Spanish Speaking Countries Map Labeling Worksheet Answers

<!DOCTYPE html>
Learning to identify the countries where Spanish is an official language is a fascinating way to understand cultural, historical, and linguistic connections across the globe. This task involves geographical knowledge as well as linguistic diversity, making it not only educational but also deeply enriching. This blog post provides detailed answers to a Spanish-speaking countries map labeling worksheet, offering insights and context to enhance your learning experience.
Mapping the Spanish-Speaking World

Before diving into the answers, it’s important to understand why this exercise is valuable. Spanish is the second most spoken language by the number of native speakers, and its spread is due to historical events like colonization and cultural exchanges:
- Colonization: Spanish explorers and settlers brought the language to the Americas during the 15th to 19th centuries.
- Geographical Spread: From Spain in Europe to Latin America, Spanish has formed a linguistic corridor.
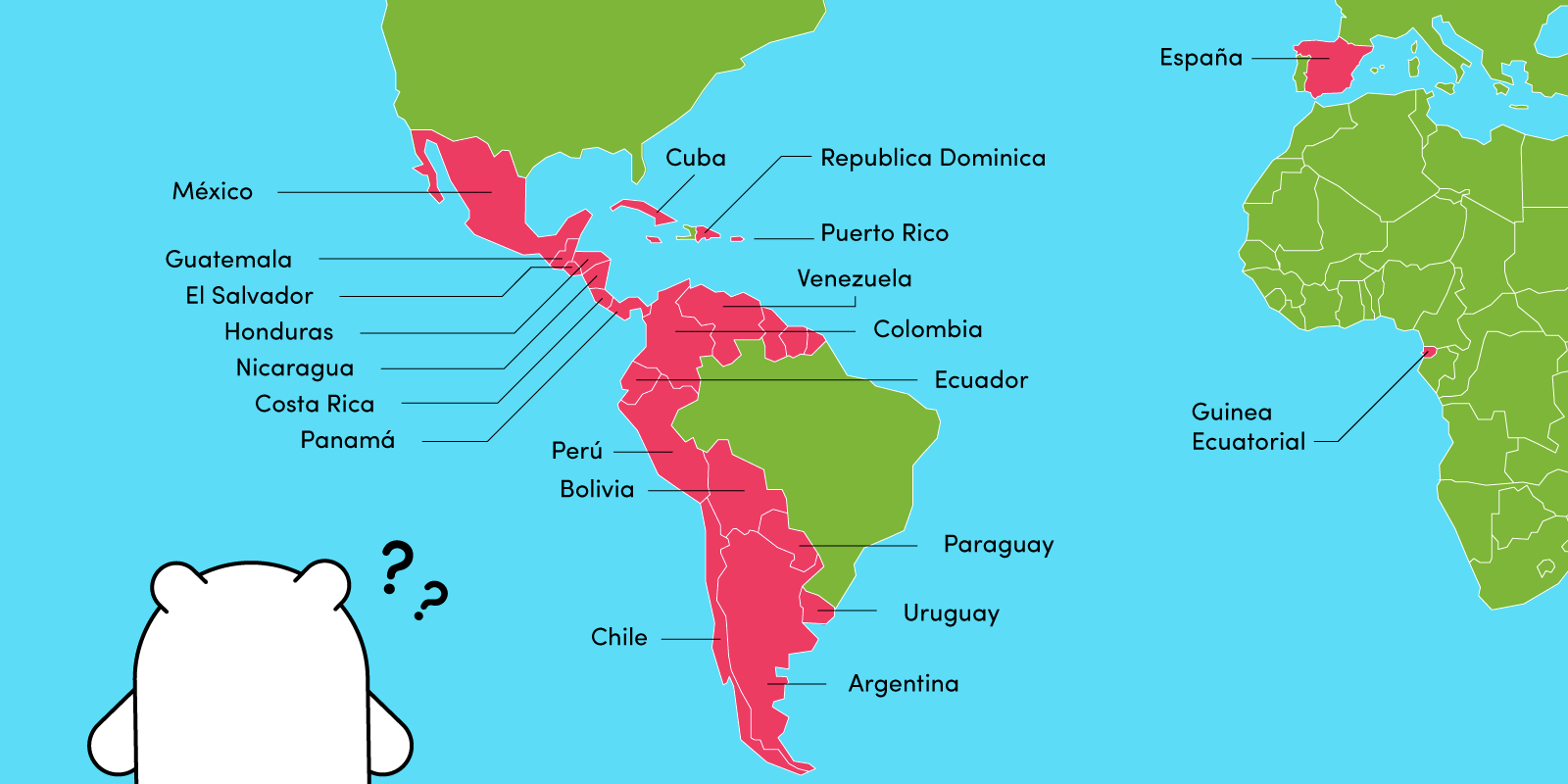
Let’s examine the map for accurate labeling:
| Continent | Country |
|---|---|
| Europe | Spain |
| North America | Mexico |
| Central America | Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama |
| Caribbean | Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico |
| South America | Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Paraguay, Chile, Argentina, Uruguay |
| Africa | Equatorial Guinea |

🗺️ Note: Remember to fill in each country on your worksheet to gain a complete understanding of Spanish-speaking regions.
Important Regions and Facts
Here are some interesting insights into Spanish-speaking regions:
- Spain: As the cradle of the Spanish language, Spain plays a pivotal role in its spread and evolution.
- Mexico: With the largest Spanish-speaking population, Mexico’s cultural and linguistic influence extends far beyond its borders.
- Argentina and Uruguay: These countries are known for their unique dialects known as Rioplatense Spanish.
🌍 Note: Despite Spanish being an official language, countries like Brazil in South America do not use it as a primary language, as Portuguese is predominant there.
Linguistic Variations and Dialects

Spanish isn’t uniform; it has a myriad of dialects and variations:
- Castilian Spanish: Primarily spoken in Spain, it’s often considered the standard.
- Latin American Spanish: Varies significantly across regions with terms, pronunciation, and vocabulary differences.
- Cariño Dialect: In Caribbean countries, Spanish often integrates indigenous, African, and European influences.
🎵 Note: These linguistic variations often reflect cultural aspects and historical events, enriching the Spanish language mosaic.
The Importance of Language Mapping

Maps can be invaluable tools in understanding:
- Language distribution and its relation to demographics.
- Historical and cultural ties between regions.
- Economic and political spheres of influence.
Understanding the geography of language is not only about learning facts; it's about appreciating the tapestry of human interaction and history. This worksheet exercise offers a glimpse into the world where Spanish connects people, cultures, and nations.
FAQs

¿Qué países de América Latina no hablan español como lengua principal?

+
Países como Brasil, donde el portugués es la lengua oficial, y las Guyanas, donde se hablan idiomas como el francés, el inglés y el holandés, no tienen el español como lengua principal.
¿Cuál es el país africano donde se habla español?

+
El único país africano con español como lengua oficial es Guinea Ecuatorial.
¿Cómo influye la geografía en la evolución del español?

+
La geografía ha jugado un papel crucial en la evolución del español, desde la colonización hasta la migración interna, creando dialectos únicos en regiones aisladas o con influencias externas como en el Caribe y América Latina.