5 Mechanisms of Evolution Simplified Worksheet

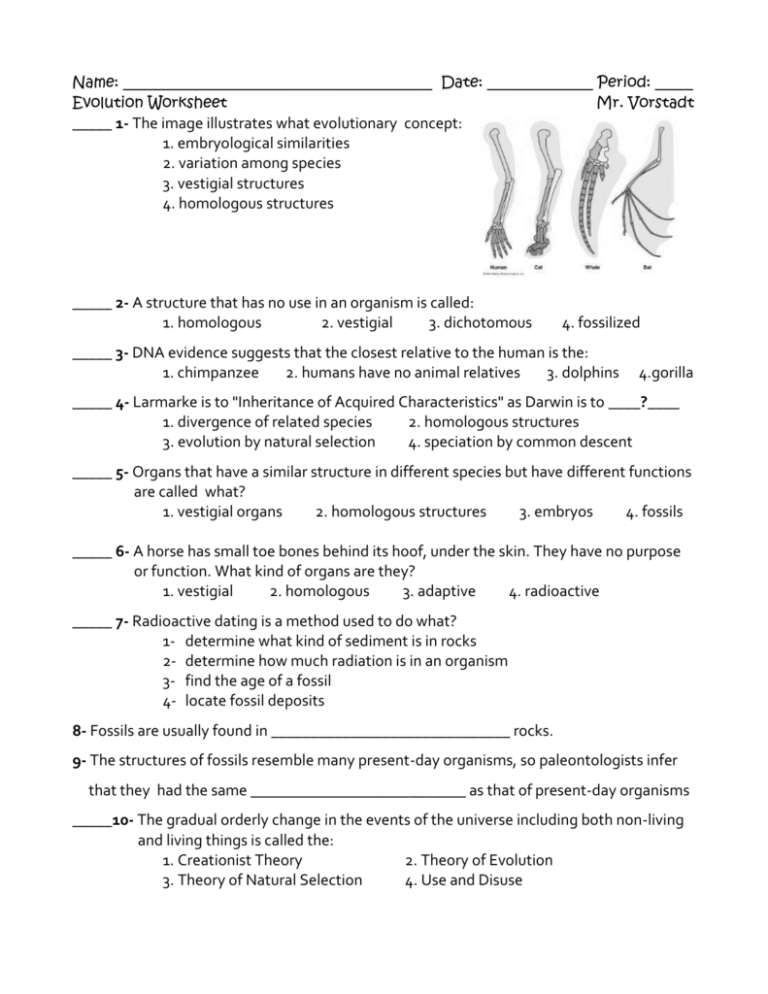
Evolution is a complex and beautiful process that has shaped all life on Earth. From the majestic whales to the tiniest microbes, evolution drives the diversity of species, the complexity of ecosystems, and the resilience of life itself. Here, we’ll explore the five mechanisms of evolution in simple terms, helping you grasp how species change over time.
1. Mutation
Mutation is the raw material for evolution. It refers to any change in the DNA sequence of an organism. These changes can occur randomly due to errors in DNA replication, exposure to radiation or chemicals, or from viruses. Here are some key points:
- Types of Mutation: Point mutations (single nucleotide changes), insertions, deletions, and duplications.
- Effect on Phenotype: Most mutations are neutral or have little effect, but some can lead to beneficial traits, harmful traits, or new protein functions.
- Genetic Variation: Mutations increase genetic variation within populations, providing a substrate for natural selection to work upon.

🔬 Note: Most mutations are not immediately noticeable in an organism's traits but can accumulate over generations, leading to significant evolutionary changes.
2. Gene Flow

Gene flow, also known as gene migration, involves the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. Here’s how it works:
- Movement of Individuals: Organisms move between populations, introducing new alleles (gene variants) to a new population.
- Mitigating Genetic Divergence: Gene flow can reduce genetic differentiation between populations, potentially preventing speciation.
- Spread of Adaptations: Beneficial traits can spread to new populations, improving the species’ overall fitness.
3. Genetic Drift

Genetic drift is a random fluctuation in allele frequencies due to random sampling of organisms. Here are its characteristics:
- Bottleneck Effect: A sudden reduction in population size can lead to a loss of genetic diversity.
- Founder Effect: A small population becomes isolated from the larger group, often leading to genetic divergence.
- Impact: Over time, drift can lead to the fixation of alleles (become 100% present in the population) or their complete disappearance.

🎲 Note: Genetic drift can be particularly strong in small populations, making it a significant evolutionary force.
4. Natural Selection

Often misunderstood as “survival of the fittest,” natural selection is the process where traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in populations. Here’s how it functions:
- Variation: There must be genetic variation within the population.
- Inheritance: Traits must be heritable.
- Differential Reproduction: Some individuals produce more offspring than others, leading to trait spread.
- Types of Selection:
- Stabilizing Selection: Favors intermediate phenotypes, reducing variation.
- Directional Selection: Favors individuals at one end of the trait spectrum.
- Disruptive Selection: Favors individuals at both ends of the trait spectrum, increasing variation.
5. Non-random Mating

Mating patterns can influence evolution. Here are the main aspects:
- Assortative Mating: Similar individuals choose each other, potentially reducing variation.
- Disassortative Mating: Dissimilar individuals mate, promoting genetic diversity.
- Inbreeding: Mating between close relatives increases homozygosity and can lead to the expression of deleterious recessive traits.

💑 Note: Non-random mating influences the genetic makeup of offspring, which in turn impacts evolutionary trajectories.
In summary, evolution occurs through intricate mechanisms that interact in complex ways. Mutation provides the necessary variation, gene flow and non-random mating can either enhance or reduce this variation, genetic drift introduces randomness, and natural selection ensures the survival of traits beneficial to the environment. Understanding these processes not only deepens our appreciation for the natural world but also informs fields like medicine, conservation, and agriculture.
What is the difference between gene flow and genetic drift?

+
Gene flow involves the movement of genes between populations through migration, while genetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies due to chance events, not involving movement between populations.
Can evolution happen without natural selection?

+
Yes, evolution can occur through mechanisms like genetic drift and mutations without the involvement of natural selection, though these changes might not always be beneficial or directional.
How does inbreeding affect evolution?

+
Inbreeding can increase the expression of harmful recessive traits due to the reduced genetic diversity, potentially leading to inbreeding depression, which can impact the evolutionary fitness of a population.
What role do mutations play in evolution?

+
Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation. Without mutations, there would be no new traits or characteristics for natural selection to act upon, thereby halting evolutionary progress.
Are there any other mechanisms of evolution besides these five?

+
While these five mechanisms are fundamental, other factors like cultural selection in humans or symbiosis can also influence evolutionary trajectories indirectly.