5 Ways Mendel’s Work Revolutionizes Meiosis Studies

5 Ways Mendel’s Work Revolutionizes Meiosis Studies

In the field of genetics, few names resonate as profoundly as Gregor Mendel. Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian monk, laid the foundation for modern genetics with his work on pea plants. His experiments and observations have significantly impacted our understanding of meiosis, the process through which gametes (sex cells) are produced. Here are five ways Mendel's work has revolutionized our study of meiosis:
The Law of Segregation

Mendel's first law, known as the Law of Segregation, has direct implications for how we understand the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis:
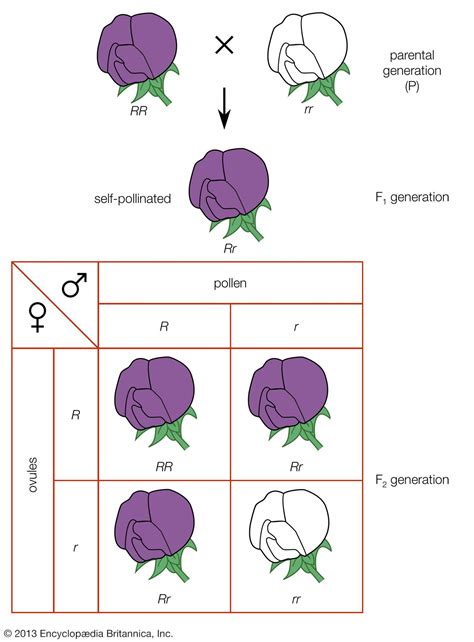
- Alleles separate during meiosis: Mendel discovered that each organism inherits two copies of each gene (alleles) but only passes one of these alleles to its offspring during sexual reproduction. This principle is mirrored in the separation of homologous chromosomes during anaphase I of meiosis.
- Meiotic divisions: The segregation of alleles aligns with the two successive divisions in meiosis, ensuring that each gamete receives one chromosome from each pair.
The Law of Independent Assortment

This law explains how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop:
- Gene independence: During metaphase I of meiosis, the alignment of chromosomes is random. This randomness ensures that the inheritance of one gene does not influence another gene located on a different chromosome, which is the essence of Mendel's law of independent assortment.
- Combinatorial genetics: This independence leads to significant genetic variation among offspring, which is crucial for evolution and adaptability.
The Role of Genes in Meiosis

Mendel's work established that genes are the basic units of heredity:
- Genes as carriers of traits: His focus on observable traits in peas highlighted the physical manifestation of genetic instructions, which meiosis physically distributes to gametes.
- Recombination: While Mendel didn't discuss genetic recombination, his findings paved the way for understanding crossing-over events during prophase I of meiosis, where genetic material between chromosomes can be exchanged, leading to further genetic diversity.
Linkage Groups
Although Mendel did not explicitly discuss linkage, his work set the stage for:
- Gene linkage: The discovery that genes located on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together (gene linkage) was an extension of Mendel's principles. This concept became essential in understanding how chromosomes are organized and the significance of genetic linkage in meiosis.
- Mitigation through recombination: Meiosis allows for the separation of linked genes through crossing over, which Mendel's laws indirectly support by highlighting the variations in offspring.
Quantitative Genetics

Mendel's principles were foundational for later developments in quantitative genetics:
- Heritability and polygenic traits: Mendel's emphasis on discrete units of inheritance (genes) was crucial for understanding how multiple genes influence traits like height or skin color, which depend on the cumulative effect of many alleles. Meiosis plays a critical role in shuffling these alleles.
- Statistical analysis: Mendel’s application of statistics to heredity also laid the groundwork for quantitative approaches to genetics, where understanding the segregation patterns during meiosis helps predict inheritance probabilities.
🧬 Note: Mendel’s work didn’t directly address the cytological events of meiosis, but his principles are essential for explaining why genetic material segregates in specific patterns during this process.
To wrap up, Mendel's insights into genetics have provided a theoretical framework for understanding meiosis. His laws of segregation and independent assortment directly correlate with the observed phenomena during meiosis, influencing our comprehension of how genetic material is passed from parents to offspring. His work not only revolutionized genetics but also continues to inform current research and educational practices, illustrating the enduring legacy of this pioneering scientist.
What are the key differences between Mendel’s laws and the mechanisms of meiosis?

+
Mendel’s laws describe the behavior of genes during inheritance, while meiosis refers to the physical process of cell division that results in the formation of gametes. Mendel’s laws are more about the outcome (inheritance pattern), whereas meiosis explains the underlying mechanism (cellular process) that supports those outcomes.
How did Mendel’s work influence the study of linkage groups?

+
Mendel’s work established the concept of discrete units of heredity (genes), which led to the understanding that genes on the same chromosome are inherited together. This concept, called linkage, was further developed post-Mendel, helping explain gene location on chromosomes and the role of meiosis in breaking these linkages.
Can Mendelian principles explain genetic recombination?

+
While Mendel did not discuss genetic recombination, his laws set the stage for understanding how genes assort independently. Genetic recombination during meiosis, particularly crossing over, explains why some offspring inherit combinations of traits not found in the parents, which aligns with the expected ratios Mendel observed.