Macromolecule Biomolecules: Study Sheet for Biology Review

Exploring Macromolecule Biomolecules

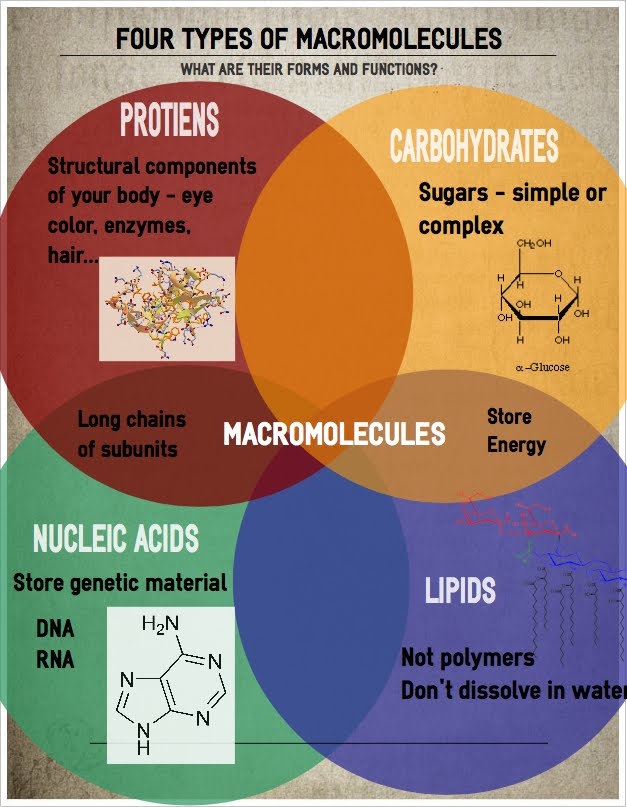
Biology is a fascinating field, full of complex structures and processes that govern life as we know it. One fundamental aspect to understand is macromolecules, which are large, complex biomolecules essential to life’s functions. Here, we’ll delve into the primary types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, detailing their structures, functions, and significance in biological systems.
Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates are often the energy source of choice for most organisms, serving as quick-to-access fuel. Here’s how they function:
- Monosaccharides: The simplest sugars like glucose and fructose, which can be absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
- Disaccharides: Formed when two monosaccharides combine, examples include sucrose and lactose.
- Polysaccharides: Long chains of monosaccharides, which serve various roles such as energy storage (e.g., starch in plants, glycogen in animals) or structural support (e.g., cellulose in plants).

🍎 Note: Carbohydrates not only provide energy but also play critical roles in cell recognition and signaling.
Lipids

Unlike carbohydrates, lipids are not polymers made from identical building blocks. Their role is diverse:
- Fatty Acids: Saturated and unsaturated fats, vital for energy storage and membrane structure.
- Phospholipids: Major components of cell membranes, with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails.
- Steroids: Including cholesterol, which serves as the precursor for many hormones.
- Triglycerides: Comprise three fatty acids linked to glycerol, providing energy storage.

Proteins

Proteins are arguably the most versatile macromolecules:
- Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins, 20 different types, each with unique properties.
- Polypeptide Chain: Sequences of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
- Protein Folding: Proteins fold into specific shapes, crucial for their function, influenced by forces like hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der Waals forces.
- Types of Proteins: From structural (e.g., collagen) to functional (e.g., enzymes, hormones).

🧬 Note: The functionality of proteins depends significantly on their tertiary and quaternary structure, which can be altered by environmental conditions like pH and temperature.
Nucleic Acids

Nucleic acids store, express, and transmit genetic information:
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): Contains the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms.
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): Plays various roles in the process of synthesizing proteins from genetic information contained in DNA.
- Nucleotides: The building blocks of nucleic acids, composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.

Interactions Between Macromolecules

Macromolecules don’t exist in isolation; they interact in complex ways:
- Enzyme-Substrate Interactions: Enzymes, which are proteins, facilitate chemical reactions by interacting with substrates, often carbohydrates or lipids.
- Cell Membrane Dynamics: Phospholipids and proteins in the cell membrane interact to regulate what goes in and out of cells.
- Gene Expression: Nucleic acids coordinate with proteins to express genes into functional traits or proteins.
Importance in Biological Systems

The significance of macromolecules can hardly be overstated:
- Energy Production: Carbohydrates and lipids are primary sources of cellular energy.
- Structural Integrity: Proteins and carbohydrates contribute to the physical structure of organisms.
- Information Storage: Nucleic acids encode genetic information critical for life processes.
- Signaling: Various macromolecules are involved in cell-to-cell communication, ensuring organisms function cohesively.
Understanding macromolecules provides a foundation for comprehending life processes at a molecular level. Their complex interactions, structures, and diverse functions are essential to life's complexity and resilience. By exploring the building blocks of life, we gain insights into how life functions, adapts, and evolves. This knowledge is not only pivotal in biology but also in medical sciences, biochemistry, genetics, and even in the development of synthetic biology and biotechnologies.
What are the primary functions of carbohydrates?

+
Carbohydrates primarily function to provide energy, store energy, and form structural components in cells, especially in plants.
How do lipids differ from other macromolecules?

+
Lipids differ by not forming polymers. They are soluble in organic solvents and play roles in energy storage, signaling, and as major components of cell membranes.
Can proteins lose their function if their structure changes?
+
Yes, when proteins denature due to changes in environmental conditions like pH, temperature, or salinity, they can lose their specific shape and function.
What is the main role of nucleic acids in life?

+
Their primary role is to store and transmit genetic information through DNA, and RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
How do macromolecules interact to perform biological functions?
+Macromolecules interact through various mechanisms; for example, enzymes catalyze reactions involving carbohydrates, lipids provide structure and energy, and nucleic acids direct protein synthesis.