5 Key Answers: Macromolecules Worksheet #2

When delving into the complex world of biology, understanding the different types of macromolecules is essential. These large molecules form the foundation of life, playing critical roles in various biological processes. In this post, we will dissect the answers to a Macromolecules Worksheet #2 to provide a deeper insight into carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
The Four Classes of Macromolecules


Macromolecules are divided into four primary categories:
- Carbohydrates - Energy storage and structural components
- Lipids - Energy storage, insulation, and hormone production
- Proteins - Functional and structural roles
- Nucleic Acids - Genetic information storage and transfer
📚 Note: Each macromolecule class has unique properties and functions that make them indispensable in cellular operations.
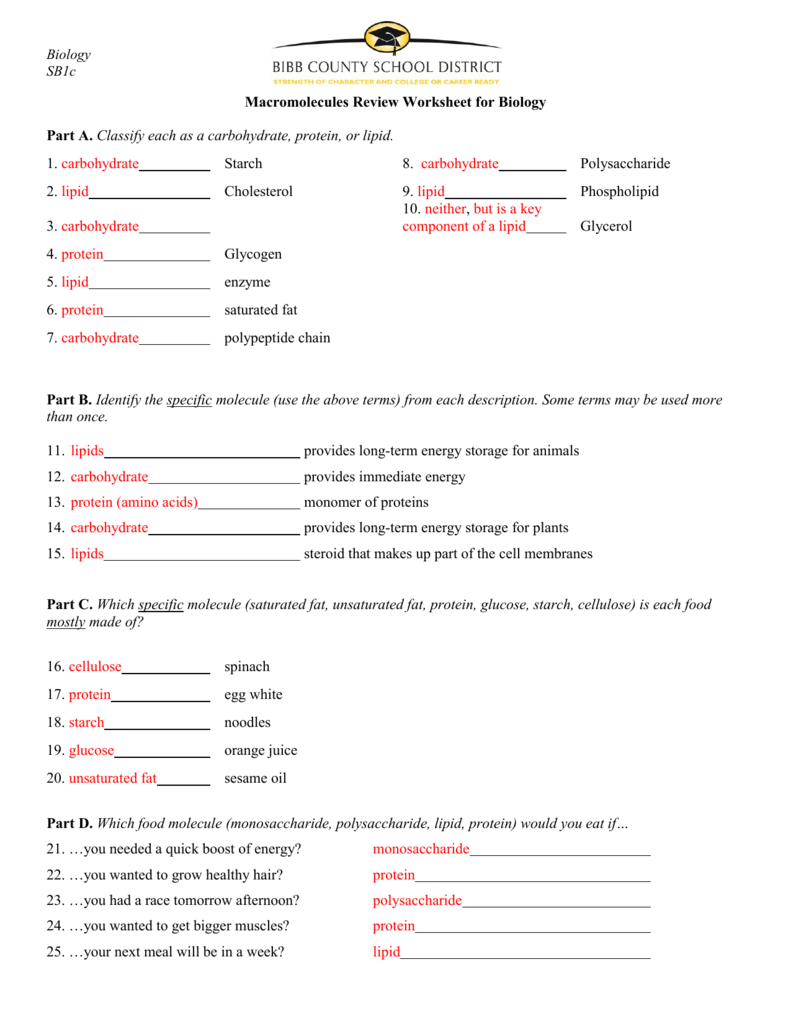
Answer 1: Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for many organisms. Their structures range from simple sugars like glucose to complex structures such as glycogen and cellulose:
| Carbohydrate Type | Example | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Monosaccharide | Glucose, Fructose | Quick energy source |
| Disaccharide | Sucrose, Lactose | Transport sugar, sweetness |
| Polysaccharide | Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen | Energy storage or structural component |

Answer 2: Lipids


Lipids are diverse in their structure but share the characteristic of being non-polar, making them important for membrane formation and energy storage:
- Fats - Triglycerides for long-term energy storage
- Phospholipids - Key components of cell membranes
- Steroids - Structurally related compounds like cholesterol and hormones
Answer 3: Proteins

Proteins are incredibly versatile, performing a multitude of functions within the body:
- Enzymes - Biological catalysts
- Structural Proteins - Like collagen for skin integrity
- Hormones - Insulin, for example, regulates blood sugar
- Transport Proteins - Hemoglobin, which carries oxygen
- Antibodies - Immune system defense
📖 Note: Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, determine the protein's shape and, consequently, its function.
Answer 4: Nucleic Acids


Nucleic acids carry genetic information in the form of DNA or RNA:
- DNA - Contains genetic blueprint
- RNA - Involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation
Answer 5: Macromolecules in Action

The real-world application of these macromolecules in biological systems is intricate:
- Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars for quick energy.
- Lipids in the form of triglycerides are broken down to release energy during prolonged fasting or intense exercise.
- Proteins are continually synthesized and degraded to maintain bodily functions.
- Nucleic acids are pivotal during cell division for the distribution of genetic material.
Ultimately, understanding macromolecules offers a window into life's mechanics. They are not just passive building blocks but active participants in the symphony of life, enabling us to comprehend how organisms function, grow, and adapt. This knowledge also translates into practical applications in fields like medicine, nutrition, and biotechnology, where the manipulation and understanding of macromolecules can lead to advancements in treatment and technology.
What’s the main difference between monosaccharides and polysaccharides?

+
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of a single sugar molecule (e.g., glucose). Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharide units, like starch, glycogen, or cellulose, used for energy storage or structural purposes.
How do lipids differ from other macromolecules?

+
Lipids differ due to their predominantly non-polar nature, which makes them insoluble in water. They serve primarily in energy storage, as structural components of cell membranes, and in signaling.
Why are proteins considered the workhorses of the cell?
+
Proteins are versatile, capable of folding into specific shapes to carry out numerous functions like catalysis, transport, structure, motion, and immune response, making them crucial for most cellular activities.
What are the roles of nucleic acids?

+
Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, store, express, and transmit genetic information. DNA contains the hereditary blueprint while RNA plays roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Can a cell survive without macromolecules?

+
A cell cannot survive without macromolecules as they are essential for structure, function, and the very fabric of life. Each macromolecule type has indispensable roles, and their absence would cause the collapse of cellular processes.