5 Military Reserve Tips

Introduction to Military Reserve

Joining the military reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering a unique opportunity to serve one’s country while also pursuing a civilian career. For those considering this path, it’s essential to understand the ins and outs of military reserve life. From the application process to deployment, every aspect requires careful consideration and preparation. In this article, we will delve into five key tips for individuals looking to join the military reserve, helping them make informed decisions about their future.
Understanding the Commitment

Before joining the military reserve, it’s crucial to understand the commitment involved. This includes not only the initial training period but also the potential for deployment and the long-term service obligation. Individuals should be aware that joining the reserve is not just a part-time job; it’s a significant commitment that can impact various aspects of life, including family, education, and career. Being prepared for the challenges and opportunities that come with serving in the reserve is vital for a successful and fulfilling experience.
Choosing the Right Branch

Choosing the right branch of the military is another critical decision for potential reservists. Each branch (Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard) has its unique mission, culture, and opportunities. Individuals should research each branch to find the best fit for their skills, interests, and career goals. For example, those interested in aviation might find the Air Force or Navy appealing, while those with a background in medicine could be well-suited for the Army or Navy’s medical corps. Making an informed decision at this stage can significantly impact one’s satisfaction and success in the military reserve.
Preparing for Basic Training

Preparing for basic training is essential for all new recruits, including those joining the reserve. Basic training, also known as boot camp, is an intensive introduction to military life, focusing on physical fitness, combat skills, and military protocol. To prepare, individuals should focus on improving their physical fitness through regular exercise, such as running, push-ups, and sit-ups. Additionally, understanding the basics of military etiquette and what to expect during training can reduce stress and make the transition smoother.
Education and Career Benefits

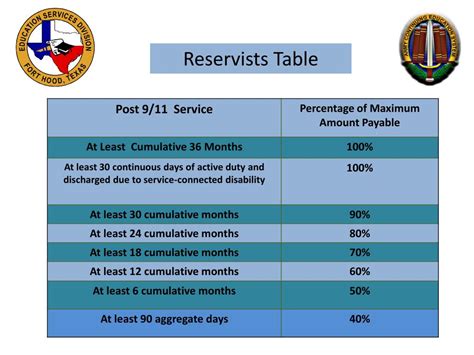
One of the significant advantages of joining the military reserve is the education and career benefits it offers. The military provides various education assistance programs, such as the Montgomery GI Bill, which can help reservists pay for college or vocational training. Moreover, the skills and experiences gained through military service can be highly valued by civilian employers, enhancing career opportunities. Individuals should explore these benefits thoroughly and understand how they can be applied to further their education and career goals.
Balancing Military and Civilian Life

Finally, balancing military and civilian life is a crucial aspect of being a reservist. This involves managing the demands of military service, including drills, training, and potential deployments, alongside civilian responsibilities such as work, family, and education. Effective time management, communication with employers and family, and a flexible mindset are key to navigating these dual responsibilities successfully. Reservists should also be aware of the resources available to help them balance their lives, such as military support services and legal protections like the Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (USERRA).
💡 Note: Understanding and preparing for the challenges of military reserve life, from the initial commitment to balancing civilian and military responsibilities, is crucial for a successful and fulfilling experience.
In summary, joining the military reserve requires careful consideration and preparation. By understanding the commitment involved, choosing the right branch, preparing for basic training, leveraging education and career benefits, and balancing military and civilian life, individuals can set themselves up for success and make the most of their reserve experience.
What are the basic requirements to join the military reserve?
+
To join the military reserve, one must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions), have a high school diploma, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
How long is the initial training period for military reservists?

+
The initial training period, known as Basic Training or Boot Camp, typically lasts about 7 to 12 weeks, depending on the branch of service. Following basic training, reservists will also attend technical school to learn their specific job skills.
Can reservists pursue higher education while serving?
+
Yes, the military offers various education benefits and programs to help reservists pursue higher education, including the Montgomery GI Bill, which can help pay for tuition and fees.