Middle Colonies Native American Relations

Introduction to Middle Colonies Native American Relations

The Middle Colonies, which consisted of present-day New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, had a unique and complex relationship with Native American tribes. The region’s diverse geography, climate, and natural resources supported a wide range of Native American communities, each with their own distinct culture, language, and traditions. As European colonization expanded, the Middle Colonies became a hub of interaction between Native Americans and European settlers, leading to a mix of cooperation, conflict, and transformation.
Native American Tribes in the Middle Colonies

The Middle Colonies were home to numerous Native American tribes, including the Iroquois, Lenape, Susquehannock, and Algonquian-speaking peoples. These tribes had developed complex societies, with their own systems of governance, agriculture, and trade. The Iroquois, for example, were a powerful and influential confederacy of six nations that played a significant role in shaping the region’s history. The Lenape, on the other hand, were a semi-nomadic people who inhabited the coastal regions and were skilled hunters and gatherers.
European Settlement and Native American Relations
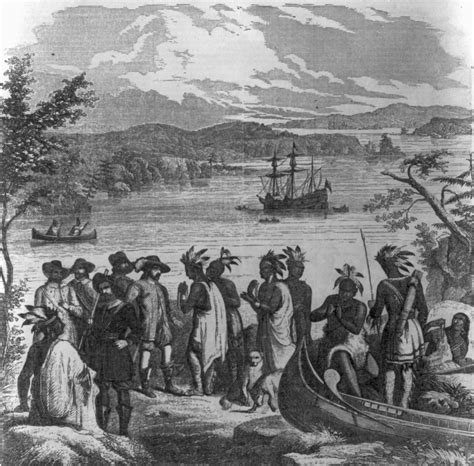

As European settlers arrived in the Middle Colonies, they brought with them new technologies, diseases, and cultural practices that would significantly impact Native American communities. The Dutch, who established the first European settlements in the region, generally maintained peaceful relations with Native American tribes, engaging in trade and diplomacy. However, the arrival of English and Swedish settlers led to increased competition for resources and territory, resulting in tensions and conflicts. The Native American tribes, who had previously enjoyed a relatively stable and autonomous existence, found themselves facing significant challenges to their way of life.
Key Events and Conflicts

Several key events and conflicts shaped the complex relationship between Native Americans and European settlers in the Middle Colonies. These include: * The Pequot War (1636-1638), which saw the English colonists and their Native American allies clash with the Pequot tribe, resulting in significant losses for the Pequot and the establishment of English dominance in the region. * The Lenape-Dutch War (1640-1645), which was sparked by disputes over land and trade, and ultimately led to the Lenape being forced to cede significant territory to the Dutch. * The Iroquois Wars (1640s-1700s), which saw the Iroquois confederacy clash with French and English colonists, as well as other Native American tribes, over issues of territory, trade, and sovereignty.
Trade and Diplomacy

Despite the conflicts, trade and diplomacy played a significant role in shaping the relationship between Native Americans and European settlers in the Middle Colonies. The fur trade, in particular, was a lucrative industry that brought together Native American trappers and European merchants. The Iroquois, with their strategic location and control of key trade routes, played a significant role in facilitating trade between European colonists and other Native American tribes. Diplomacy was also an essential tool, with both Native American leaders and European colonists engaging in negotiations and treaties to establish boundaries, resolve conflicts, and secure trade agreements.
Cultural Exchange and Transformation

The interaction between Native Americans and European settlers in the Middle Colonies led to significant cultural exchange and transformation. Native American tribes adopted European technologies, such as metal tools and firearms, which transformed their economies and societies. European settlers, on the other hand, adopted Native American agricultural practices, such as maize cultivation, and learned from their expertise in hunting and gathering. The exchange of ideas, cultures, and technologies had a profound impact on the region, shaping the course of history and leaving a lasting legacy.
| Native American Tribe | Traditional Territory | European Colonizer |
|---|---|---|
| Iroquois | Present-day New York state | English, French |
| Lenape | Present-day New Jersey, Delaware | Dutch, English |
| Susquehannock | Present-day Pennsylvania, Maryland | English, Swedish |

📝 Note: The interactions between Native Americans and European settlers in the Middle Colonies were complex and multifaceted, and this table provides a simplified overview of the traditional territories and European colonizers associated with each tribe.
In the end, the relationship between Native Americans and European settlers in the Middle Colonies was marked by both cooperation and conflict, leading to significant transformations in the region’s cultures, economies, and societies. As we reflect on this complex history, we are reminded of the importance of understanding and respecting the diverse perspectives and experiences of all individuals and communities involved.
What were the main Native American tribes in the Middle Colonies?

+
The main Native American tribes in the Middle Colonies included the Iroquois, Lenape, Susquehannock, and Algonquian-speaking peoples.
What was the significance of the fur trade in the Middle Colonies?

+
The fur trade was a lucrative industry that brought together Native American trappers and European merchants, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between the two cultures.
How did the interaction between Native Americans and European settlers shape the region’s history?

+
The interaction between Native Americans and European settlers led to significant transformations in the region’s cultures, economies, and societies, shaping the course of history and leaving a lasting legacy.