Macromolecules of Life Worksheet Answers Revealed

Understanding macromolecules is crucial for anyone studying biology, chemistry, or even basic human physiology. Macromolecules, or large molecules, are essential for life as they serve as the building blocks of life, contributing to everything from structural components to enzymatic catalysis. In this post, we will delve into the answers of a common worksheet that tackles macromolecules of life, ensuring you understand their types, functions, and significance in biological systems.
Types of Macromolecules

Let's start with an overview:
- Proteins: Essential for nearly all cellular functions including muscle contraction, immune response, transport, and enzymatic reactions.
- Carbohydrates: Primary energy source for most organisms, also play structural roles (e.g., cellulose in plant cell walls).
- Lipids: Important for energy storage, hormone synthesis, and cell membrane structure.
- Nucleic Acids: Carriers of genetic information, crucial for protein synthesis and other cellular processes.
Macromolecules Worksheet Answer Key
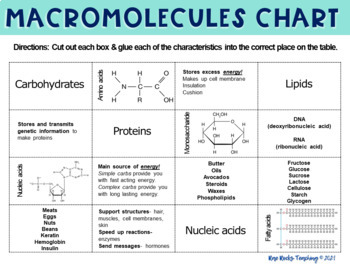
1. Proteins
- Function: Proteins are involved in almost every biological process. They can act as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, form structural components of cells, transport molecules, control movement, and even defend against infections.
- Structure: Composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins can be classified into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
- Examples: Enzymes (catalase, amylase), structural proteins (keratin, collagen), transport proteins (hemoglobin), hormones (insulin).
2. Carbohydrates

- Function: They are the main energy source for most organisms, provide structure (in plants), and participate in cellular recognition.
- Structure: Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms with a general formula (CH2O)n. They can be monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides.
- Examples: Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), disaccharides (sucrose), and polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose).
🧬 Note: Carbohydrates in the form of glycans also play critical roles in cell-cell communication and the immune system.
3. Lipids

- Function: Lipids are excellent at energy storage, insulation, hormone production, and forming the barrier of cells.
- Structure: Unlike the other macromolecules, lipids do not form long polymers. They are diverse, including fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids.
- Examples: Triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids (cell membrane component), cholesterol (precursor for steroid hormones), and waxes.
4. Nucleic Acids

- Function: Store, transmit, and express genetic information. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) holds the code for life, while RNA (ribonucleic acid) is involved in protein synthesis.
- Structure: Composed of nucleotides, which consist of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is typically single-stranded.
- Examples: DNA (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine) and RNA (adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil).
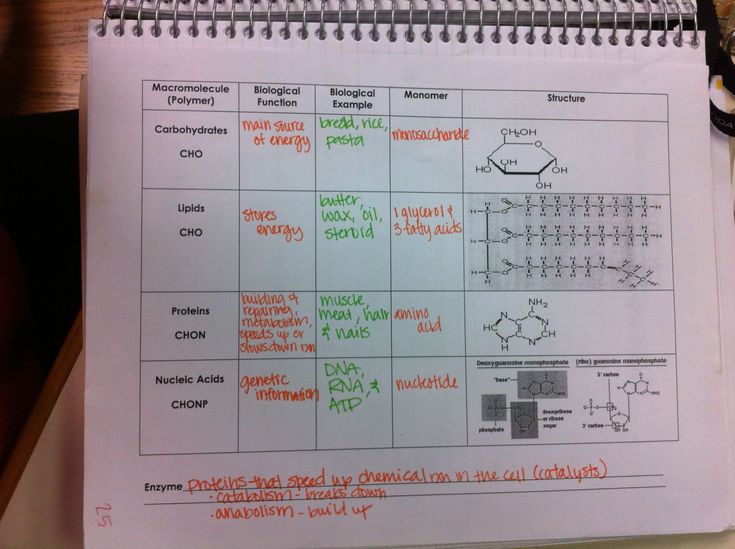
| Macromolecule | Subunits (Monomers) | Polymer Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | Amino Acids | Polypeptide | Enzymes, antibodies |
| Carbohydrates | Monosaccharides | Polysaccharide | Starch, glycogen |
| Lipids | Fatty acids and glycerol | N/A | Triglycerides, phospholipids |
| Nucleic Acids | Nucleotides | Nucleic Polymer | DNA, RNA |

To wrap up our exploration of macromolecules, it's clear that these giant molecules are not only foundational in building life forms but are also intricately involved in the complex processes that keep life going. Proteins catalyze reactions, carbohydrates provide energy, lipids form barriers and store energy, and nucleic acids hold the blueprint of life. Understanding these macromolecules allows us to delve deeper into biological systems, offering insights into disease, metabolism, and cellular functions. As we continue to research these biomolecules, we uncover more about the complexity and beauty of life at the molecular level.
What is the primary function of lipids?

+
Lipids primarily function as energy storage molecules, insulators, components of cell membranes, and in hormone synthesis.
How do nucleic acids differ from other macromolecules?

+
Nucleic acids differ in their function of storing and transmitting genetic information, unlike carbohydrates which are energy sources, or proteins which have structural and functional roles.
Can carbohydrates be part of protein structures?

+
Yes, carbohydrates can be covalently bonded to proteins, forming glycoproteins, which are crucial for cell signaling and immune responses.
What happens if there is a protein folding problem?

+
Mis-folding of proteins can lead to a range of diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s, prion diseases, and certain forms of cancer.
Why are macromolecules critical for life?

+
Macromolecules are integral to life because they perform essential functions ranging from energy storage to genetic information transfer, structural support, and catalysis of reactions.