5 Macromolecule Matching Worksheet Answers You Need

Unlocking the Mystery: Macromolecules and Their Functions

The world of biochemistry is fascinating and complex, filled with building blocks that sustain life. These building blocks, known as macromolecules, are fundamental to biological processes. In this guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the four main macromolecules—proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—and provide you with answers to the common worksheets you might encounter in your studies. Let’s embark on a journey of understanding macromolecule identification, properties, and functions.
Understanding Macromolecules

Macromolecules are large molecules essential for various life processes. They are:
- Proteins: Composed of amino acids, they serve numerous functions such as catalysis, structural support, and more.
- Carbohydrates: Primarily used for energy, with roles in structural support and communication.
- Lipids: Known for their energy storage, insulation, and membrane building capabilities.
- Nucleic acids: These carry genetic information and facilitate its expression.
Macromolecule Matching Worksheet Answers

Here are some common questions from macromolecule matching worksheets and their answers:
1. Matching the Functions

Match the following functions with the correct macromolecule:
| Function | Macromolecule |
|---|---|
| Energy Storage | Carbohydrates |
| Structural Support | Proteins, Carbohydrates |
| Genetic Information | Nucleic acids |
| Enzyme Activity | Proteins |
| Cell Membrane | Lipids |

💡 Note: Some functions, like structural support, can be attributed to more than one macromolecule.
2. Identifying Macromolecules by Monomers

Match the monomer to its respective macromolecule:
- Amino acids: Proteins
- Monosaccharides: Carbohydrates
- Nucleotides: Nucleic acids
- Glycerol and fatty acids: Lipids
3. Understanding Macromolecule Composition
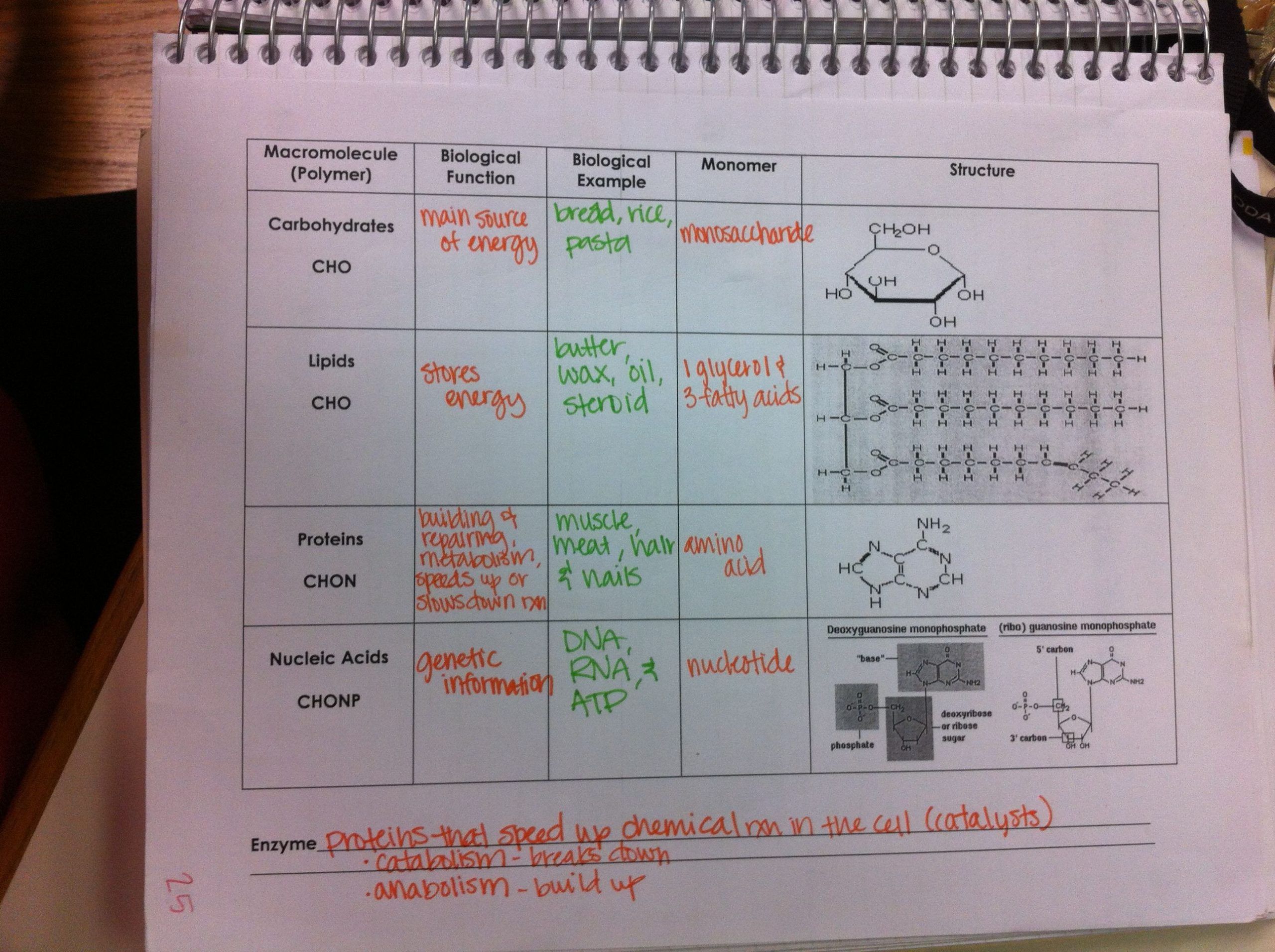
Fill in the blanks:
- Proteins are composed of amino acids.
- Carbohydrates are made up of monosaccharides.
- Lipids consist of glycerol and fatty acids or sterols.
- Nucleic acids are built from nucleotides.
4. Functions of Macromolecules

