Mastering Molecules and Atoms: Interactive Worksheet Guide

The study of molecules and atoms forms the foundation of chemistry, a discipline that's both intriguing and immensely important. Understanding these minute building blocks of matter not only quenches our curiosity about the world around us but also provides crucial insights into how substances behave and interact. This interactive worksheet guide is designed to delve into this fundamental aspect of science, offering an engaging way for students to learn about the structure, properties, and interactions of atoms and molecules. Let's embark on a journey through the microscopic realm of chemistry.
Understanding Atoms


Atoms are the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties. Here's a brief overview:
- Nucleus: The central part of an atom composed of protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral).
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels.
- The mass of an atom is primarily due to protons and neutrons since electrons have negligible mass.
⚛️ Note: Although most atoms have neutrons, hydrogen-1, the most common isotope of hydrogen, has none.
Exploring Molecules


Molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together. Here's what you need to know:
- They can be formed from atoms of the same element (e.g., O2) or different elements (e.g., H2O).
- The properties of molecules differ significantly from those of their constituent atoms.
- Bonds in molecules can be covalent (sharing of electrons) or ionic (transfer of electrons).
| Property | Atoms | Molecules |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | Individual Element | Combination of Elements |
| Bonding | N/A | Covalent, Ionic, etc. |
| Behavior | Reacts as Per Element | Unique Properties |

🔬 Note: In certain contexts, especially in solid state physics, the distinction between atoms and molecules can become somewhat blurred with definitions like lattice structure.
Interactive Learning with Worksheets

Worksheets can transform learning into an interactive, engaging experience. Here are steps to create or use an effective worksheet for mastering atoms and molecules:
- Start with Visuals: Include diagrams of atoms and simple molecules to help visualize their structure.
- Fill in the Blanks: Provide questions where students can fill in blanks regarding atomic and molecular properties.
- Matching Exercises: Students can match elements or molecules to their uses or properties.
- Labeling Diagrams: Ask learners to label different parts of an atom or molecule structure.
- True or False: Test understanding of basic concepts through true or false statements.
- Short Answer Questions: Challenge students to explain concepts in their own words.
Key Takeaways

- Atoms are fundamental to understanding chemistry; they are the smallest unit of an element.
- Molecules result from atoms bonding, creating substances with unique properties.
- Interactive worksheets make learning about atoms and molecules engaging and effective.
In the realm of science, comprehending the behavior and interaction of molecules and atoms opens up a world of possibilities, from explaining why water is wet to understanding the complexity of DNA. This interactive worksheet guide not only enriches understanding but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the chemistry that underpins our existence.
What’s the difference between an atom and a molecule?

+
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical identity, while a molecule consists of two or more atoms bonded together, which can be of the same or different elements.
Can molecules exist without atoms?
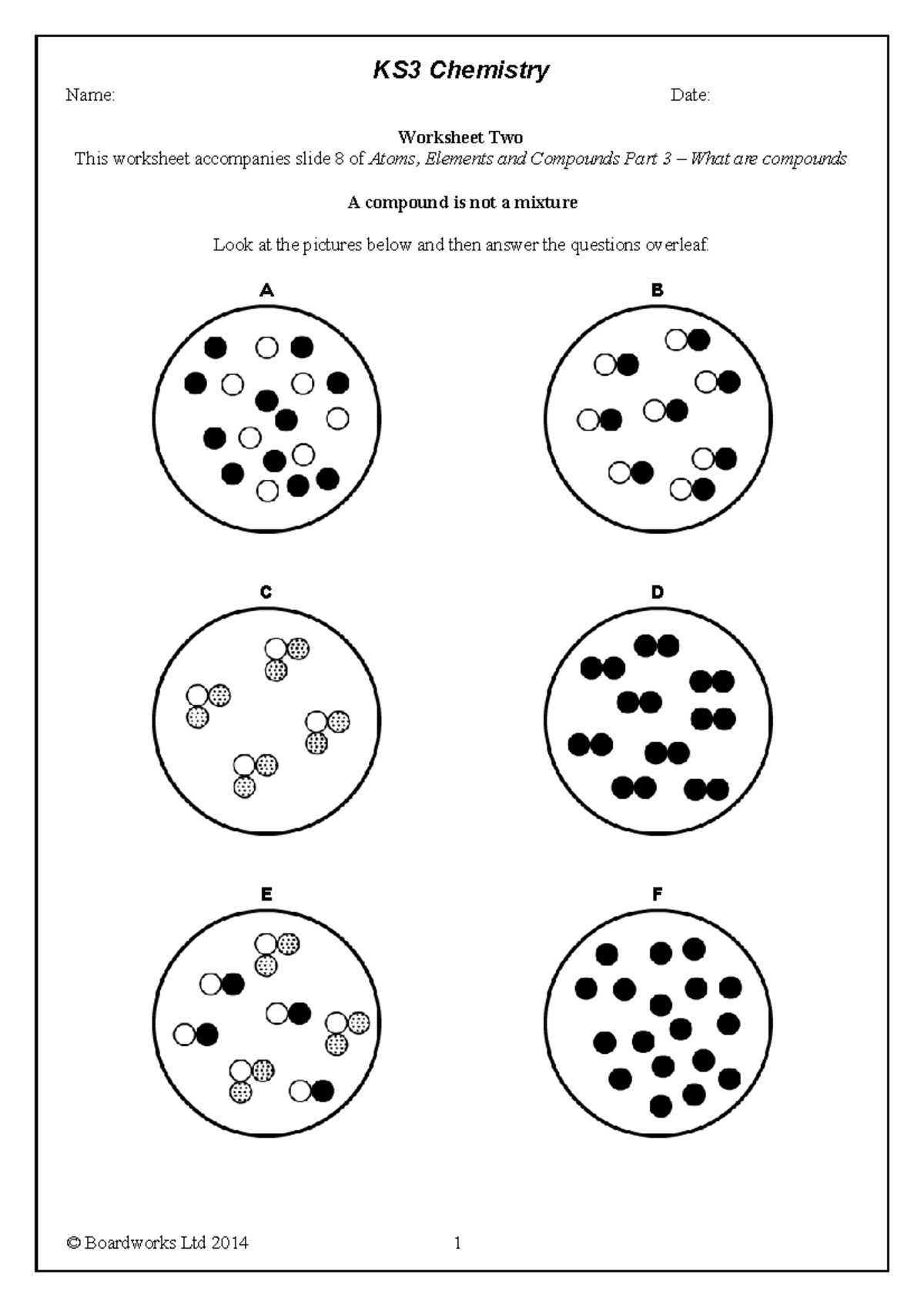
+
No, molecules are composed of atoms. A molecule needs at least two atoms bonded together to be considered a molecule.
Why are worksheets useful for learning about atoms and molecules?

+
Worksheets provide a structured way to engage with complex concepts through visual aids, interactive questions, and practical exercises, which helps in reinforcing and solidifying the understanding of these topics.
Can an atom become a different element?

+
Yes, through processes like nuclear transmutation, where the number of protons in the nucleus changes, an atom can be transformed into an atom of a different element. However, this does not occur in chemical reactions, which involve only the sharing or transfer of electrons.