5 Facts About Molar Weight of Air

Understanding the Molar Weight of Air
The molar weight of air, also known as the molecular weight of air, is a crucial concept in various fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. It is essential to understand the composition of air and its molar weight to calculate the properties of air, such as its density and specific heat capacity. In this article, we will explore five key facts about the molar weight of air.
Fact #1: Composition of Air
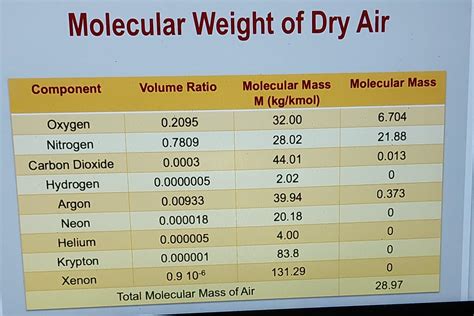
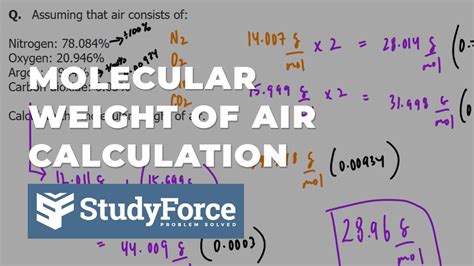
Air is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), argon (Ar), and carbon dioxide (CO2). The approximate composition of air by volume is:
- Nitrogen (N2): 78.08%
- Oxygen (O2): 20.95%
- Argon (Ar): 0.93%
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): 0.04%
- Other gases: 0.01%
Fact #2: Calculating Molar Weight

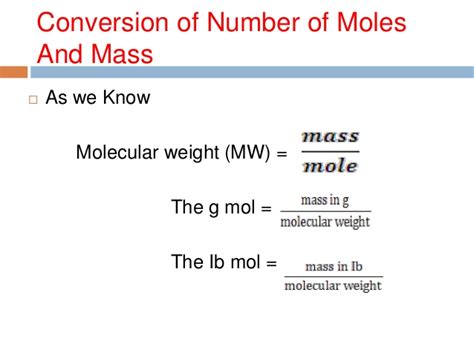
The molar weight of air is calculated by taking the weighted average of the molar weights of its constituent gases. The molar weight of each gas is calculated by summing the atomic weights of its constituent atoms.
| Gas | Molecular Formula | Molar Weight (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | N2 | 28.01 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 32.00 |
| Argon | Ar | 39.95 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 44.01 |

Using the composition of air, we can calculate the molar weight of air as follows:
Molar weight of air = (0.7808 x 28.01) + (0.2095 x 32.00) + (0.0093 x 39.95) + (0.0004 x 44.01) ≈ 28.97 g/mol
Fact #3: Variations in Molar Weight

The molar weight of air can vary slightly depending on factors such as:
- Altitude: The composition of air changes with altitude, which affects the molar weight.
- Humidity: Water vapor in the air can affect the molar weight.
- Location: The composition of air can vary depending on the location, such as near the ocean or in urban areas.
However, these variations are relatively small, and the molar weight of air is generally considered to be constant.
Fact #4: Importance in Calculations

The molar weight of air is essential in various calculations, such as:
- Gas density: The density of a gas is calculated using the molar weight and the gas constant.
- Specific heat capacity: The specific heat capacity of air is calculated using the molar weight and the heat capacity of the constituent gases.
- Gas flow calculations: The molar weight of air is used in calculations involving gas flow, such as in pipelines and compressors.
📝 Note: The molar weight of air is a critical parameter in many engineering and scientific applications, and it is essential to use the correct value to ensure accurate calculations.
Fact #5: Comparison with Other Gases
The molar weight of air is relatively low compared to other gases, such as:
- Helium: 4.00 g/mol
- Methane: 16.04 g/mol
- Carbon dioxide: 44.01 g/mol
This is because air is primarily composed of nitrogen and oxygen, which have relatively low atomic weights.
In conclusion, the molar weight of air is a fundamental concept that is essential in various fields. Understanding the composition of air and its molar weight is crucial for accurate calculations and applications.
What is the molar weight of air?

+
The molar weight of air is approximately 28.97 g/mol.
Why is the molar weight of air important?

+
The molar weight of air is essential in various calculations, such as gas density, specific heat capacity, and gas flow calculations.
Can the molar weight of air vary?

+
Yes, the molar weight of air can vary slightly depending on factors such as altitude, humidity, and location.
Related Terms:
- molecular weight of air g mol
- Molecular weight of dry air
- cp cv of air
- Mass of air
- Mol atm calculator
- G mol to lbm lbmol