Match the specific function to the correct macromolecule:
| Specific Function | Macromolecule |
|---|---|
| Act as enzymes | Proteins |
| Store and transfer genetic information | Nucleic acids |
| Provide cell structure and insulation | Lipids |
| Serve as quick energy sources | Carbohydrates |
5. Properties of Macromolecules

List two properties of each macromolecule:
- Proteins:
- Amphoteric (can act as acids or bases).
- Highly diverse in structure and function.
- Carbohydrates:
- Hydrophilic due to many hydroxyl groups.
- Form polymers through glycosidic bonds.
- Lipids:
- Hydrophobic, insoluble in water.
- Can form bilayers and other membrane structures.
- Nucleic acids:
- Carry genetic information.
- Long, linear polymers with a backbone of alternating sugar and phosphate groups.
🧬 Note: Understanding the interactions between macromolecules can be key to comprehending their function within living organisms.
To conclude, learning about macromolecules isn't just about memorizing facts; it's about understanding the incredible tapestry of life at its most fundamental level. Through the answers to these common worksheet questions, we've unveiled a glimpse into the world of biochemistry where each macromolecule plays a unique role in the symphony of life processes. Keep exploring, testing your knowledge, and appreciating the complexity of life's chemistry, and you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the beautiful complexity of life itself.
Why are macromolecules essential for life?

+
Macromolecules are the building blocks of life. They provide structural support, energy storage, genetic information, and facilitate a myriad of cellular processes, making them indispensable for the functioning of all living organisms.
How are macromolecules identified in lab experiments?

+
Macromolecules are identified through specific chemical tests like the Biuret test for proteins, Benedict’s or iodine tests for carbohydrates, Sudan IV for lipids, and electrophoresis for nucleic acids, along with various chromatography techniques.
Can macromolecules function independently?

+
While macromolecules have their specific roles, they often work in concert with one another within biological systems. Proteins might need lipids to form membranes, and nucleic acids rely on proteins to express genes, highlighting their interdependent nature.



