Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Unlock Your Potential

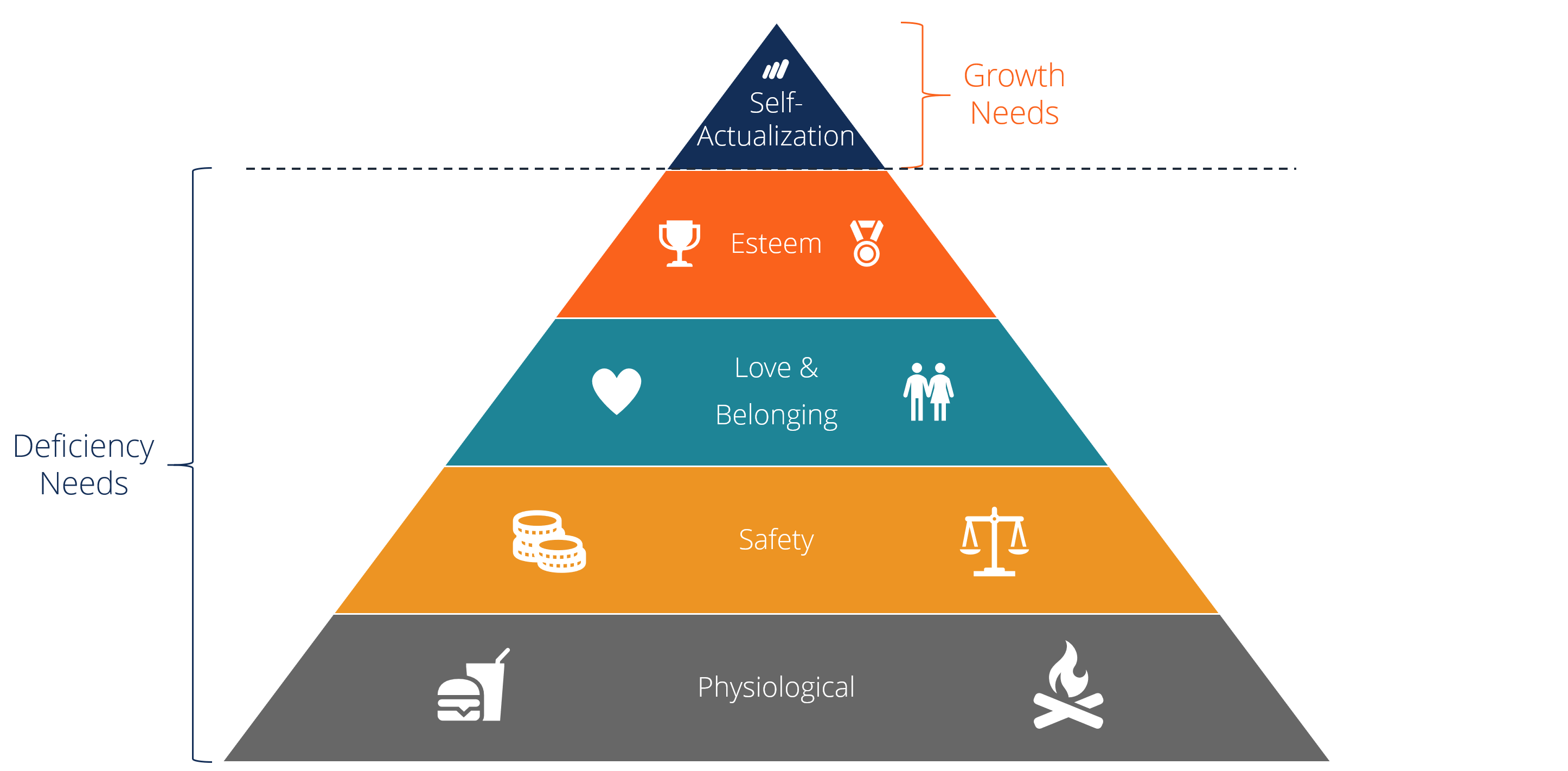
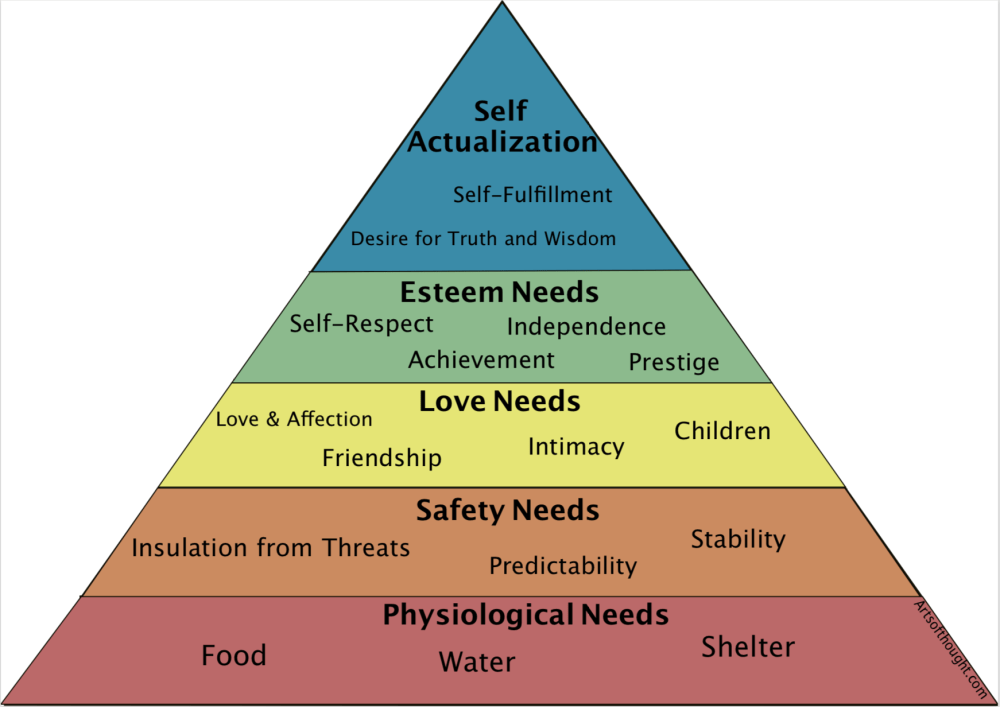
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a fundamental theory in psychology that explains how human motivation is influenced by a series of needs, often depicted as a pyramid. Each level of the pyramid represents different needs that must be satisfied in a specific order. This model not only helps us understand our own behaviors but also provides a framework for personal growth and achieving our full potential. Let's delve into each level of Maslow's pyramid to uncover how these layers work together to foster self-actualization and personal satisfaction.
1. Physiological Needs


