Mastering Mixed Operations with Fractions: Free Worksheet

Understanding mixed operations with fractions is a cornerstone in developing proficiency in mathematics. Whether you're balancing a checkbook, measuring ingredients for a recipe, or solving complex engineering problems, the ability to work seamlessly with fractions enhances your mathematical literacy. This comprehensive blog post will guide you through the maze of mixed operations with fractions, offering both theoretical explanations and practical applications in an engaging format. Let's dive into the world of fractions!
Introduction to Mixed Operations with Fractions

The beauty of working with fractions lies in their flexibility. Unlike integers, fractions can denote values between whole numbers, which are often needed in real-world scenarios. Fractions come in various forms, each with its own set of rules:
- Proper Fractions: The numerator is less than the denominator, like 3⁄4.
- Improper Fractions: The numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, for example, 7⁄4.
- Mixed Numbers: A whole number combined with a proper fraction, such as 1¾.
Basic Operations with Fractions

To master mixed operations, you need to get comfortable with individual operations first. Here are the basic operations:
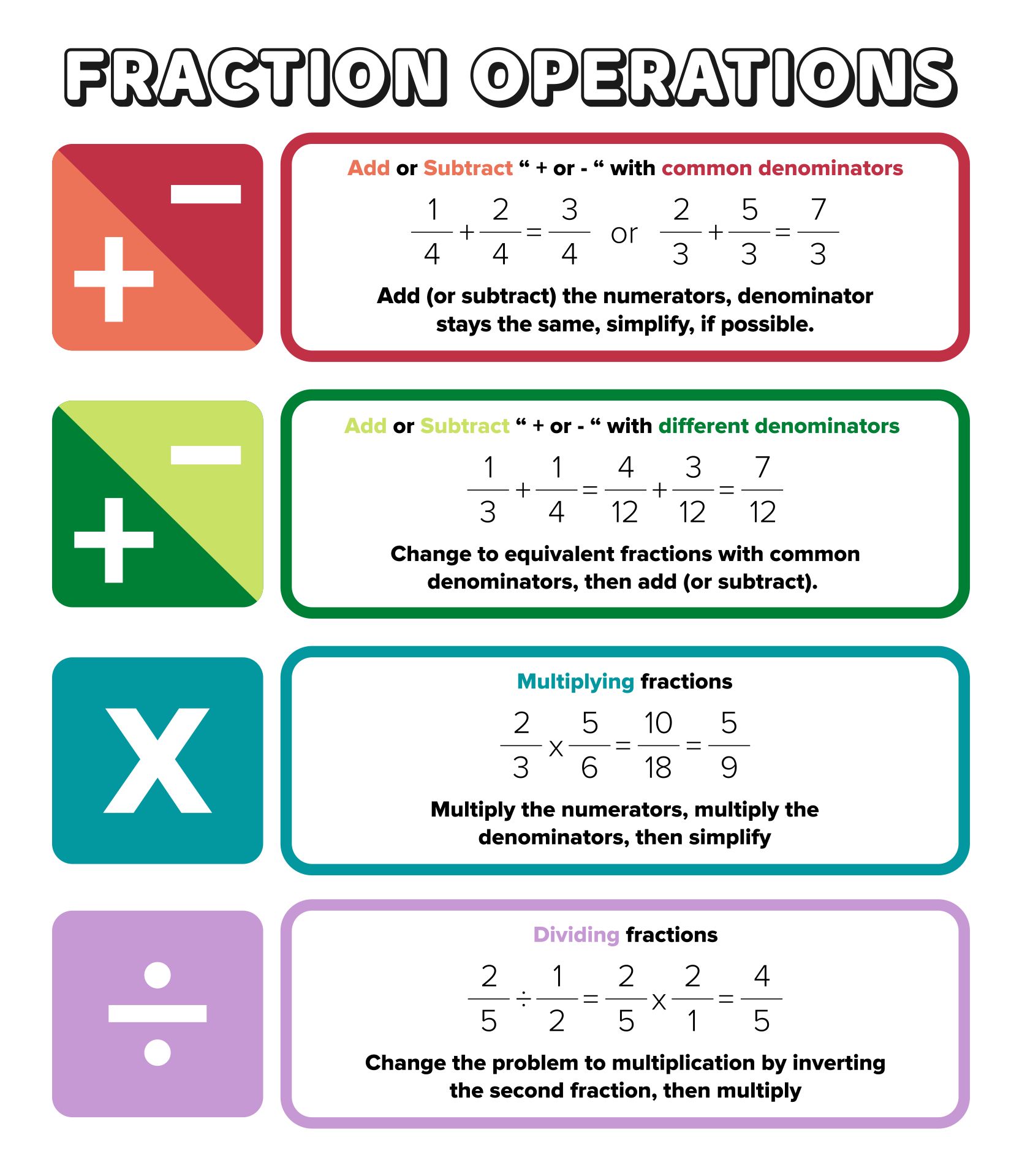
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions

