7 Ways to Maximize Military Pay After Taxes
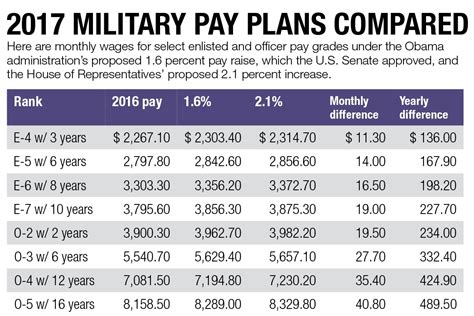
Understanding Military Pay and Taxes

Military personnel often face unique financial challenges, from frequent relocations to deployments. However, the military offers various forms of compensation that can help maximize take-home pay. In this article, we’ll explore seven ways to minimize taxes and maximize military pay.
Tax-Advantaged Savings Options

One of the most effective ways to reduce taxes and increase take-home pay is to utilize tax-advantaged savings options. Here are a few options available to military personnel:
- Thrift Savings Plan (TSP): The TSP is a retirement savings plan that offers tax benefits and low fees. Contributions are made before taxes, reducing taxable income.
- Roth Individual Retirement Account (IRA): A Roth IRA allows contributions to be made with after-tax dollars, but the money grows tax-free and withdrawals are tax-free in retirement.
- Military Savings Accounts: Some military savings accounts, such as the Military Savings Account, offer tax benefits and competitive interest rates.
Take Advantage of Tax Credits

Tax credits can significantly reduce tax liability, increasing take-home pay. Here are a few tax credits available to military personnel:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): The EITC is a refundable tax credit for low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families.
- Child Tax Credit: The Child Tax Credit is a refundable tax credit for families with qualifying children.
- Education Credits: Education credits, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit, can help offset education expenses.
Utilize Tax-Free Allowances
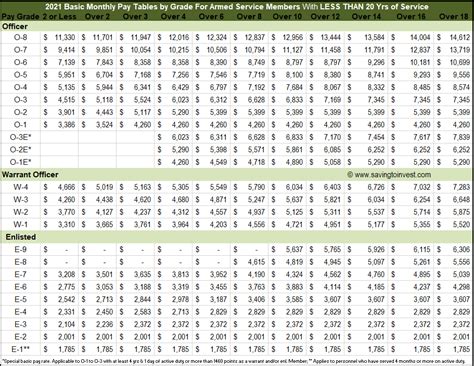
The military offers various tax-free allowances that can help reduce taxes and increase take-home pay. Here are a few examples:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): BAH is a tax-free allowance that helps offset housing expenses.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): BAS is a tax-free allowance that helps offset food expenses.
- Special Duty Pay: Special duty pay, such as hazardous duty pay, is tax-free.
Leverage Military-Specific Tax Benefits
The military offers various tax benefits that can help reduce taxes and increase take-home pay. Here are a few examples:
- Combat Zone Tax Exclusion: Military personnel serving in combat zones may be eligible for a tax exclusion on their income.
- Moving Expense Deduction: Military personnel may be eligible to deduct moving expenses on their tax return.
- Uniform and Equipment Deduction: Military personnel may be eligible to deduct uniform and equipment expenses on their tax return.
Consider a Roth Conversion

A Roth conversion involves converting a traditional retirement account, such as a TSP or IRA, to a Roth account. This can help reduce taxes in retirement and increase take-home pay.
Seek Professional Tax Advice
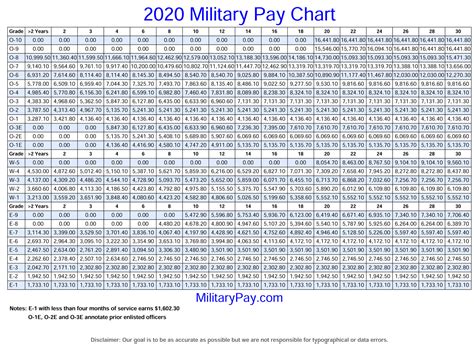
Tax laws and regulations can be complex, so it’s essential to seek professional tax advice to ensure you’re taking advantage of all the tax benefits available to you.
Conclusion

Maximizing military pay after taxes requires a comprehensive understanding of tax laws and regulations. By utilizing tax-advantaged savings options, taking advantage of tax credits, leveraging tax-free allowances, and seeking professional tax advice, military personnel can reduce taxes and increase take-home pay.
What is the Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)?

+
The TSP is a retirement savings plan that offers tax benefits and low fees. Contributions are made before taxes, reducing taxable income.
What is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)?

+
The EITC is a refundable tax credit for low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families.
What is the Combat Zone Tax Exclusion?

+
Military personnel serving in combat zones may be eligible for a tax exclusion on their income.