At the base of Maslow’s pyramid are the physiological needs, which are the most basic human requirements essential for survival:
- Food: Without proper nutrition, our energy levels and cognitive abilities decrease.
- Water: Our bodies require hydration to function effectively.
- Shelter: Adequate living conditions protect us from environmental stressors.
- Clothing: Proper clothing helps maintain body temperature.
- Medical Care: Essential for addressing health issues and maintaining physical well-being.
🍎 Note: Ensuring these basic physiological needs are met is critical before progressing to higher levels of the pyramid.
2. Safety Needs

Once physiological needs are sufficiently met, individuals seek to fulfill their safety needs, which include:
- Security: Stability and safety from fear of harm or danger.
- Stability: A predictable environment where one feels safe and secure.
- Financial Security: The ability to provide for oneself and one’s family.
- Social Safety: Being part of a safe community with rules and laws protecting citizens.
- Health and Well-being: Confidence in one’s physical health and well-being.
🛡️ Note: Safety can extend beyond physical security to include emotional and financial stability.
3. Love and Belongingness Needs

Next in the hierarchy are love and belongingness needs, which drive the desire for:
- Relationships: Strong bonds with family, friends, and romantic partners.
- Love: Receiving and giving affection, ensuring emotional intimacy.
- Acceptance: Feeling part of a group or community where one is valued.
- Intimacy: Developing close, personal relationships with others.
When these needs are not met, individuals might feel loneliness, social anxiety, or estrangement, which can impede progress to the next level.
4. Esteem Needs

Higher up in the pyramid are the esteem needs, encompassing:
- Self-esteem: A sense of personal worth and confidence in one’s abilities.
- Recognition: Respect and recognition from others.
- Status: The desire for a good reputation or social standing.
- Achievement: The need to accomplish goals and feel competent.
- Independence: The freedom to make decisions without undue influence.
Achieving esteem needs helps us feel confident in our capabilities and valued in society, which is vital for self-actualization.
5. Self-Actualization
At the pinnacle of Maslow’s pyramid lies self-actualization, the quest to:
- Discover and fulfill one’s potential.
- Engage in creative pursuits.
- Pursue personal growth and learning.
- Develop a sense of purpose or mission in life.
- Achieve personal fulfillment and self-expression.
This level is not about becoming perfect but rather about striving to be the best version of oneself, where personal growth and understanding are continuous.
🌱 Note: Self-actualization is not a destination but an ongoing journey towards personal excellence.
This theory suggests that as one layer of needs is met, individuals naturally progress to the next. However, it's worth noting that not everyone will reach the top of the pyramid, and at times, one might find themselves oscillating between levels due to life's unpredictability.
Recognizing and Applying Maslow’s Model

Understanding Maslow’s Hierarchy can be transformative for both individuals and organizations. Here are some practical steps:
- Self-reflection: Assess which level of the pyramid you feel you’re currently focused on.
- Goal Setting: Align personal or organizational goals with the hierarchy to ensure balanced growth.
- Supporting Others: Help family, friends, or colleagues meet their needs, promoting an environment conducive to their self-actualization.
- Workplace Culture: In the workplace, cultivate a culture that values employee safety, belonging, and esteem, leading to greater productivity and job satisfaction.
📝 Note: Applying Maslow's Hierarchy can lead to more meaningful life planning and work environments.
In summary, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs serves as a comprehensive guide to human behavior and motivation. By recognizing and addressing each level of needs, we can unlock our potential for growth, fulfillment, and happiness. This model encourages us to strive not only for personal satisfaction but also for a deeper connection with our surroundings, fostering both personal and collective well-being.
Can Maslow’s Hierarchy be applied to all cultures?
+
Yes, while the order and significance of the needs might differ slightly across cultures, the fundamental human needs Maslow identifies are universal.
Is there empirical support for Maslow’s model?

+
Yes, many studies support parts of Maslow’s theory, although some researchers argue that the hierarchy might not be as rigid as initially proposed, with needs sometimes overlapping or appearing simultaneously.
How can I apply Maslow’s model to my career progression?

+
Consider your job’s ability to meet your needs from physiological (salary) to esteem (recognition) and how it aligns with your personal goals for self-actualization.
Can someone reach self-actualization if lower needs are not completely met?

+
While it’s less common, some individuals can focus on higher needs even if lower needs are not fully satisfied, perhaps through alternative means like meditation, creativity, or social support systems.