When adding or subtracting fractions, follow these steps:
- Ensure Common Denominators: Find a common multiple for the denominators or convert one fraction to match the other’s denominator.
- Add or Subtract Numerators: Perform the arithmetic on the numerators while keeping the common denominator.
- Simplify if Possible: Reduce the result to its simplest form.
Here’s a table to illustrate:
| Fraction 1 | Fraction 2 | Operation | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄3 | 2⁄3 | Addition | 1 |
| 5⁄6 | 1⁄6 | Subtraction | 2⁄3 |

Multiplication of Fractions

Multiplying fractions is straightforward:
- Multiply the numerators together and the denominators together.
- Simplify the resulting fraction if possible.
🌟 Note: Cross-cancelling can save time by reducing the numbers before multiplication.
Division of Fractions

To divide by a fraction:
- Flip the divisor fraction (the second fraction) to create its reciprocal.
- Multiply the first fraction by this reciprocal.
- Simplify as needed.
📌 Note: Dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
Performing Mixed Operations
Real-world problems often involve a mix of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with fractions. Here’s how to approach mixed operations:
Order of Operations

Remember the acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)):
- Handle any operations inside parentheses or brackets first.
- Deal with exponents (although not common with fractions).
- Perform multiplication and division in order from left to right.
- Finally, address addition and subtraction in order from left to right.
Examples of Mixed Operations

- Example 1: 3⁄4 + 1⁄2 - 1⁄3 x 2⁄3
- Example 2: (5⁄6 - 1⁄3) ÷ 1⁄2
Each example shows how to apply the rules of operations in sequence, taking care with the numerators and denominators to ensure accuracy.
Tips for Mastering Fraction Calculations
Here are some practical tips to help you become more efficient with fraction operations:
- Learn Common Denominators: Familiarize yourself with least common multiples for common denominators.
- Practice Estimation: Estimation can help in quickly determining if your answer is reasonable.
- Convert When Necessary: Sometimes converting mixed numbers to improper fractions simplifies calculations.
To enhance your skills in handling mixed operations with fractions, here are some practical exercises:
- Worksheet Download: Engage in mixed operations with fractions by downloading our comprehensive free worksheet on our website. This tool provides exercises that reinforce understanding and offer real-world applications of what you've learned.
🔔 Note: Regular practice is key to mastering these skills. Engage with tools and resources available online for continual practice.
To wrap up, mastering mixed operations with fractions is not just about understanding the rules but also about the flexibility to apply these in various contexts. The skills you hone through this practice are indispensable in many areas of life, from daily tasks to complex problem-solving. We've discussed the basic operations, tackled how to perform mixed operations, and provided tips for efficiency, culminating in a practical exercise to solidify your learning.
Why is it important to understand mixed operations with fractions?

+
Understanding mixed operations with fractions is crucial for various applications in everyday life and advanced mathematical calculations. From finance to engineering, accurate handling of fractions is key to solving real-world problems.
How do I handle exponents in fraction operations?

+
Although exponents are not commonly involved with simple fractions, when they are, you treat the numerator and denominator separately, applying the exponent to each according to the rules of exponentiation.
Can I always simplify fractions before performing operations?

+
Simplifying fractions before performing operations like multiplication or division can save time and reduce the complexity of calculations. However, it’s not always necessary and should be used judiciously.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with fractions?

+
Common mistakes include forgetting to find a common denominator, neglecting the order of operations, incorrectly simplifying, or not treating each fraction uniformly during operations.
Where can I find more practice on mixed operations with fractions?

+
Engage with educational websites, online calculators, or academic resources that offer worksheets, tutorials, and interactive exercises for additional practice on mixed operations with fractions.


