Solve Mixture Problems Easily: Ultimate Worksheet Guide
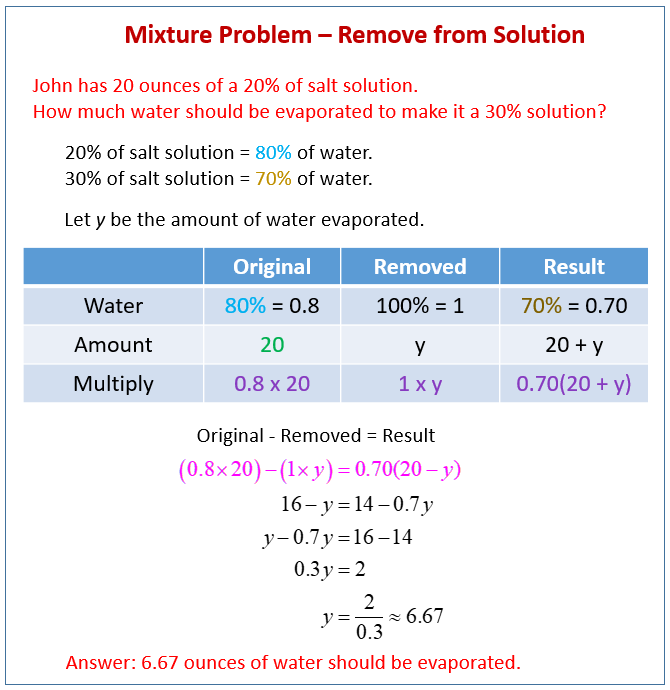
In the realm of mathematics, solving mixture problems can be a daunting task for many students and professionals alike. However, with a systematic approach and a bit of practice, these problems can become much more manageable. This guide aims to demystify mixture problems by providing a comprehensive worksheet designed to help you master these equations with ease.
Understanding Mixture Problems

Mixture problems typically involve blending substances with different concentrations to achieve a desired concentration in a final mixture. Here's what you need to know:
- Substances: These are the materials being mixed, often with different levels of a specific component (e.g., alcohol).
- Concentration: Usually expressed as a percentage or decimal, this is the amount of the component in each substance.
- Equation: Mixture problems use algebra to balance the components in the substances to find the unknown variables.
Steps to Solve Mixture Problems

1. Define Variables

Start by clearly defining what your variables represent:
- Let X be the amount of substance A.
- Let Y be the amount of substance B.
2. Setup Equations

Using the total amount of the mixture and the concentration:
- Equation for the total mixture: X + Y = Total Mixture
- Equation for concentration:
Substance Concentration Amount A CA X B CB Y Mixture CM X + Y 
3. Solve the System of Equations

Now, use algebra to solve for X and Y:
- Substitute the expressions for X or Y from one equation into the other.
- Simplify and solve for one variable.
- Use this result to find the other variable.
4. Check Your Solution

Always verify your results to ensure they make sense:
- Substitute X and Y back into your original equations.
- Ensure both equations are satisfied.
📝 Note: It's crucial to keep units consistent when setting up and solving the equations.
Example Worksheet

Here is an example worksheet to help you practice:
Problem 1:

A coffee shop needs to create a special blend using 35% Arabica beans and 75% Robusta beans to make 50 pounds of a mixture that is 50% Arabica.
- What quantities of each type of bean should be used?
- Set up the equations as:
- Let A be the amount of Arabica beans.
- Let R be the amount of Robusta beans.
- A + R = 50
- 0.35A + 0.75R = 0.50 * 50
- Solve these equations to find A and R.
Problem 2:

An alloy is made from copper, which is 60% pure, and another alloy that is 40% pure to produce 200 grams of 50% pure alloy.
- How many grams of each alloy are needed?
- Set up the equations as:
- Let C be the amount of copper alloy.
- Let A be the amount of the second alloy.
- C + A = 200
- 0.60C + 0.40A = 0.50 * 200
- Solve these equations to find C and A.
📝 Note: When solving, make sure to account for both the sum of the weights and the total amount of the component in the mixture.
Tips for Success

- Use a systematic approach: Organize your work with clear steps for clarity.
- Practice with Real-World Scenarios: Apply mixture problems to real-world examples like food, chemicals, or finance.
- Check Units: Be vigilant with units to avoid miscalculations.
Mixture problems, while challenging, provide a practical understanding of algebra. By following this guide, practicing with the provided worksheets, and keeping these tips in mind, you can significantly improve your ability to solve these problems with confidence. Remember, the key to mastery in mathematics lies in consistent practice and the application of learned concepts to various scenarios. With this approach, what was once a complex problem becomes a manageable task, enhancing not only your mathematical skills but also your problem-solving capabilities in everyday situations.
What is a mixture problem?

+
A mixture problem is a type of algebra word problem where two or more substances with known concentrations are combined to form a mixture with a new, desired concentration.
Why do we need to set up two equations in mixture problems?

+
Two equations are necessary in mixture problems because one equation deals with the total quantity (the amount of each substance), and the second equation addresses the concentration of the mixture to achieve the desired result.
Can mixture problems have more than two substances?

+
Yes, mixture problems can involve more than two substances. In such cases, you would need to set up additional equations to account for the extra variables involved.



