied problems, and leveraging technology, you set yourself up for success in understanding chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and much more. Whether for academic pursuits or a deeper appreciation of the natural world, these strategies will equip you with the skills needed to excel in your chemical journey.
What is the difference between a mole and molar mass?

+
A mole is a unit that represents 6.022 x 10^23 entities, which can be atoms, molecules, or ions. Molar mass, on the other hand, is the mass of one mole of a substance in grams. It’s essentially the atomic or molecular weight expressed in grams per mole.
How can I remember Avogadro’s number?

+
Avogadro’s number can be challenging to memorize, but there are tricks:
- Associate it with something memorable, like the number of your favorite athlete’s jersey or a significant date.
- Write it out in full form (602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000) to visually understand its magnitude.
- Use mnemonic devices like “Avo<>ca<>d<>o has 6.022×10^23 fruits!”
Why are mole calculations important in chemistry?

+
Mole calculations are essential because they help chemists quantify how substances interact in reactions. They provide a link between microscopic entities (atoms and molecules) and macroscopic measurements like mass, which are necessary for understanding stoichiometry, limiting reactants, reaction yields, and solution concentrations.